多目标跟踪之数据关联算法——匈牙利算法
零、Track和Detection的cost matrix,distance metric。距离计算的方式有如下几种:
- 距离cost distance metric,track和detection的距离矩阵。
外观距离appearance distance,来自检测切片ROI的网络特征提取;——余弦距离
运动模型距离 马氏距离,来自检测-跟踪的kalman校正距离,马氏距离==二维高斯分布,利用相关可以去除维度间的量纲影响,并考虑维度间的相关性。比如x,y,a,h四者的相关性和量纲差异,可以不被考虑。 - 距离矩阵的分配算法——匈牙利算法Hungarian,这里指的是Kuhn&Munkres Hungarian, KM匈牙利算法(加权的匈牙利算法)
① KM匈牙利,n个轨迹,m个检测。padding方式为max(n,m)
② KM匈牙利,直接对矩形n×m进行分配,不进行任何形式的padding
③ KM匈牙利,padding方式为(n+m)*(n+m),主对角有数值。其余分别为inf和0
这些算法的优缺点和差异分别为什么? - 距离矩阵进入匈牙利算法可以有不同的padding形式,他们对分配结果的差异是怎样的?

track_t CTrack::CalcDistCenter(const CRegion& reg) const
{
Point_t diff = m_predictionPoint - reg.m_rrect.center;
return sqrtf(sqr(diff.x) + sqr(diff.y));
}
track_t CTrack::CalcDistRect(const CRegion& reg) const
{
std::array diff;
diff[0] = reg.m_rrect.center.x - m_lastRegion.m_rrect.center.x;
diff[1] = reg.m_rrect.center.y - m_lastRegion.m_rrect.center.y;
diff[2] = static_cast(m_lastRegion.m_rrect.size.width - reg.m_rrect.size.width);
diff[3] = static_cast(m_lastRegion.m_rrect.size.height - reg.m_rrect.size.height);
diff[4] = static_cast(m_lastRegion.m_rrect.angle - reg.m_rrect.angle);
track_t dist = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < diff.size(); ++i)
{
dist += sqr(diff[i]);
}
return sqrtf(dist);
}
track_t CTrack::CalcDistJaccard(const CRegion& reg) const
{
track_t intArea = static_cast((reg.m_brect & m_lastRegion.m_brect).area());
track_t unionArea = static_cast(reg.m_brect.area() + m_lastRegion.m_brect.area() - intArea) + 1e-6;
return std::fabs(1 - intArea / unionArea);
}
track_t CTrack::CalcDistHist(const RegionEmbedding& embedding) const
{
track_t res = 1;
if (!embedding.m_hist.empty() && !m_regionEmbedding.m_hist.empty())
{
#if (((CV_VERSION_MAJOR == 4) && (CV_VERSION_MINOR < 1)) || (CV_VERSION_MAJOR == 3))
res = static_cast(cv::compareHist(embedding.m_hist, m_regionEmbedding.m_hist, CV_COMP_BHATTACHARYYA));
//res = 1.f - static_cast(cv::compareHist(hist, m_regionEmbedding.m_hist, CV_COMP_CORREL));
#else
res = static_cast(cv::compareHist(embedding.m_hist, m_regionEmbedding.m_hist, cv::HISTCMP_BHATTACHARYYA));
#endif
}
else
{
assert(0);
CV_Assert(!embedding.m_hist.empty());
CV_Assert(!m_regionEmbedding.m_hist.empty());
}
return res;
}
track_t CTrack::CalcMahalanobisDist(const cv::RotatedRect& rrect) const
{
cv::Mat res1, predictPoint;
// res1 = Hn * Pn+1|n+1 * Hn^T + Rn+1 error covariance
// res2 = Hn * Xn+1|n
m_kalman.GetPtStateAndResCov(res1, predictPoint);
double mahaDist = 0.0;
if (!res1.empty() && !predictPoint.empty())
{
cv::Mat icovar_Pn;
cv::invert(res1, icovar_Pn, cv::DECOMP_SVD);
cv::Mat measurePoint;
if (predictPoint.rows == 2) // PointUpdate
measurePoint = (cv::Mat_(2, 1) << rrect.center.x, rrect.center.y); // detection
else
measurePoint = (cv::Mat_(4, 1) << rrect.center.x, rrect.center.y, rrect.size.width, rrect.size.height); // predict
mahaDist = cv::Mahalanobis(measurePoint, predictPoint, icovar_Pn);
mahaDist += std::log(cv::determinant(res1));
}
return static_cast(mahaDist);
}
std::pair CTrack::CalcCosine(const RegionEmbedding& embedding) const
{
track_t res = 1;
if (!embedding.m_embedding.empty() && !m_regionEmbedding.m_embedding.empty())
{
double xy = embedding.m_embedding.dot(m_regionEmbedding.m_embedding);
double norm = sqrt(embedding.m_embDot * m_regionEmbedding.m_embDot) + 1e-6;
#if 0
res = 1.f - 0.5f * fabs(static_cast(xy / norm));
#else
res = 0.5f * static_cast(1.0 - xy / norm);
#endif
//std::cout << "CTrack::CalcCosine: " << embedding.m_embedding.size() << " - " << m_regionEmbedding.m_embedding.size() << " = " << res << std::endl;
return { res, true };
}
else
{
//assert(0);
//CV_Assert(!embedding.m_embedding.empty());
//CV_Assert(!m_regionEmbedding.m_embedding.empty());
return { 0, false };
}
}
一、匈牙利算法维基百科:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/匈牙利算法
- 匈牙利算法最早是由匈牙利数学家Dénes Kőnig康尼格和Jenő Egerváry用来求矩阵中0元素的个数的一种方法。由此他证明『矩阵中独立0元素的最多个数等于能覆盖cover所有0元素的最少直线数』
- 匈牙利算法是一种在多项式时间内求解任务分配问题的组合优化算法,并推动了后来的原始对偶方法。
- 1955年,美国数学家哈罗德·库恩W.W.Kuhn(库恩)Harold W. Kuhn在求解著名的指派问题时引用了这一结论,并对具体算法做了改进,仍然称为匈牙利算法。此算法之所以被称作匈牙利算法,是因为算法很大一部分是基于以前匈牙利数学家Dénes Kőnig和Jenő Egerváry的工作之上创建起来的。[1][2]
- 1957年,詹姆士·芒克勒斯Munkres在1957年回顾了该算法,并发现它的时间复杂度为(强)多项式时间。[3] 此后该算法被称为Kuhn–Munkres算法或Munkres分配算法。原始算法的时间复杂度为
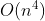 ,但杰克·爱德蒙斯与卡普发现可以修改算法达到
,但杰克·爱德蒙斯与卡普发现可以修改算法达到 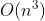 运行时间,富泽也独立发现了这一点。L·R·福特和D·R·福尔克森将该方法推广到了一般运输问题。2006年发现卡尔·雅可比 Jacobis bound在19世纪就解决了指派问题,该解法在他死后在1890年以拉丁文发表。[4]
运行时间,富泽也独立发现了这一点。L·R·福特和D·R·福尔克森将该方法推广到了一般运输问题。2006年发现卡尔·雅可比 Jacobis bound在19世纪就解决了指派问题,该解法在他死后在1890年以拉丁文发表。[4]
参考书目
- R.E. Burkard, M. Dell'Amico, S. Martello: Assignment Problems (Revised reprint). SIAM, Philadelphia (PA.) 2012. ISBN 978-1-61197-222-1
- M. Fischetti, "Lezioni di Ricerca Operativa", Edizioni Libreria Progetto Padova, Italia, 1995.
- R. Ahuja, T. Magnanti, J. Orlin, "Network Flows", Prentice Hall, 1993.
- S. Martello, "Jeno Egerváry: from the origins of the Hungarian algorithm to satellite communication". Central European Journal of Operations Research 18, 47–58, 2010
参考文献
- ^ Harold W. Kuhn, "The Hungarian Method for the assignment problem", Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 2: 83–97, 1955. Kuhn's original publication.
- ^ Harold W. Kuhn, "Variants of the Hungarian method for assignment problems", Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 3: 253–258, 1956.
https://econweb.ucsd.edu/~v2crawford/hungar.pdf Kuhn的paper1960年9月29日。 - ^ J. Munkres, "Algorithms for the Assignment and Transportation Problems", Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 5(1):32–38, 1957 March.
- ^ JACOBI'S BOUND
外部链接
- Bruff, Derek, "The Assignment Problem and the Hungarian Method", [1] (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- Mordecai J. Golin, Bipartite Matching and the Hungarian Method, Course Notes, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
- R. A. Pilgrim, Munkres' Assignment Algorithm. Modified for Rectangular Matrices (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆), Course notes, Murray State University.
- Mike Dawes, The Optimal Assignment Problem, Course notes, University of Western Ontario.
- On Kuhn's Hungarian Method – A tribute from Hungary, András Frank, Egervary Research Group, Pazmany P. setany 1/C, H1117, Budapest, Hungary.
- Lecture: Fundamentals of Operations Research - Assignment Problem - Hungarian Algorithm, Prof. G. Srinivasan, Department of Management Studies, IIT Madras.
- Extension: Assignment sensitivity analysis (with O(n^4) time complexity), Liu, Shell.
- Solve any Assignment Problem online, provides a step by step explanation of the Hungarian Algorithm.
各种语言的算法实现链接
(请注意,并非所有这些都满足 ![]() 时间约束。)
时间约束。)
- C implementation with O ( n 3 ) time complexity
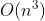
- Java implementation of O ( n 3 ) time variant
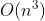
- Python implementation (see also here)
- Ruby implementation with unit tests
- C# implementation
- D implementation with unit tests (port of the Java O ( n 3 ) version)
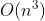
- Online interactive implementation Please note that this implements a variant of the algorithm as described above.
- Graphical implementation with options (Java applet)
- Serial and parallel implementations.
- Implementation in Matlab and C
- Perl implementation
- Lisp implementation
- C++ (STL) implementation (multi-functional bipartite graph version)
- C++ implementation
- C++ implementation of the O ( n 3 ) algorithm
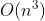 C++ implementation of the O ( n 3 ) algorithm (BSD style open source licensed)
C++ implementation of the O ( n 3 ) algorithm (BSD style open source licensed) - Another C++ implementation with unit tests
- Another Java implementation with JUnit tests (Apache 2.0)[永久失效链接]
- MATLAB implementation
-
上面的matlab实现,代码见『2.1Matlab代码』
-
的 https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/6543-functions-for-the-rectangular-assignment-problem
-
- C implementation
- Javascript implementation
- The clue R package proposes an implementation, solve_LSAP
二、Matlab版本的匈牙利Hungarian算法
- Matlab实现一: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/6543-functions-for-the-rectangular-assignment-problem
- Matlab实现二:C:\Users\XXXX\Documents\MATLAB\Examples\vision\MotionBasedMultiObjectTrackingExample 中的 [assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, costOfNonAssignment); 函数就调用了匈牙利算法。
- matlab exchange 上面关于匈牙利算法的所有实现:https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange?q=Hungarian+algorithm
2.1 matlab代码 by Alexander Melin
地址为:https://web.archive.org/web/20120816044907/http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/11609-hungarian-algorithm/content/Hungarian.m
function [Matching,Cost] = Hungarian(Perf)
%
% [MATCHING,COST] = Hungarian_New(WEIGHTS)
%
% A function for finding a minimum edge weight matching given a MxN Edge
% weight matrix WEIGHTS using the Hungarian Algorithm.
%
% An edge weight of Inf indicates that the pair of vertices given by its
% position have no adjacent edge.
%
% MATCHING return a MxN matrix with ones in the place of the matchings and
% zeros elsewhere.
%
% COST returns the cost of the minimum matching
% Written by: Alex Melin 30 June 2006
% Initialize Variables
Matching = zeros(size(Perf));
% Condense the Performance Matrix by removing any unconnected vertices to
% increase the speed of the algorithm
% Find the number in each column that are connected
num_y = sum(~isinf(Perf),1);
% Find the number in each row that are connected
num_x = sum(~isinf(Perf),2);
% Find the columns(vertices) and rows(vertices) that are isolated
x_con = find(num_x~=0);
y_con = find(num_y~=0);
% Assemble Condensed Performance Matrix
P_size = max(length(x_con),length(y_con));
P_cond = zeros(P_size);
P_cond(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con)) = Perf(x_con,y_con);
if isempty(P_cond)
Cost = 0;
return
end
% Ensure that a perfect matching exists
% Calculate a form of the Edge Matrix
Edge = P_cond;
Edge(P_cond~=Inf) = 0;
% Find the deficiency(CNUM) in the Edge Matrix
cnum = min_line_cover(Edge);
% Project additional vertices and edges so that a perfect matching
% exists
Pmax = max(max(P_cond(P_cond~=Inf)));
P_size = length(P_cond)+cnum;
P_cond = ones(P_size)*Pmax;
P_cond(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con)) = Perf(x_con,y_con);
%*************************************************
% MAIN PROGRAM: CONTROLS WHICH STEP IS EXECUTED
%*************************************************
exit_flag = 1;
stepnum = 1;
while exit_flag
switch stepnum
case 1
[P_cond,stepnum] = step1(P_cond);
case 2
[r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(P_cond);
case 3
[c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,P_size);
case 4
[M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov,M);
case 5
[M,r_cov,c_cov,stepnum] = step5(M,Z_r,Z_c,r_cov,c_cov);
case 6
[P_cond,stepnum] = step6(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov);
case 7
exit_flag = 0;
end
end
% Remove all the virtual satellites and targets and uncondense the
% Matching to the size of the original performance matrix.
Matching(x_con,y_con) = M(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con));
Cost = sum(sum(Perf(Matching==1)));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% STEP 1: Find the smallest number of zeros in each row
% and subtract that minimum from its row
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step1(P_cond)
P_size = length(P_cond);
% Loop throught each row
for ii = 1:P_size
rmin = min(P_cond(ii,:));
P_cond(ii,:) = P_cond(ii,:)-rmin;
end
stepnum = 2;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 2: Find a zero in P_cond. If there are no starred zeros in its
% column or row start the zero. Repeat for each zero
%**************************************************************************
function [r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(P_cond)
% Define variables
P_size = length(P_cond);
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
M = zeros(P_size); % A mask that shows if a position is starred or primed
for ii = 1:P_size
for jj = 1:P_size
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
M(ii,jj) = 1;
r_cov(ii) = 1;
c_cov(jj) = 1;
end
end
end
% Re-initialize the cover vectors
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
stepnum = 3;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 3: Cover each column with a starred zero. If all the columns are
% covered then the matching is maximum
%**************************************************************************
function [c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,P_size)
c_cov = sum(M,1);
if sum(c_cov) == P_size
stepnum = 7;
else
stepnum = 4;
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 4: Find a noncovered zero and prime it. If there is no starred
% zero in the row containing this primed zero, Go to Step 5.
% Otherwise, cover this row and uncover the column containing
% the starred zero. Continue in this manner until there are no
% uncovered zeros left. Save the smallest uncovered value and
% Go to Step 6.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov,M)
P_size = length(P_cond);
zflag = 1;
while zflag
% Find the first uncovered zero
row = 0; col = 0; exit_flag = 1;
ii = 1; jj = 1;
while exit_flag
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
row = ii;
col = jj;
exit_flag = 0;
end
jj = jj + 1;
if jj > P_size; jj = 1; ii = ii+1; end
if ii > P_size; exit_flag = 0; end
end
% If there are no uncovered zeros go to step 6
if row == 0
stepnum = 6;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = 0;
Z_c = 0;
else
% Prime the uncovered zero
M(row,col) = 2;
% If there is a starred zero in that row
% Cover the row and uncover the column containing the zero
if sum(find(M(row,:)==1)) ~= 0
r_cov(row) = 1;
zcol = find(M(row,:)==1);
c_cov(zcol) = 0;
else
stepnum = 5;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = row;
Z_c = col;
end
end
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 5: Construct a series of alternating primed and starred zeros as
% follows. Let Z0 represent the uncovered primed zero found in Step 4.
% Let Z1 denote the starred zero in the column of Z0 (if any).
% Let Z2 denote the primed zero in the row of Z1 (there will always
% be one). Continue until the series terminates at a primed zero
% that has no starred zero in its column. Unstar each starred
% zero of the series, star each primed zero of the series, erase
% all primes and uncover every line in the matrix. Return to Step 3.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,stepnum] = step5(M,Z_r,Z_c,r_cov,c_cov)
zflag = 1;
ii = 1;
while zflag
% Find the index number of the starred zero in the column
rindex = find(M(:,Z_c(ii))==1);
if rindex > 0
% Save the starred zero
ii = ii+1;
% Save the row of the starred zero
Z_r(ii,1) = rindex;
% The column of the starred zero is the same as the column of the
% primed zero
Z_c(ii,1) = Z_c(ii-1);
else
zflag = 0;
end
% Continue if there is a starred zero in the column of the primed zero
if zflag == 1;
% Find the column of the primed zero in the last starred zeros row
cindex = find(M(Z_r(ii),:)==2);
ii = ii+1;
Z_r(ii,1) = Z_r(ii-1);
Z_c(ii,1) = cindex;
end
end
% UNSTAR all the starred zeros in the path and STAR all primed zeros
for ii = 1:length(Z_r)
if M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) == 1
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 0;
else
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 1;
end
end
% Clear the covers
r_cov = r_cov.*0;
c_cov = c_cov.*0;
% Remove all the primes
M(M==2) = 0;
stepnum = 3;
% *************************************************************************
% STEP 6: Add the minimum uncovered value to every element of each covered
% row, and subtract it from every element of each uncovered column.
% Return to Step 4 without altering any stars, primes, or covered lines.
%**************************************************************************
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step6(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov)
a = find(r_cov == 0);
b = find(c_cov == 0);
minval = min(min(P_cond(a,b)));
P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) = P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) + minval;
P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) = P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) - minval;
stepnum = 4;
function cnum = min_line_cover(Edge)
% Step 2
[r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(Edge);
% Step 3
[c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,length(Edge));
% Step 4
[M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(Edge,r_cov,c_cov,M);
% Calculate the deficiency
cnum = length(Edge)-sum(r_cov)-sum(c_cov);2.2 Matlab代码,MotionBasedMultiObjectTrackingExample.m官方例子中的assignDetectionsToTracks.m
- 使用第二个实现方法来分析匈牙利算法的过程,核心代码如下:
James Munkres' variant of the Hungarian assignment algorithm.
References:
- Matt L. Miller, Harold S. Stone, and Ingemar J. Cox. Optimizing Murty's Ranked Assignment Method. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 33(3), 1997
- James Munkres, Algorithms for Assignment and Transportation Problems, Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Volume 5, Number 1, March, 1957
- R. A. Pilgrim. Munkres' Assignment Algorithm Modified for Rectangular Matrices http://csclab.murraystate.edu/bob.pilgrim/445/munkres.html
[assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = assignDetectionsToTracks(costMatrix, costOfNonAssignment)
- costMatrix 是一个 M×N 矩阵,其中 M 是轨道数,N 是检测数。
- costMatrix(i,j) 是将第 j 个检测分配给第 i 个轨道的成本。成本越低,分配的可能性就越大。
- costOfNonAssignment 是一个标量,它表示未分配的轨道或检测remain unassigned仍然未被分配的成本。costOfNonAssignment 值越大,表明每个现有轨道都会以较高的可能性将被分配一个检测。
- 输出:assignments 是一个 L×2 的索引对轨道和相应的检测矩阵,其中 L 是对的数量。第一列包含轨道索引,第二列包含相应的检测索引。 unassignedTracks 是 P 元素,其中 P 是未分配轨道的数量。每个元素是未分配检测的轨道的索引。未分配检测是 Q 元素向量,其中 Q 是未分配检测的数量。每个元素是未分配给任何轨道的检测索引。这些检测可以开始新的轨道。
..assignDetectionsToTracks(costMatrix,unassignedTrackCost,..unassignedDetectionCost) 分别指定未分配轨迹和检测的cost。
- 输入:unassignedTrackCost 是标量或 M 元素向量,其中 M 是轨迹数。对于 M 元素向量,每个元素表示不给每个track分配任何检测的cost。标量输入表示未分配所有轨道的相同成本。成本可能会因您对每个轨道和场景的了解而异。例如,如果物体即将离开视野,相应轨迹的未分配的代价应该很低。
- unassignedDetectionCost是标量或N元素向量,其中N是检测次数。对于N元素向量,每个元素表示为该检测启动新轨道的cost。标量输入表示未分配所有轨道的相同成本。成本可能会因您对每个检测和场景的了解而有所不同。例如,如果检测图像出现在靠近图像边缘的位置,它更有可能是一个新物体。
关闭科学计数法: MATLAB关闭科学计数法显示_Ray-Soft的博客-CSDN博客_matlab取消科学计数法
小数位个数变少: format short e
代码源码如下所示:
function [matches, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
assignDetectionsToTracks(costMatrix, costUnassignedTracks, ...
costUnassignedDetections)
%#codegen
%#ok<*EMCLS>
%#ok<*EMCA>
% Parse and check inputs
checkCost(costMatrix);
checkUnassignedCost(costUnassignedTracks, 'costUnassignedTracks');
coder.internal.errorIf(nargin == 2 && ~isscalar(costUnassignedTracks), ...
'vision:assignDetectionsToTracks:costOfNotMatchingMustBeScalar');
coder.internal.errorIf(~isa(costMatrix, class(costUnassignedTracks)), ...
'vision:assignDetectionsToTracks:allInputsMustBeSameClass');
if nargin > 2
checkUnassignedCost(costUnassignedDetections, ...
'costUnassignedDetections');
coder.internal.errorIf(~isa(costMatrix, class(costUnassignedDetections)), ...
'vision:assignDetectionsToTracks:allInputsMustBeSameClass');
coder.internal.errorIf(~isscalar(costUnassignedTracks) && ...
(numel(costUnassignedTracks) ~= size(costMatrix, 1)), ...
'vision:assignDetectionsToTracks:costUnmatchedTracksInvalidSize');
coder.internal.errorIf(~isscalar(costUnassignedDetections) && ...
(numel(costUnassignedDetections) ~= size(costMatrix, 2)), ...
'vision:assignDetectionsToTracks:costUnmatchedDetectionsInvalidSize');
end
theClass = class(costMatrix);
costUnmatchedTracksVector = ones(1, size(costMatrix, 1), theClass) .* ...
costUnassignedTracks;
if nargin > 2
costUnmatchedDetectionsVector = ones(1, size(costMatrix, 2), theClass) ...
.* costUnassignedDetections;
else
costUnmatchedDetectionsVector = ones(1, size(costMatrix, 2), theClass) .*...
costUnassignedTracks;
end
[matches, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
cvalgAssignDetectionsToTracks(costMatrix, costUnmatchedTracksVector, ...
costUnmatchedDetectionsVector);
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function tf = checkCost(cost)
validateattributes(cost, {'numeric'}, ...
{'real', 'nonsparse', 'nonnan', '2d'}, ...
'assignDetectionsToTracks', 'cost');
tf = true;
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function tf = checkUnassignedCost(val, varName)
validateattributes(val, {'numeric'}, ...
{'vector', 'finite', 'real', 'nonsparse'}, ...
'assignDetectionsToTracks', varName);
tf = true;
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [matches, unmatchedTracks, unmatchedDetections] = ...
cvalgAssignDetectionsToTracks(cost, costUnmatchedTracks, ...
costUnmatchedDetections)
% add dummy rows and columns to account for the possibility of
% unassigned tracks and observations
paddedCost = getPaddedCost(cost, costUnmatchedTracks, ...
costUnmatchedDetections);
% solve the assignment problem
[rowInds, colInds] = find(hungarianAssignment(paddedCost));
rows = size(cost, 1);
cols = size(cost, 2);
unmatchedTracks = uint32(rowInds(rowInds <= rows & colInds > cols));
unmatchedDetections = uint32(colInds(colInds <= cols & rowInds > rows));
matches = uint32([rowInds, colInds]);
matches = matches(rowInds <= rows & colInds <= cols, :);
if isempty(matches)
matches = zeros(0, 2, 'uint32');
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function paddedCost = getPaddedCost(cost, costUnmatchedTracks,...
costUnmatchedDetections)
% replace infinities with the biggest possible number
bigNumber = getTheHighestPossibleCost(cost);
cost(isinf(cost)) = bigNumber;
% create a "padded" cost matrix, with dummy rows and columns
% to account for the possibility of not matching
rows = size(cost, 1);
cols = size(cost, 2);
paddedSize = rows + cols;
paddedCost = ones(paddedSize, class(cost)) * bigNumber;
paddedCost(1:rows, 1:cols) = cost;
for i = 1:rows
paddedCost(i, cols+i) = costUnmatchedTracks(i);
end
for i = 1:cols
paddedCost(rows+i, i) = costUnmatchedDetections(i);
end
paddedCost(rows+1:end, cols+1:end) = 0;
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function bigNumber = getTheHighestPossibleCost(cost)
if isinteger(cost)
bigNumber = intmax(class(cost));
else
bigNumber = realmax(class(cost));
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function assignment = hungarianAssignment(cost)
assignment = true(size(cost));
if isempty(cost)
return;
end
fprintf("原始padding cost=\n")
disp(cost)
% step 1: subtract row minima
cost = bsxfun(@minus, cost, min(cost, [], 2));
fprintf("step1-减去行最小值后: \ncost=\n")
disp(cost)
% step 2: make an initial assignment by "starring" zeros
stars = makeInitialAssignment(cost);
fprintf("step2-初始猜测 \nstar=\n")
disp(stars)
% step 3: cover all columns containing starred zeros
colCover = any(stars);
while ~all(colCover)
% uncover all rows and unprime all zeros
rowCover = false(1, size(cost, 1));
primes = false(size(stars));
Z = ~cost; % mark locations of the zeros
Z(:, colCover) = false;
while 1
shouldCreateNewZero = true;
% step 4: Find a noncovered zero and prime it.
[zi, zj] = findNonCoveredZero(Z);
while zi > 0
primes(zi, zj) = true;
% find a starred zero in the column containing the primed zero
starredRow = stars(zi, :);
if any(starredRow)
% if there is one, cover the its row and uncover
% its column.
rowCover(zi) = true;
colCover(starredRow) = false;
Z(zi, :) = false;
Z(~rowCover, starredRow) = ~cost(~rowCover, starredRow);
[zi, zj] = findNonCoveredZero(Z);
else
shouldCreateNewZero = false;
% go to step 5
break;
end
end
if shouldCreateNewZero
% step 6: create a new zero
[cost, Z] = createNewZero(cost, rowCover, colCover);
fprintf("step 6-创建新的0\n cost = \n")
disp(cost)
else
break;
end
end
% step 5: Construct a series of alternating primed and starred zeros.
stars = alternatePrimesAndStars(stars, primes, zi, zj);
fprintf("step 5-重新标记0 stars=\n")
disp(stars)
% step 3: cover all columns containing starred zeros
colCover = any(stars);
end
assignment = stars;
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function stars = makeInitialAssignment(cost)
rowCover = false(1, size(cost, 1));
colCover = false(1, size(cost, 2));
stars = false(size(cost));
[zr, zc] = find(cost == 0);
for i = 1:numel(zr)
if ~rowCover(zr(i)) && ~colCover(zc(i))
stars(zr(i), zc(i)) = true;
rowCover(zr(i)) = true;
colCover(zc(i)) = true;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [zi, zj] = findNonCoveredZero(Z)
fprintf("step 4- 查找Z是否有0\nZ=\n")
disp(Z)
[i, j] = find(Z, 1);
if isempty(i)
zi = -1;
zj = -1;
else
zi = i(1);
zj = j(1);
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [cost, Z] = createNewZero(cost, rowCover, colCover)
Z = false(size(cost));
% find a minimum uncovered value
uncovered = cost(~rowCover, ~colCover);
minVal = min(uncovered(:));
% add the minimum value to all intersections of covered rows and cols
cost(rowCover, colCover) = cost(rowCover, colCover) + minVal;
% subtract the minimum value from all uncovered entries creating at
% least one new zero
cost(~rowCover, ~colCover) = uncovered - minVal;
% mark locations of all uncovered zeros
Z(~rowCover, ~colCover) = ~cost(~rowCover, ~colCover);
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Step 5.
% Construct a series of alternating primed and starred zeros.
% Start with the primed uncovered zero Z0 at (zi, zj). Find a starred zero
% Z1 in the column of Z0. Star Z0, and unstar Z1. Find a primed zero Z2 in
% the row of Z1. If the are no starred zeros in the column of Z2, stop.
% Otherwise repeat with Z0 = Z2.
function stars = alternatePrimesAndStars(stars, primes, zi, zj)
nRows = size(stars, 1);
nCols = size(stars, 2);
% create a logical index of Z0
lzi = false(1, nRows);
lzj = false(1, nCols);
lzi(zi) = true;
lzj(zj) = true;
% find a starred zero Z1 in the column of Z0
rowInd = stars(1:nRows, lzj);
% star Z0
stars(lzi, lzj) = true;
while any(rowInd(:))
% unstar Z1
stars(rowInd, lzj) = false;
% find a primed zero Z2 in Z1's row
llzj = primes(rowInd, 1:nCols);
lzj = llzj(1, :);
lzi = rowInd;
% find a starred zero in Z2's column
rowInd = stars(1:nRows, lzj);
% star Z2
stars(lzi, lzj) = true;
end
2.3 分配算法举例说明——Matlab2.2代码为例
例子来源于:The Algorithm Workshop - Bevilacqua Research Corporation
用上面的2.2的matlab代码跑一个简单的demo,并输出的中间过程为:
假设cost为: [1,2,3;2,4,6;3,6,9]
调用方法为:[assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, 20);
上述代码基本上与下述的过程是一致的。
三、分配算法会有哪些问题?
3.1 在cost正常情况下,强行给出匹配结果(cost过大,detect应该新建一个Track,但还是被分配了一个Track)
cost =
1 2 30
2 4 30
3 6 30
step 5-重新标记0 stars=
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 1
还是给第三个检测分配了第三个ID,但是第三个检测是都不匹配的,已经都超出我的距离范畴了。还在匹配,这就出现了问题。
如何fix这个问题???
3.2 with/without padding 两种的填充矩阵的实现对匈牙利分配结果的影响
目前的实现中,发现对矩阵的预处理(主要是填充)有三种处理方式:
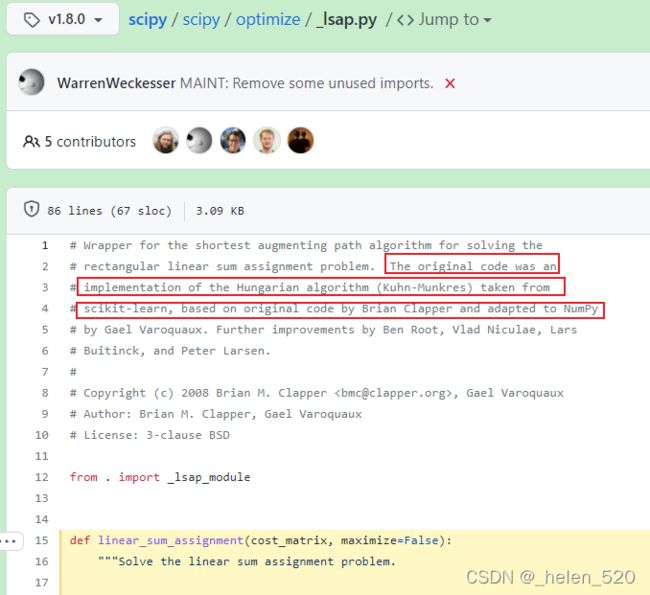
- 不填充:如 scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment 源码位置:https://github.com/scipy/scipy/blob/v1.8.0/scipy/optimize/_lsap.py#L15-L86
最终python调用的是C代码,属于:最短增广路径的矩阵分配算法。
不填充:sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ 在0.23.0的版本之前才有。源码位置:https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/0.17.1/sklearn/utils/linear_assignment_.py
sklearn在0.23.0之后的版本中,弃用了sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ 函数,并没有提供替代函数。只能使用scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment 函数 - max(n,m)填充:
① max(n,m) padding ——matlab代码:https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/20652-hungarian-algorithm-for-linear-assignment-problems-v2-3?s_tid=srchtitle
② max(n,m) padding —— python代码地址:https://pypi.org/project/munkres/1.1.4/ 新版本or旧版本,都是要是square的方阵,padding为padding 0;也可以自定义padding的值。
③ opencv-contrib
- (n+m)*(n+m)填充:
① Matlab 官方多目标跟踪教程的例子:C:\Users\XXXX\Documents\MATLAB\Examples\vision\MotionBasedMultiObjectTrackingExample 中的
[assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, costOfNonAssignment); 函数就调用了匈牙利算法。
| 填充方式 | 注意事项 |
| 不填充:scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ |
|
| max(n,m)填充 填充全0; 给多的track或者多的detect无匹配的选择 |
|
| (n+m)*(n+m)填充; 可以同时给出不分配的track和不分配的detection |
|
现在比较max(n,m)填充和(n+m)*(n+m)填充的差异:
- matlab代码① matlab的完全填充的代码为——矩阵填充后的大小为(m+n)*(m+n) :C:\Users\XXXX\Documents\MATLAB\Examples\vision\MotionBasedMultiObjectTrackingExample 中的 [assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, costOfNonAssignment); 函数就调用了匈牙利算法。
-
matlab代码② padding—— padding为方阵,填0。矩阵填充后的大小为max(m,n) * max(m,n)
max(n,m) padding ——matlab代码:https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/20652-hungarian-algorithm-for-linear-assignment-problems-v2-3?s_tid=srchtitle
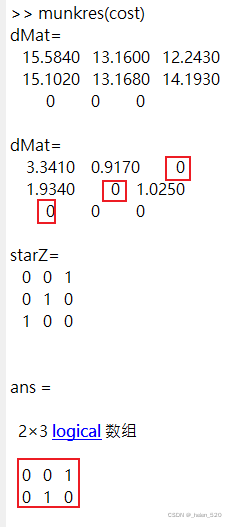
假设现在的cost 矩阵如下:2×3的矩阵。
cost =
15.5841 13.1604 12.2434
15.1019 13.1676 14.1931
3.2.1 matlab代码② ——max(n,m) padding的计算过程如下:只需要一次的迭代,分配结果一致
matlab代码② 源码如下:
function [assignment,cost] = munkres(costMat)
% MUNKRES Munkres Assign Algorithm
%
% [ASSIGN,COST] = munkres(COSTMAT) returns the optimal assignment in ASSIGN
% with the minimum COST based on the assignment problem represented by the
% COSTMAT, where the (i,j)th element represents the cost to assign the jth
% job to the ith worker.
%
% This is vectorized implementation of the algorithm. It is the fastest
% among all Matlab implementations of the algorithm.
% Examples
% Example 1: a 5 x 5 example
%{
[assignment,cost] = munkres(magic(5));
[assignedrows,dum]=find(assignment);
disp(assignedrows'); % 3 2 1 5 4
disp(cost); %15
%}
% Example 2: 400 x 400 random data
%{
n=400;
A=rand(n);
tic
[a,b]=munkres(A);
toc % about 6 seconds
%}
% Reference:
% "Munkres' Assignment Algorithm, Modified for Rectangular Matrices",
% http://csclab.murraystate.edu/bob.pilgrim/445/munkres.html
% version 1.0 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 17th June 2008
assignment = false(size(costMat));
cost = 0;
costMat(costMat~=costMat)=Inf;
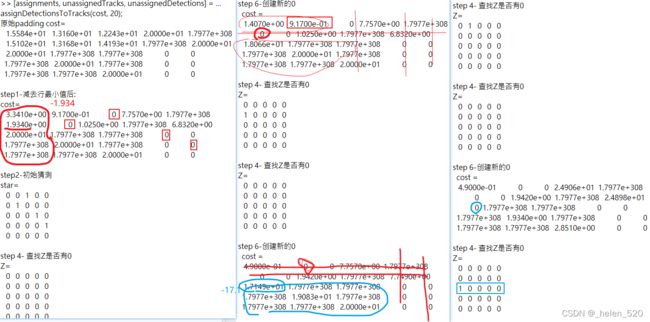
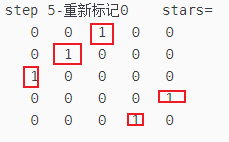
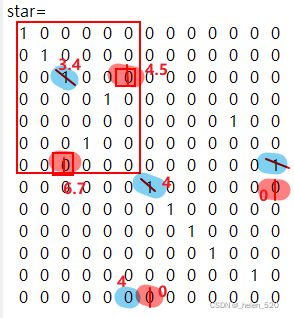
validMat = costMat3.2.2 matlab代码① ——(m+n)*(m+n)的计算过程如下:迭代次数更多,分配结果一致
一直在step4中,
① 若该行有新的0,但是该行有star0了,0*,取消这个star,
② 然后看取消的这个0*的列的~cost重新赋值过来看看。
③ 继续看有没有新的0*,继续考察。到第五行,发现此行没有star 0 的;那么第一个0就是star 0。
star Z0; unstar Z1;star Z2 over
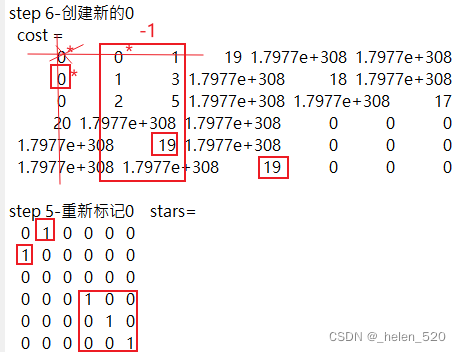
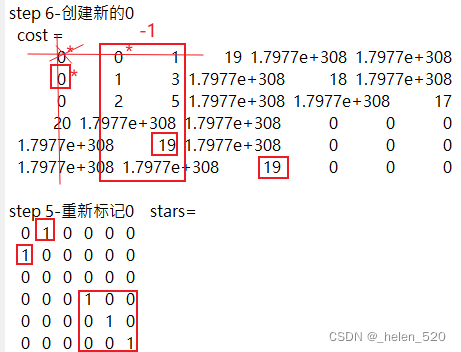
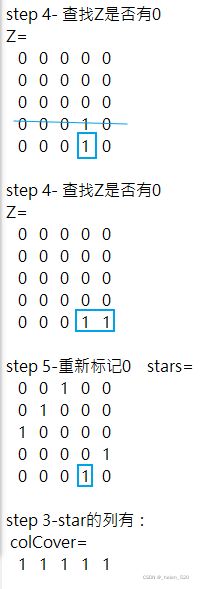
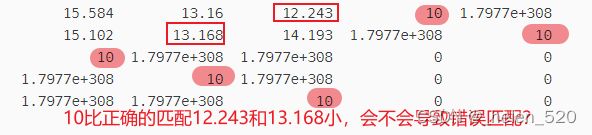
3.3 如果padding value主对角线的值,不合适,比如比正确的值小,会对分配结果产生怎样的影响?
我们填充的这个数值大小会不会对正确的分配造成误导?会不会产生误匹配?什么时候会产生?什么时候不会产生?
结论是:在这种场景下,是不会改变分配的结果的。只不过,算法经历了更多次的迭代!!
算法的迭代过程如下:
>> [assignments, unassignedTracks, unassignedDetections] = ...
assignDetectionsToTracks(cost, 10);
原始padding cost=
15.584 13.16 12.243 10 1.7977e+308
15.102 13.168 14.193 1.7977e+308 10
10 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 10 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 10 0 0
step1-减去行最小值后:
cost=
5.584 3.16 2.243 0 1.7977e+308
5.102 3.168 4.193 1.7977e+308 0
10 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 10 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 10 0 0
step2-初始猜测
star=
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 6-创建新的0
cost =
3.341 0.917 0 0 1.7977e+308
2.859 0.925 1.95 1.7977e+308 0
7.757 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 7.757 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 7.757 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
step 5-重新标记0 stars=
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 3-star的列有:
colCover=
0 0 1 1 1
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 6-创建新的0
cost =
2.424 0 0 0 1.7977e+308
1.942 0.008 1.95 1.7977e+308 0
6.84 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 6.84 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 7.757 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 6-创建新的0
cost =
2.424 0 0 0.008 1.7977e+308
1.934 0 1.942 1.7977e+308 0
6.832 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 6.832 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 7.749 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 1
step 5-重新标记0 stars=
0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 3-star的列有:
colCover=
0 1 1 1 1
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 6-创建新的0
cost =
0.49 0 0 0.008 1.7977e+308
0 0 1.942 1.7977e+308 0
4.898 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 6.832 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 7.749 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 6-创建新的0
cost =
0.49 0 0 4.906 1.7977e+308
0 0 1.942 1.7977e+308 4.898
0 1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.934 1.7977e+308 0 0
1.7977e+308 1.7977e+308 2.851 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1
step 4- 查找Z是否有0
Z=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
step 5-重新标记0 stars=
0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0
step 3-star的列有:
colCover=
1 1 1 1 1
3.4 『python 不填充 完全匹配』 scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment——python包的匈牙利算法源码
scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment 源码位置:https://github.com/scipy/scipy/blob/v1.8.0/scipy/optimize/_lsap.py#L15-L86
_lsap.py 来自于sklearn的实现。
调用了如下_lsap_module模块:
return _lsap_module.calculate_assignment(cost_matrix, maximize = false)https://github.com/scipy/scipy/blob/v1.8.0/scipy/optimize/_lsap_module.c
int ret = solve_rectangular_linear_sum_assignment(
num_rows, num_cols, cost_matrix, maximize,
PyArray_DATA((PyArrayObject*)a),
PyArray_DATA((PyArrayObject*)b));调用 https://github.com/scipy/scipy/blob/v1.8.0/scipy/optimize/rectangular_lsap/rectangular_lsap.cpp
中的solve_retangular_linear_sum_assignment。
又调用solve函数。
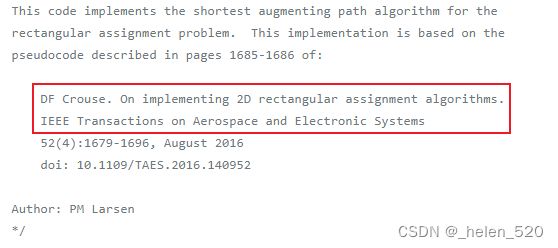
最终python调用的是C代码,基于以下paper实现的。属于:最短增广路径的矩阵分配算法。
This code implements the shortest augmenting path algorithm for the
rectangular assignment problem. This implementation is based on the
pseudocode described in pages 1685-1686 of:
DF Crouse. On implementing 2D rectangular assignment algorithms.
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems
52(4):1679-1696, August 2016
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140952部分源代码如下:
scipy代码的逻辑跟KM匈牙利算法有差异,目前还没看出来差异在哪。这就是linear_sum_assignment算法的最终实现
3.5 『python 不填充 最大匹配』sklearn的sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_'
① sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ 在0.23.0的版本之前才有。
② 源码位置:https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/0.17.1/sklearn/utils/linear_assignment_.py
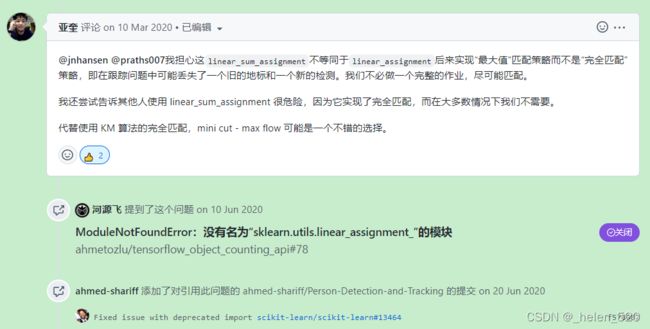
在跟踪的匹配问题上,应该使用maximum value匹配,而不是complete matching完全匹配。我们没必要做一个完全匹配。
不使用KM的完全匹配,而用mini-cut-max flow替代可能是一个比较好的选择
完全匹配——我猜测是尽可能多的匹配对;在乎大家都一个匹配起来。
而实际上,我们需要尽量多的正确匹配,不想要错误的匹配。不想要新ID一定要匹配一个不合适的track,尽量避免这种情况。这样会ID切换,跳ID跳来跳去的。
https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/issues/13464 中有表明:sklearn在0.23以后的版本中弃用了sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_
# from sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ import linear_assignment
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment as linear_assignmentsklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ 源码解析:
不padding,n×m矩阵。
3.6 opencv-contrib中的KM算法
// This file is part of OpenCV project.
// It is subject to the license terms in the LICENSE file found in the top-level directory
// of this distribution and at http://opencv.org/license.html.
#include "precomp.hpp"
#include "kuhn_munkres.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
namespace cv {
namespace detail {
inline namespace tracking {
KuhnMunkres::KuhnMunkres() : n_() {}
std::vector KuhnMunkres::Solve(const cv::Mat& dissimilarity_matrix) {
CV_Assert(dissimilarity_matrix.type() == CV_32F);
double min_val;
cv::minMaxLoc(dissimilarity_matrix, &min_val);
CV_Assert(min_val >= 0);
n_ = std::max(dissimilarity_matrix.rows, dissimilarity_matrix.cols);
dm_ = cv::Mat(n_, n_, CV_32F, cv::Scalar(0));
marked_ = cv::Mat(n_, n_, CV_8S, cv::Scalar(0));
points_ = std::vector(n_ * 2);
dissimilarity_matrix.copyTo(dm_(
cv::Rect(0, 0, dissimilarity_matrix.cols, dissimilarity_matrix.rows)));
is_row_visited_ = std::vector(n_, 0);
is_col_visited_ = std::vector(n_, 0);
Run();
std::vector results(static_cast(marked_.rows), static_cast(-1));
for (int i = 0; i < marked_.rows; i++) {
const auto ptr = marked_.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < marked_.cols; j++) {
if (ptr[j] == kStar) {
results[i] = j;
}
}
}
return results;
}
void KuhnMunkres::TrySimpleCase() {
auto is_row_visited = std::vector(n_, 0);
auto is_col_visited = std::vector(n_, 0);
for (int row = 0; row < n_; row++) {
auto ptr = dm_.ptr(row);
auto marked_ptr = marked_.ptr(row);
auto min_val = *std::min_element(ptr, ptr + n_);
for (int col = 0; col < n_; col++) {
ptr[col] -= min_val;
if (ptr[col] == 0 && !is_col_visited[col] && !is_row_visited[row]) {
marked_ptr[col] = kStar;
is_col_visited[col] = 1;
is_row_visited[row] = 1;
}
}
}
}
bool KuhnMunkres::CheckIfOptimumIsFound() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
const auto marked_ptr = marked_.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
if (marked_ptr[j] == kStar) {
is_col_visited_[j] = 1;
count++;
}
}
}
return count >= n_;
}
cv::Point KuhnMunkres::FindUncoveredMinValPos() {
auto min_val = std::numeric_limits::max();
cv::Point min_val_pos(-1, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
if (!is_row_visited_[i]) {
auto dm_ptr = dm_.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
if (!is_col_visited_[j] && dm_ptr[j] < min_val) {
min_val = dm_ptr[j];
min_val_pos = cv::Point(j, i);
}
}
}
}
return min_val_pos;
}
void KuhnMunkres::UpdateDissimilarityMatrix(float val) {
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
auto dm_ptr = dm_.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
if (is_row_visited_[i]) dm_ptr[j] += val;
if (!is_col_visited_[j]) dm_ptr[j] -= val;
}
}
}
int KuhnMunkres::FindInRow(int row, int what) {
for (int j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
if (marked_.at(row, j) == what) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
int KuhnMunkres::FindInCol(int col, int what) {
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
if (marked_.at(i, col) == what) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void KuhnMunkres::Run() {
TrySimpleCase();
while (!CheckIfOptimumIsFound()) {
while (true) {
auto point = FindUncoveredMinValPos();
auto min_val = dm_.at(point.y, point.x);
if (min_val > 0) {
UpdateDissimilarityMatrix(min_val);
} else {
marked_.at(point.y, point.x) = kPrime;
int col = FindInRow(point.y, kStar);
if (col >= 0) {
is_row_visited_[point.y] = 1;
is_col_visited_[col] = 0;
} else {
int count = 0;
points_[count] = point;
while (true) {
int row = FindInCol(points_[count].x, kStar);
if (row >= 0) {
count++;
points_[count] = cv::Point(points_[count - 1].x, row);
int col1 = FindInRow(points_[count].y, kPrime);
count++;
points_[count] = cv::Point(col1, points_[count - 1].y);
} else {
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count + 1; i++) {
auto& mark = marked_.at(points_[i].y, points_[i].x);
mark = mark == kStar ? 0 : kStar;
}
is_row_visited_ = std::vector(n_, 0);
is_col_visited_ = std::vector(n_, 0);
marked_.setTo(0, marked_ == kPrime);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}}} // namespace 四、DeepSort算法中的在分配时遇到的问题
- openmmlab mmtracking中的deepsort代码
使用的是linear_sum_assignment对IOU的dists进行分配。
使用的是sort的代码,没有把deepsort代码利用起来。使用的是sort的基于IOU的分配。有kalman,但是kalman用于更新track的bbox,用于同detect bbox做IOU。
kalman的运动模型距离(马氏距离)并没有利用起来。
① IOU的dists不准,在拥挤密集场景,以及重叠等场景下,性能不鲁棒。属于distance metric导致的cost matrix鲁棒性不够。分配算法也无能为力。
② 对n*m矩阵进行分配 linear_sum_assignment,无法同时处理unsigned track和unsigned detection情况,始终都会给出分配
网址:DeepSORT官方代码: https://github.com/nwojke/deep_sort
环境搭建:放弃——TensorFlow需要,目前不好搭,且没有requirement.txt文件。放弃搭建。转为寻找环境更容易搭建的pytorch替代版本 -
使用Yolov5_Deepsort_pytorch复现的代码,代替官方DeepSort代码,来看效果。代码开源仓库地址为:https://github.com/mikel-brostrom/Yolov5_DeepSort_Pytorch
DeepSort对象 初始化时:reID特征提取初始化;sort跟踪器初始化。
①extractor
②tracker(sort)
deepsort.update
发现错误匹配还是非常多的!!
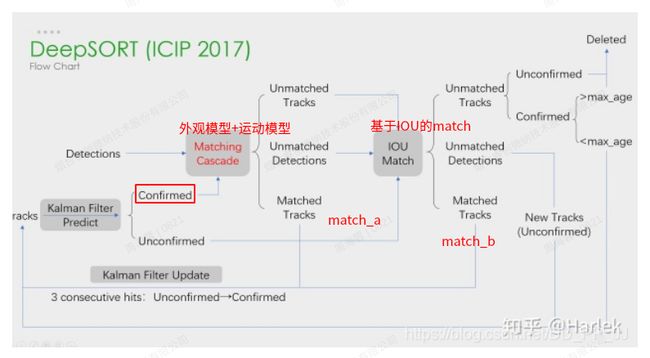
- 级联匹配:第一次靠外观距离(feature distance)或者运动模型距离(马氏距离)来匹配。
① 由于使用的是n*m的scipy的linear_assignment_或者sklearn的linear_sum_assignment函数,不好处理unsignedTrack和unsignedDetection情况。所以有阈值预处理超过Thresh的置为inf,再进入assign分配算法。
② 由于上面会导致一个目标前后两帧的bbox新建多个track,所以靠IOU级联匹配来打补丁。- 我计划把匹配改为单纯的运动模型距离(马氏距离)来匹配,看效果!
- 获取检测框的特征;
- 跟踪器predict
- 跟踪器update——级联匹配是如何实现的?
- 三次连续的分配成功,才能变为Confirmed。confirmend才能进入二级匹配。
-
第一次confirmed都为0,所以都是IOU分配。IOU连续分配3次,hits超过3次,连续3次有匹配,才是confirmed,交给外观和运动模型匹配。
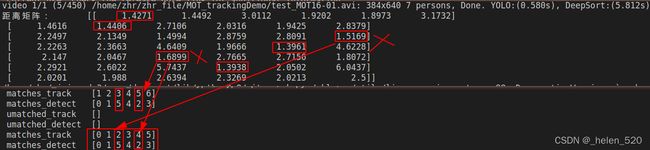
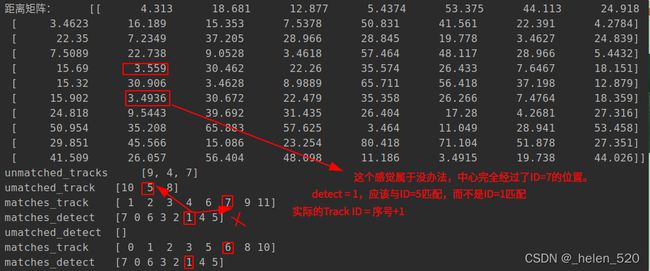
4.1 Yolov5_Deepsort_pytorch 马氏距离获得的cost martix存在bug
- 白色框为检测框,track=5的轨迹丢失了检测框(漏检)
- ID=3的track目标附近多了一个检测框,detect=5,白色的框5。
- 正确的处理情况:trackID=5没有检测分配,预测一帧;trackID=3与detect=2匹配,detect=5无匹配,新建一条track
但是,匹配的结果为:trackID=5与detect=2匹配,trackID=3与detect=5匹配,这里就是两个错误的匹配,这是什么原因???
是cost matrix导致的,不是分配算法导致的。是距离计算矩阵出现了问题!
其cost矩阵如下所示:
导致了两个匹配的原因,在于:
① (5,2)的distance为1.6899
② (3,5)的distance为1.5159
③ (3,2)的distance为1.4994.
本来(3,2)应该选择1.4994,但是由于1.4994+1.8072 > 1.5169 + 1.6899,导致了ID交换匹配了。
也就是说,此处出现的问题为:5刚好丢失了检测,此时附近刚好又冒出一个新目标,然后扰乱了这个cost矩阵的意义了!!!!
此处,我的看法是:明明5与2距离那么远,他们的distance竟然没有想象的那么大。
也就是明明运动距离很远,但是马氏距离cost distance却差距不大!!!!!!这个是需要反思的。在漏检出现的时候,考验着cost matrix距离矩阵的鲁棒性!!!
这里可以发现,误匹配的数值是比较小的,1.68,区分度不够。是被除以了一个数,归一化过了。
4.2 C++ 马氏距离,相同视频 (frameNumber = 6/450)的costMatrix
track共13个,detection共10个。
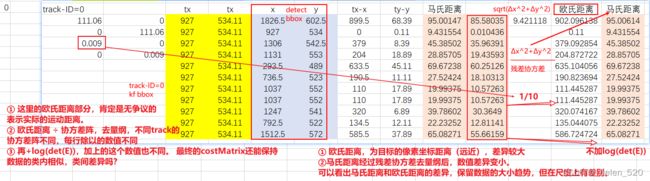
4.2.1 马氏距离的计算过程,以第一行为例
detect bbox 有10个,x,y
以第一行为例,欧氏距离和马氏距离,在量纲上有差异。
对于不同的行来说,使用了不同的协方差阵做乘积和加法。这部分是影响costMatrix数值的关键。
其中我认为后面的l+log|E|的部分影响是更大的。对于一个新的检测,和轨迹而言,新检测要与存在的轨迹的差距都拉开,尽量不匹配。
那么所有的track的数值都要比较大才好。此时,在不同的log|E|的作用下,要让数值都比较大,covariance中的过程噪声和观测噪声决定了所有trackID的convarance的数值,希望让新检测的那一列的数值都很大,这样才不会匹配。
对于检测丢失的track而言,也是所有检测都远。这个自然能够避免,为什么?因为这一行的数值都大,是因为这一行的covraince都一样,只要距离的分子够大,就可以避免匹配的。
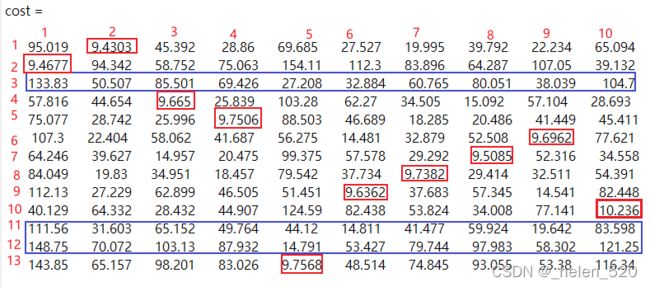
cost =
95.019 9.4303 45.392 28.86 69.685 27.527 19.995 39.792 22.234 65.094
9.4677 94.342 58.752 75.063 154.11 112.3 83.896 64.287 107.05 39.132
133.83 50.507 85.501 69.426 27.208 32.884 60.765 80.051 38.039 104.7
57.816 44.654 9.665 25.839 103.28 62.27 34.505 15.092 57.104 28.693
75.077 28.742 25.996 9.7506 88.503 46.689 18.285 20.486 41.449 45.411
107.3 22.404 58.062 41.687 56.275 14.481 32.879 52.508 9.6962 77.621
64.246 39.627 14.957 20.475 99.375 57.578 29.292 9.5085 52.316 34.558
84.049 19.83 34.951 18.457 79.542 37.734 9.7382 29.414 32.511 54.391
112.13 27.229 62.899 46.505 51.451 9.6362 37.683 57.345 14.541 82.448
40.129 64.332 28.432 44.907 124.59 82.438 53.824 34.008 77.141 10.236
111.56 31.603 65.152 49.764 44.12 14.811 41.477 59.924 19.642 83.598
148.75 70.072 103.13 87.932 14.791 53.427 79.744 97.983 58.302 121.25
143.85 65.157 98.201 83.026 9.7568 48.514 74.845 93.055 53.38 116.34
这是matlab代码的分配结果,与实际的对应一下。
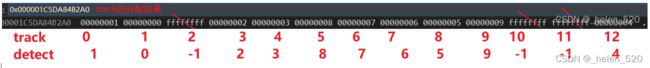
以第二行的数据为例,trackID=1,即cost矩阵的第二行。与白色检测框ID的距离,在图中所示如下:
将第二行的数据与图中对应起来看,发现了运动模型距离与实际的距离是一致的。
上述匹配的结果也是准确的。
① ID=2的track,在第6帧丢失了检测框,属于unsignedTrack
② ID=12的track与检测框ID=4匹配,但是刚刚建立起来,还没显示出来。
③ ID=10和11的track也丢失了检测框。
与实际情况一致。
也就是第6帧中:detection=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] 10个detection都有track与之匹配。没有没有匹配的白色检测框。
匹配结果为:
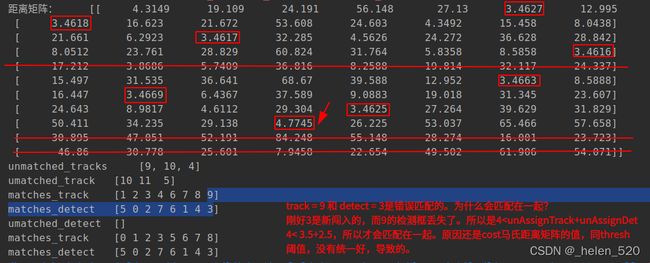
4.3.1 错误匹配的原因——匈牙利分配算法不是按照cost最小得到的,可能按照0的先后顺序得到的。谁先置为0,谁就占着分配。
cost=[4.13,4.9,25.7,13.0,5.9,28.56;
4.9, 4.12, 23.0, 15.6, 7.5, 25.8;
25.7, 23.1, 4.12, 38, 29, 5.08;
5.8, 7.5, 28.4, 10.2, 4.13, 31.165;
15.9, 13.5, 10.9, 27.71, 19.47, 13.70;
12.8, 15.35, 37.301, 4.139, 10.317, 40.081;
17.6, 15.375, 8.1, 28.518, 20.188, 10.011]
左侧为trackID,右侧为detect序号。
ID=7应该无匹配,而ID=3应该匹配detect=2。这里匹配错了!!!!
从这里可以看出,右侧的初始分配,就差一红色框列在最底部画1,就是最优解了。
但是匈牙利分配算法给整成左边的分配格局了。左边的分配的cost》右边的分配cost的,这是为什么会产生这样的结果呢???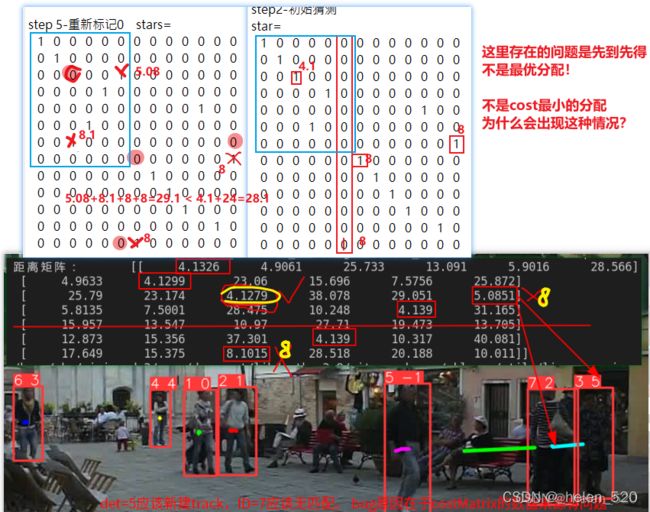
 可能的解决方案:右边的对角线填充,与下方的对角线填充不一样的值!!why?
可能的解决方案:右边的对角线填充,与下方的对角线填充不一样的值!!why?
————————————等一下,先要确保costMatrix的合理性,才能来动这里,这里的问题晚些时候再来讨论,需要先解决前面的问题。
漏检的track:
新出现的detect:
天然的优势是:由新检测框新建的track都在末尾,出现的晚。所以最后考虑匹配它。优先考虑先把前面的行或列匹配好。
找到了问题所在!!!!!!—— thresh的值不合理,导致匹配错误,thresh的值太大了。
我把它设计为3.5之后,成功解决了大部分的匹配失误问题!!!!!!!
4.3.2 错误匹配的原因——costMatrix矩阵的数值不可靠,影响了分配
距离近的cost反而比距离远的cost大,这是cost矩阵计算的就不合理。kalman的covariance是否有问题???
原因:①unMatchedTrack的协方差过大,初始化时为diag[200,200];unMatchedTrack的协方差可以到几万。
②导致,costMatrix的距离很小,很容易跟一些新出现的detect bbox匹配起来。
所以关键原因在于unMatchedTrack只有kalman predict,没有kalman correct。所以这个是deepsort中的逻辑,来看一下没有correct的后果!
上面的原因在于代码写错了。应该是track的变量写到共用的kalman中去了,导致了track使用了上一个ID的变量。出现了这么奇怪的bug
4.3.4 原因在于unAssignedTrack没有用上一次的估计信息来做kalman correct
这样导致的问题:
① kalman的Pn协方差,没有经过校正一步,会不断的上涨,导致cost减小,容易产生较多的误匹配。
② 经过bug修正后,预测的部分没有乱的折线了。但是静止的和穿越的时候,还是频繁切换ID。