CIBERSORT 学习笔记
文章目录
- CIBERSORT
- 一、CIBERSORT 是什么
- 二、CIBERSORT 怎么用
- 三、CIBERSORT 结果可视化
CIBERSORT
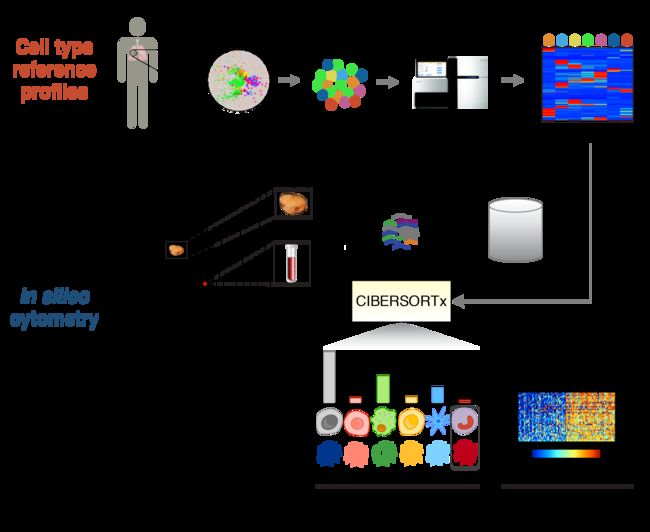
CIBERSORT is an analytical tool from the Alizadeh Lab developed by Newman et al. to provide an estimation of the abundances of member cell types in a mixed cell population, using gene expression data.
CIBERSORTx, the next generation version of CIBERSORT, is now available (Newman et al.), with support for single-cell RNA-seq and cell type-specific gene expression purification. We recommend moving over to the CIBERSORTx website. For users who registered with CIBERSORT prior to 2018, you may log in with your CIBERSORT account credentials, otherwise please register for a new account.
CIBERSORT 旧版官网入口:https://cibersort.stanford.edu/
现在新版本名字加了一个x,叫CIBERSORTx,主要增加了适配大量组织(bulk tissue)样本单细胞测序方面的功能,新版入口:https://cibersortx.stanford.edu/
原文地址:https://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth.3337
一、CIBERSORT 是什么
CIBERSORTx is an analytical tool from the Alizadeh Lab and Newman Lab to impute gene expression profiles and provide an estimation of the abundances of member cell types in a mixed cell population, using gene expression data. (输入基因表达矩阵,输出样本中的各种细胞类型的丰度。比较有意思的是,CIBERSORT的设计之初的核心目标是“predicting fractions of multiple cell types in gene expression profiles (GEPs)”,可能例子里22个免疫细胞 signature让人太过印象深刻,几乎全互联网的教程都是基于免疫细胞的,CIBERSORT也被认为是专门用来量化免疫浸润的,其实signature是可以按需求自行选择的。)
二、CIBERSORT 怎么用
CIBERSORT可以在线用(第一部分有官网,里面有详细教程),也可以在本地用R环境跑。CIBERSORT是基于线性支持向量回归(SVR)开发的,gene作为输入在计算过程中去卷积化。CIBERSORT主要需要ν-SVR算法的库, 用R去执行CIBERSORT的话,需要加载 R package e1071作为前置条件。CIBERSORT R script v1.04 代码:
# CIBERSORT R script v1.04 (last updated 10-24-2016)
# Note: Signature matrix construction is not currently available; use java version for full functionality.
# Author: Aaron M. Newman, Stanford University ([email protected])
# Requirements:
# R v3.0 or later. (dependencies below might not work properly with earlier versions)
# install.packages('e1071')
# install.pacakges('parallel')
# install.packages('preprocessCore')
# if preprocessCore is not available in the repositories you have selected, run the following:
# source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R")
# biocLite("preprocessCore")
# Windows users using the R GUI may need to Run as Administrator to install or update packages.
# This script uses 3 parallel processes. Since Windows does not support forking, this script will run
# single-threaded in Windows.
#
# Usage:
# Navigate to directory containing R script
#
# In R:
# source('CIBERSORT.R')
# results <- CIBERSORT('sig_matrix_file.txt','mixture_file.txt', perm, QN, absolute, abs_method)
#
# Options:
# i) perm = No. permutations; set to >=100 to calculate p-values (default = 0)
# ii) QN = Quantile normalization of input mixture (default = TRUE)
# iii) absolute = Run CIBERSORT in absolute mode (default = FALSE)
# - note that cell subsets will be scaled by their absolute levels and will not be
# represented as fractions (to derive the default output, normalize absolute
# levels such that they sum to 1 for each mixture sample)
# - the sum of all cell subsets in each mixture sample will be added to the ouput
# ('Absolute score'). If LM22 is used, this score will capture total immune content.
# iv) abs_method = if absolute is set to TRUE, choose method: 'no.sumto1' or 'sig.score'
# - sig.score = for each mixture sample, define S as the median expression
# level of all genes in the signature matrix divided by the median expression
# level of all genes in the mixture. Multiple cell subset fractions by S.
# - no.sumto1 = remove sum to 1 constraint
#
# Input: signature matrix and mixture file, formatted as specified at http://cibersort.stanford.edu/tutorial.php
# Output: matrix object containing all results and tabular data written to disk 'CIBERSORT-Results.txt'
# License: http://cibersort.stanford.edu/CIBERSORT_License.txt
#Core algorithm
CoreAlg <- function(X, y, absolute, abs_method){
#try different values of nu
svn_itor <- 3
res <- function(i){
if(i==1){nus <- 0.25}
if(i==2){nus <- 0.5}
if(i==3){nus <- 0.75}
model<-svm(X,y,type="nu-regression",kernel="linear",nu=nus,scale=F)
model
}
if(Sys.info()['sysname'] == 'Windows') out <- mclapply(1:svn_itor, res, mc.cores=1) else
out <- mclapply(1:svn_itor, res, mc.cores=svn_itor)
nusvm <- rep(0,svn_itor)
corrv <- rep(0,svn_itor)
#do cibersort
t <- 1
while(t <= svn_itor) {
weights = t(out[[t]]$coefs) %*% out[[t]]$SV
weights[which(weights<0)]<-0
w<-weights/sum(weights)
u <- sweep(X,MARGIN=2,w,'*')
k <- apply(u, 1, sum)
nusvm[t] <- sqrt((mean((k - y)^2)))
corrv[t] <- cor(k, y)
t <- t + 1
}
#pick best model
rmses <- nusvm
mn <- which.min(rmses)
model <- out[[mn]]
#get and normalize coefficients
q <- t(model$coefs) %*% model$SV
q[which(q<0)]<-0
if(!absolute || abs_method == 'sig.score') w <- (q/sum(q)) #relative space (returns fractions)
if(absolute && abs_method == 'no.sumto1') w <- q #absolute space (returns scores)
mix_rmse <- rmses[mn]
mix_r <- corrv[mn]
newList <- list("w" = w, "mix_rmse" = mix_rmse, "mix_r" = mix_r)
}
#do permutations
doPerm <- function(perm, X, Y, absolute, abs_method){
itor <- 1
Ylist <- as.list(data.matrix(Y))
dist <- matrix()
while(itor <= perm){
#print(itor)
#random mixture
yr <- as.numeric(Ylist[sample(length(Ylist),dim(X)[1])])
#standardize mixture
yr <- (yr - mean(yr)) / sd(yr)
#run CIBERSORT core algorithm
result <- CoreAlg(X, yr, absolute, abs_method)
mix_r <- result$mix_r
#store correlation
if(itor == 1) {dist <- mix_r}
else {dist <- rbind(dist, mix_r)}
itor <- itor + 1
}
newList <- list("dist" = dist)
}
#main function
CIBERSORT <- function(sig_matrix, mixture_file, perm=0, QN=TRUE, absolute=FALSE, abs_method='sig.score'){
#dependencies
require(e1071)
require(parallel)
require(preprocessCore)
if(absolute && abs_method != 'no.sumto1' && abs_method != 'sig.score') stop("abs_method must be set to either 'sig.score' or 'no.sumto1'")
#read in data
X <- read.table(sig_matrix,header=T,sep="\t",row.names=1,check.names=F)
Y <- read.table(mixture_file, header=T, sep="\t",check.names=F)
#to prevent crashing on duplicated gene symbols, add unique numbers to identical names
dups <- dim(Y)[1] - length(unique(Y[,1]))
if(dups > 0) {
warning(paste(dups," duplicated gene symbol(s) found in mixture file!",sep=""))
rownames(Y) <- make.names(Y[,1], unique=TRUE)
}else {rownames(Y) <- Y[,1]}
Y <- Y[,-1]
X <- data.matrix(X)
Y <- data.matrix(Y)
#order
X <- X[order(rownames(X)),]
Y <- Y[order(rownames(Y)),]
P <- perm #number of permutations
#anti-log if max < 50 in mixture file
if(max(Y) < 50) {Y <- 2^Y}
#quantile normalization of mixture file
if(QN == TRUE){
tmpc <- colnames(Y)
tmpr <- rownames(Y)
Y <- normalize.quantiles(Y)
colnames(Y) <- tmpc
rownames(Y) <- tmpr
}
#store original mixtures
Yorig <- Y
Ymedian <- max(median(Yorig),1)
#intersect genes
Xgns <- row.names(X)
Ygns <- row.names(Y)
YintX <- Ygns %in% Xgns
Y <- Y[YintX,]
XintY <- Xgns %in% row.names(Y)
X <- X[XintY,]
#standardize sig matrix
X <- (X - mean(X)) / sd(as.vector(X))
#empirical null distribution of correlation coefficients
if(P > 0) {nulldist <- sort(doPerm(P, X, Y, absolute, abs_method)$dist)}
header <- c('Mixture',colnames(X),"P-value","Correlation","RMSE")
if(absolute) header <- c(header, paste('Absolute score (',abs_method,')',sep=""))
output <- matrix()
itor <- 1
mixtures <- dim(Y)[2]
pval <- 9999
#iterate through mixtures
while(itor <= mixtures){
y <- Y[,itor]
#standardize mixture
y <- (y - mean(y)) / sd(y)
#run SVR core algorithm
result <- CoreAlg(X, y, absolute, abs_method)
#get results
w <- result$w
mix_r <- result$mix_r
mix_rmse <- result$mix_rmse
if(absolute && abs_method == 'sig.score') {
w <- w * median(Y[,itor]) / Ymedian
}
#calculate p-value
if(P > 0) {pval <- 1 - (which.min(abs(nulldist - mix_r)) / length(nulldist))}
#print output
out <- c(colnames(Y)[itor],w,pval,mix_r,mix_rmse)
if(absolute) out <- c(out, sum(w))
if(itor == 1) {output <- out}
else {output <- rbind(output, out)}
itor <- itor + 1
}
#save results
write.table(rbind(header,output), file="CIBERSORT-Results.txt", sep="\t", row.names=F, col.names=F, quote=F)
#return matrix object containing all results
obj <- rbind(header,output)
obj <- obj[,-1]
obj <- obj[-1,]
obj <- matrix(as.numeric(unlist(obj)),nrow=nrow(obj))
rownames(obj) <- colnames(Y)
if(!absolute){colnames(obj) <- c(colnames(X),"P-value","Correlation","RMSE")}
else{colnames(obj) <- c(colnames(X),"P-value","Correlation","RMSE",paste('Absolute score (',abs_method,')',sep=""))}
obj
}
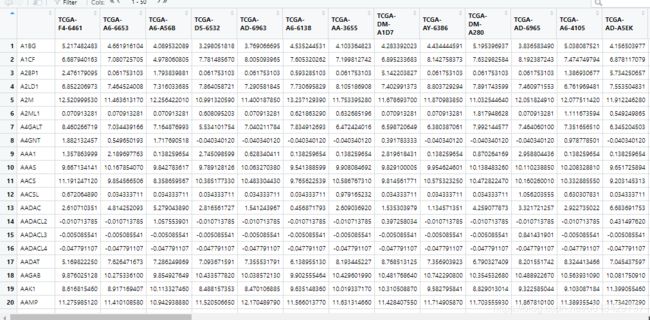
例子数据来自:https://github.com/zomithex/CIBERSORT,当然也可以从官网下,就是LM22后缀不一样,一个是txt,另一个是csv。
首先加载包,source脚本,读取数据:
# 我的例子是TCGA数据库大肠癌的100个样本
library("limma")
library('e1071')
source("CIBERSORT.R")
exp <- read.csv("TCGA_ROAD_100.csv",header=T,check.names=F)
# 整理一下行名,列名,删除表达特别低的基因
exp=as.matrix(exp)
rownames(exp)=exp[,1]
exp=exp[,2:ncol(exp)]
dimnames=list(rownames(exp),colnames(exp))
data=matrix(as.numeric(as.matrix(exp)),nrow=nrow(exp),dimnames=dimnames)
data=avereps(data)
data=data[rowMeans(data)>0,]
值得一提的事,CIBERSORT里面,自带log2转换功能。
#anti-log if max < 50 in mixture file
if(max(Y) < 50) {Y <- 2^Y}
当然log2转换也可以自己手动做,因为limma中负责Transform RNA-Seq Data Ready for Linear Modelling的voom函数不接受负值。
#把准备输入CIBERSORT的数据保存一下
v <-voom(data, plot = F, save.plot = F)
out=v$E
out=rbind(ID=colnames(out),out)
write.table(out,file="TCGA_100_ready.txt",sep="\t",quote=F,col.names=F)
CIBERSOFT 搞定
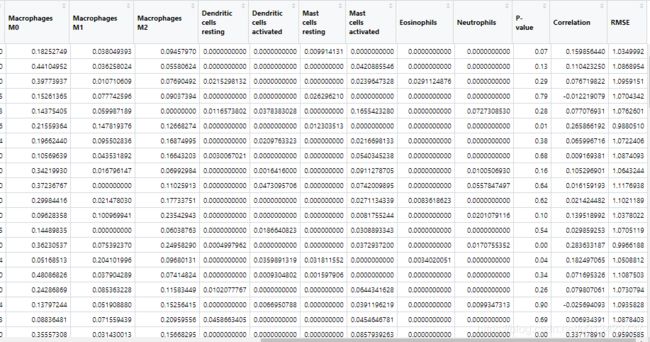
results=CIBERSORT("LM22.txt", "TCGA_100_ready.txt", perm=100, QN=TRUE)
write.csv(results,"TCGA_100_CIBERSORT_Output.csv")
输出的结果应该有25行,除了22种免疫细胞,还有P-value,Correlation, RMSE三行,滤掉不符合要求的样本就可以做可视化了。
三、CIBERSORT 结果可视化
简单做一个可视化吧。
#调包日常
pkgs <- c("matrixStats", "pheatmap", "RColorBrewer", "tidyverse", "cowplot","ggpubr","bslib","ggthemes")
lapply(pkgs, library, character.only = T)
# Read in results ---------------------------------------------------------
cibersort_raw <- read.csv("TCGA_100_CIBERSORT_Output.csv",row.names = 1,header = T)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
dd1 <- cibersort_raw %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
rownames_to_column("sample") %>%
pivot_longer(cols = 2:23,
names_to = "CellType",
values_to = "Composition")
plot.info <- dd1[,c(5,1,6)]
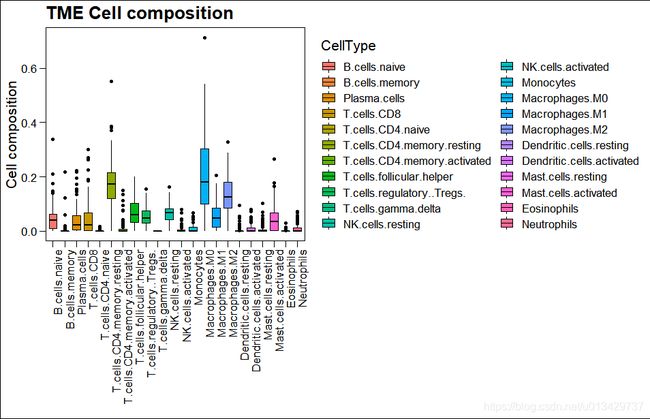
画两个棒棒图,都是彩虹色。
ggboxplot(
plot.info,
x = "CellType",
y = "Composition",
color = "black",
fill = "CellType",
xlab = "",
ylab = "Cell composition",
main = "TME Cell composition") +
theme_base() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(
angle = 90,
hjust = 1,
vjust = 1
))
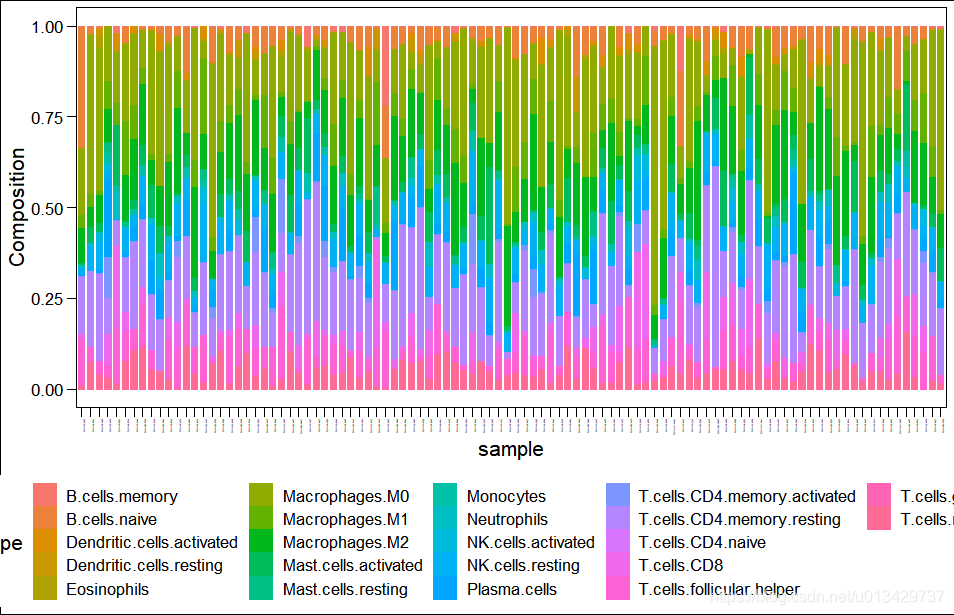
ggbarplot(
plot.info,
x = "sample",
y = "Composition",
size = 0,
fill = "CellType",
color = "CellType",
) +
theme_base() +
theme(
axis.text.x = element_text(
angle = 90,
hjust = 1,
vjust = 1,
size = 1
),
legend.position = "bottom"
)