“深度学习”学习日记。神经网络的推理处理
2023.1.6
今天终于考完试了正式放寒假,前几天阳了而且得备考,一直没有继续“深度学习”。
今天学习了利用MNIST数据集来进行神经网络得推理处理,学习得感悟就是编程得基础就是数学
import numpy as np
import sys, os
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
import pickle # pickle是python序列化的一个工具!可以用来把对象来以文件的形式存储起来,用的时候再加载
# pickle模块只能在python中使用,python中的几乎所有的数据类型都可以序列化!但是序列化以后得到的文件人看不懂
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
# 我们导入的x数据是28×28=784的图片
def get_data():
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False)
return x_test, t_test
# normalize= 归一化(正规化)将输入图片归化为0.0~1.0的值
# flatten= 设置是否将图像变成一维数组
# one_hot_label= 表示仅正确解标签1,其余的归化为0
# 现在这个阶段没学习的神经网络是如何学习得到参数的,假设“学习”好了,将学习好的权重参数保存到"sample_weight.pkl"
# 该文件以字典变量的形式保存权重和参数
def init_network():
with open("sample_weight.pkl", 'rb') as f: # rb: 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于只读。文件指针将会放在文件的开头
network = pickle.load(f) # load()函数的作用是反序列化恢复成python对象
return network
# predict()函数以numpy数组的形式输出各个标签的对应的概率
def predict(network, x):
W1, W2, W3 = network['W1'], network['W2'], network['W3']
b1, b2, b3 = network['b1'], network['b2'], network['b3']
a1 = np.dot(x, W1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(z1, W2) + b2
z2 = sigmoid(a2)
a3 = np.dot(z2, W3) + b3
y = softmax(a3) # 输出层设计 分类问题 通过线性代数的运算,得到符合我们需要的10个输出层
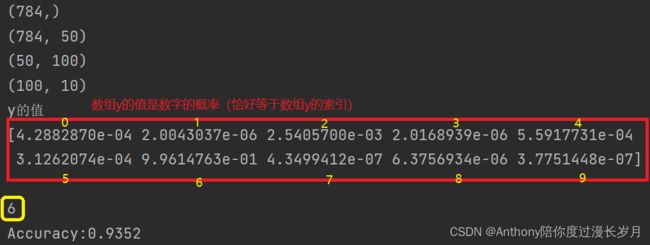
print(x.shape) # (784,)
print(W1.shape) # (784, 50)
print(W2.shape) # (50, 100)
print(W3.shape) # (100, 10)
print("y的值")
print(y, '\n')
return y
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def softmax(x): # 一种神经网络的激活函数
if x.ndim == 2: # 判断数组x的维度是否为2
x = x.T # 数组(矩阵)x的转置
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x)
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
x, t = get_data()
print("x的值", x, '\n', "t的值", t, '\n')
network = init_network()
accuracy_cnt = 0
for i in range(len(x)):
y = predict(network, x[i])
p = np.argmax(y) # 获取概率最高的元素的索引
print(t[i])
if p == t[i]:
accuracy_cnt += 1
print("Accuracy:" + str(float(accuracy_cnt) / len(x)))看看运行结果
MNIST数据导入的代码:
# coding: utf-8
try:
import urllib.request
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('You should use Python 3.x')
import os.path
import gzip
import pickle
import os
import numpy as np
url_base = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
key_file = {
'train_img': 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'train_label': 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
'test_img': 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'test_label': 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
}
dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
save_file = dataset_dir + "/mnist.pkl"
train_num = 60000
test_num = 10000
img_dim = (1, 28, 28)
img_size = 784
def _download(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
if os.path.exists(file_path):
return
print("Downloading " + file_name + " ... ")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_base + file_name, file_path)
print("Done")
def download_mnist():
for v in key_file.values():
_download(v)
def _load_label(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
print("Done")
return labels
def _load_img(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
data = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16)
data = data.reshape(-1, img_size)
print("Done")
return data
def _convert_numpy():
dataset = {}
dataset['train_img'] = _load_img(key_file['train_img'])
dataset['train_label'] = _load_label(key_file['train_label'])
dataset['test_img'] = _load_img(key_file['test_img'])
dataset['test_label'] = _load_label(key_file['test_label'])
return dataset
def init_mnist():
download_mnist()
dataset = _convert_numpy()
print("Creating pickle file ...")
with open(save_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(dataset, f, -1)
print("Done!")
def _change_one_hot_label(X):
T = np.zeros((X.size, 10))
for idx, row in enumerate(T):
row[X[idx]] = 1
return T
def load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):
"""读入MNIST数据集
Parameters
----------
normalize : 将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0
one_hot_label :
one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回
one-hot数组是指[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]这样的数组
flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组
Returns
-------
(训练图像, 训练标签), (测试图像, 测试标签)
"""
if not os.path.exists(save_file):
init_mnist()
with open(save_file, 'rb') as f:
dataset = pickle.load(f)
if normalize:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].astype(np.float32)
dataset[key] /= 255.0
if one_hot_label:
dataset['train_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['train_label'])
dataset['test_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['test_label'])
if not flatten:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return (dataset['train_img'], dataset['train_label']), (dataset['test_img'], dataset['test_label'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
init_mnist()