深蓝-视觉slam-第五节习题
#include cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16.3)
project(COMPUTEORB)
set(CMAEK_CXX_STANDARD 17)
#IF (NOT DEFINED ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE})
SET(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
#ENDIF()
MESSAGE(STATUS "CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE IS ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}")
SET(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
find_package(OpenCV 3.4.15 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} "/usr/local/include/eigen3" "/usr/local/include/sophus")
SET(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/OUTPUT)
add_executable(computeORB computeORB.cpp)
target_link_libraries(computeORB ${OpenCV_LIBS} tbb)
实现效果:

注意,当使用题目中给定的应验值d_max = 50时,会存在误匹配,的不出筛选后的匹配图,所以本题中我将d_max改为40,匹配达到最好。
从第一次运行时间可以看出,单线程和多线程时间好像并没有对运行性能有所提升。
2.4
<1> 因为ORB的brief(描述子)是通过在特征点附近随即的选取若干个点对,将这些点对的灰度值的大小,组合成一个二进制串。
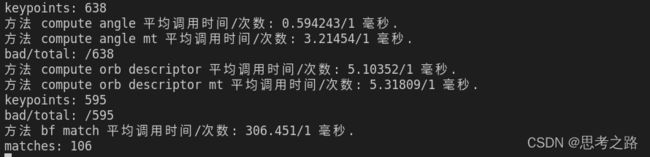
<2> 我的机器上匹配时,选阈值为40最合适,超过50,会出现误匹配的情况,低于40,导致匹配的点对太少,进行地图重建的时候,由于匹配的点对太少,出现地图稀疏的情况,不适合建图,更适合定位。
<3>暴力匹配
![]()
暴力匹配平均调用时间:0.3s
当特征点数量很大时,暴力匹配法的运算量将变得很大,特别的当想要匹配某个帧和一张地图的时候,这不符合在SLAM中的时实性需求,而FLANN(快速近似最近邻)算法更适合于匹配点数量极多的情况,从而实现快速高效匹配。
FLANN,参考:https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=124145732
<4>性能方面,多进程比单进程快些,单具体性能提升多少随运行次数在改变。

CMakeLists.txt中需要链接tbb的库,否则会报上述错误;
#include CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16)
project(E2RT)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
#添加头文件
include_directories( "/usr/include/eigen3")
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(E2Rt E2Rt.cpp)
#链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries(E2Rt ${Sophus_LIBRARIES} fmt)
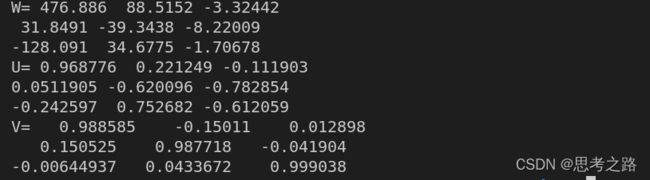
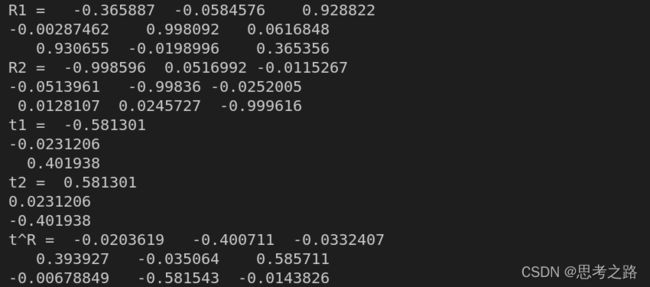
运行结果:
3,用G-N实现Bundle Adjustment中的位姿估计

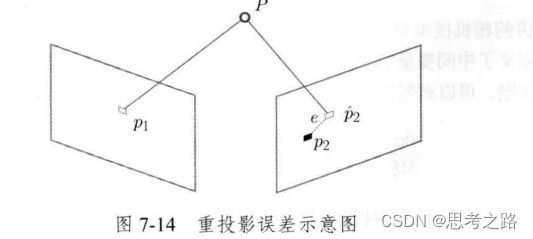
1.重投影误差:像素坐标(观测的到的投影位置)与3D点按照当前估计的相机位姿进行投影得到的位置作差.
2.
.
3. 通过李群到李代数的指数映射,将更新量dx的指数映射乘到估计位姿态上即可;
T_esti = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * T_esti;
实现代码:
#include CMakeLists.txt
project(GN)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4)
find_package(OpenCV 3.4.15 REQUIRED)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
set(Sophus_LIBRARIES libSophus.so)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(gn GN-BA.cpp)
target_link_libraries(gn ${Sophus_LIBRARIES})

4,用ICP实现轨迹的对齐

两条轨迹的观测坐标系不同,需要通过ICP的SVD方法算出R,t,然后将真实位姿乘以求出的T(R,t),将其变换到相机坐标下进行显示:
实现代码:
#include CMakeLists.txt
project(ICP)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
find_package(OpenCV 3.4.15 REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
include_directories( ${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
include_directories( ${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(draw_trajectory draw_trajectory.cpp)
target_link_libraries(draw_trajectory ${Sophus_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES})