python networkx库学习、使用笔记
项目中用到了networkx库,这个库实现了图论里面很多经典的算法,包括最短路径算法,有向图的最长路径算法。
import networkx as nx # 导入networkx库
然后我们自定义一个图:图中每个键对应的值存储的是该节点的父节点列表和子节点列表
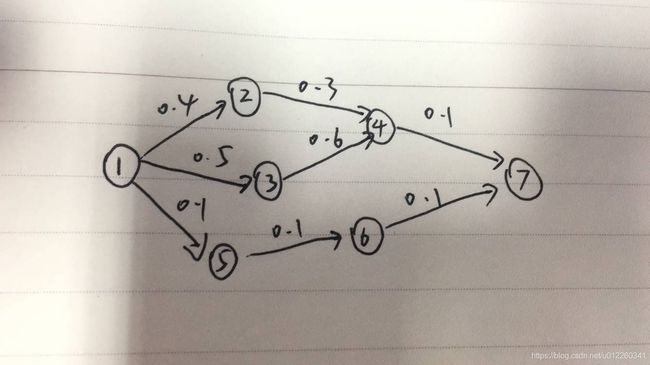
graph_dict = {1: [[], [2, 3, 5]], 2: [[1], [4]], 3: [[1], [4]], 4: [[2, 3], [7]], 5: [[1], [6]], 6: [[5], [7]],
7: [[6, 4], []]}
weight_dict = {1: [[], [0.4, 0.5, 0.1]], 2: [[0.4], [0.3]], 3: [[0.5], [0.6]], 4: [[0.3, 0.6], [0.1]],
5: [[0.1], [0.1]], 6: [[0.1], [0.1]], 7: [[0.1, 0.1], []]}
图大概长这样子:
然后创建一个图实例:
G = nx.DiGraph()
接下来构建图中的边:
for (k1, v1), v2 in zip(graph_dict.items(), weight_dict.values()):
for node, w in zip(v1[1], v2[1]):
G.add_edge(str(k1), str(node), weight=w) # 添加边,这里的weight为边的权值
现在,我们要计算从源点1到目标点7的最短路径,那么使用:
res = nx.shortest_path(G, source='1', target='7', weight='weight') # weight参数默认是None,因此需要改成'weight'
输出res得到 ['1', '5', '6', '7']
由于我们的图是一个有向无环图(DAG)并且图中的权值都是正数,那么我们还可以找到图中的最长路径:
res = nx.dag_longest_path(G)
输出res得到 ['1', '3', '4', '7']
另外,还可以判断图是否是DAG:
print nx.is_directed_acyclic_graph(G)
以及拓扑排序结果:
res = nx.topological_sort(G) print list(res) # 以点的方式输出['1', '5', '6', '2', '3', '4', '7']
res = nx.topological_sort(nx.line_graph(G))
print list(res) # 以边的方式输出[('1', '3'), ('3', '4'), ('1', '5'), ('5', '6'), ('6', '7'), ('1', '2'), ('2', '4'), ('4', '7')]