动态规划(dynamic programming):
DP='careful bruteforce'
DP='subproblem'+'subproblem'+...
DP=memoize + bottom up + recursive
斐波那契数列:
1) naive recursive algorithm
def fib(n):
if n <= 2:f = 1
else:f = fib(n-2) + fib(n-1)
return f
Q:good or not?
A:O()=exponential time
2) memoize + recursive DP algorithm
memo=[]
def fib(n):
if n in memo:return memo[n]
if n <= 2: f = 1
else: f = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
memo[n] = f
return f
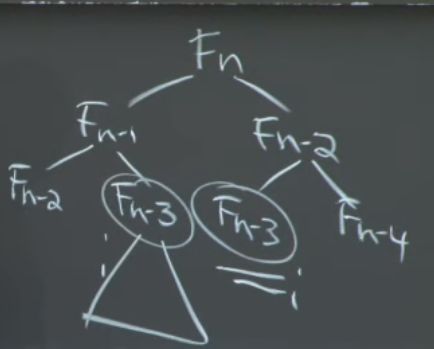
recursion tree:在naive recursive算法中,相同的位置上的数字要计算很多次,比如Fn-3需要进行三次运算,Fn-2的计算又复出现在了Fn-1的下面,重复计算的太多.DP算法则牺牲空间换速度,建立一个DP table来减少重复的计算.
3) bottom up DP algorithm
fib = []
for k in range(1,n+1):
if k <= 2: f = 1
else: f = fib[k-1] + fib[k-2]
fib[k] = f
return fib[n]
bottom up exactly do the same computation as memoize + recursive
if don't need to compute, calling the value from the table need 1 operation, taking value from fib(1) to fib(n) take n times,time = O(n)
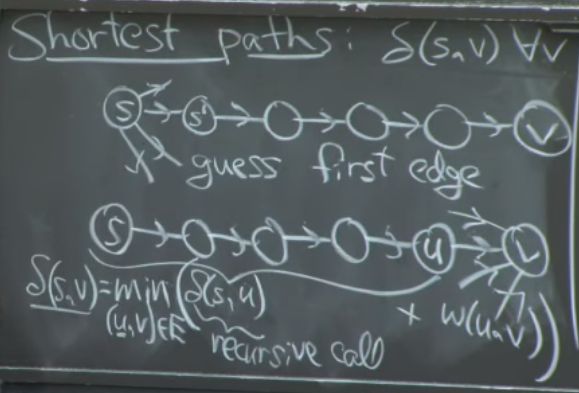
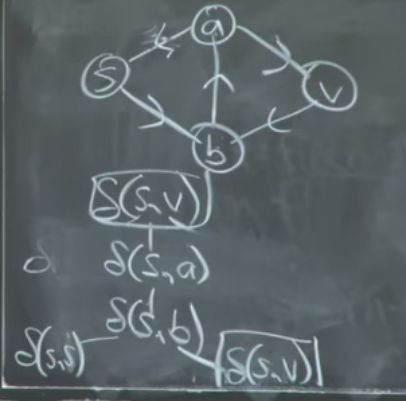
最短路径:
to solve: try all the guesses(take the best one)
solution: subproblem->...
problem: need to compute the over and over again, the time would be infinite time because the graph is cycle
to solve the problem: using DP, it is also bellman-ford algorithm
five easy steps to DP:
- define subproblems
- guess(part of solutions)
- relate subproblems and solutions(always using recursion)
- recurse/memoize/bottom up
- solve the original problem
Blackjack
Rule:
Suppose that we want to play Blackjack against a dealer (with no other players). Suppose, in addition, that we have x-ray vision that allows us to see the entire deck (c0, c1, ..., cn−1). As in a casino, the dealer will use a fixed strategy that we know ahead of time (stand-on-17), and that we allowed to make $1 bets (so with each round, we can either win $1, lose $1, or tie and make no profits and no losses). How do we maximize our winnings in this game? When should we hit or stand?
Python Code:
返回值:当前卡牌顺序下,player能够赢到的最多的金额
import random
'''
dealer->庄家
player->玩家
'''
pokes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]*4
random.shuffle(pokes)
print(pokes)
def cmp(a, b):
if a > b:
return 1
elif a < b:
return -1
return 0
def bj(i, cards, options): # 一次游戏,当前牌顶的牌为cards[i]
suboptions = []
n = len(cards[i:])
if n < 4:
return 0
for p in range(2, n - 1): # guess
# player 拿牌阶段,第一张和第三张是他的,然后还可以拿第3张到第i+p+2张(choices)
# player 拿的牌的组合可能性有2 ~ n-2张(-2是因为有两张牌在dealer手中)
player = cards[i] + cards[i + 2] + sum(cards[i + 4:i + p + 2])
if player > 21:
# boom player爆了直接下一场游戏
options.append(-1 + bj(i + p + 2, cards, suboptions)) # 本场游戏输一块,开始下一场
break
dealer = 0
cur = 0
for d in range(2, n - p+1):
cur = d
# dealer 拿牌阶段,第二张和第四张是他的,然后在player拿完牌后,还可以拿第i+p+3张到i+p+d张(choices)
dealer = cards[i + 1] + cards[i + 3] + sum(cards[i + p + 2:i + p + d])
if dealer >= 17:
break # stand
if dealer > 21:
dealer = 0
options.append(cmp(player, dealer) + bj(i + p + cur, cards, suboptions))
return max(options)
print(bj(0, pokes, []))
参考:
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-006-introduction-to-algorithms-fall-2011/recitation-videos/MIT6_006F11_rec20.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OQ5jsbhAv_M&t=7s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ENyox7kNKeY