Ceres使用(三)
Powell’s Function
现在,考虑更复杂一点的情况,最小化Powell方程。令 x=[x1,x2,x3,x4] ,并且
F(x) 是一个有四个参数的方程,有四个残差,我们想要找到一个 x ,使得12∥F(x)∥2 最小。
第一步,定义评估目标函数项的函数。这里是评估 f4(x1,x4) 的代码:
struct F4 {
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x1, const T* const x4, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = T(sqrt(10.0)) * (x1[0] - x4[0]) * (x1[0] - x4[0]);
return true;
}
};类似的,我们可以定义类F1,F2,F3来分别评估 f1(x1,x2) , f2(x3,x4) 和 f3(x2,x3) 。使用这些,可以构造problem:
double x1 = 3.0; double x2 = -1.0; double x3 = 0.0; double x4 = 1.0;
Problem problem;
// Add residual terms to the problem using the using the autodiff
// wrapper to get the derivatives automatically.
problem.AddResidualBlock(
new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F1), NULL, &x1, &x2);
problem.AddResidualBlock(
new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F2), NULL, &x3, &x4);
problem.AddResidualBlock(
new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F3), NULL, &x2, &x3)
problem.AddResidualBlock(
new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F4), NULL, &x1, &x4); 注意,每个ResidualBlock只依赖于残差对应的两个参数,而不是全部四个参数。完整代码:
#include 1, 1, 1>(new F1);
CostFunction* cost_function2 = new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F2);
CostFunction* cost_function3 = new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F3);
CostFunction* cost_function4 = new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(new F4);
// 设置残差模块,参数(代价函数,核函数,待估计参数)
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function1, NULL, &x1, &x2);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function2, NULL, &x3, &x4);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function3, NULL, &x2, &x3);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function4, NULL, &x1, &x4);
// 设置求解器选项
Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 100;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; //增量方程的求解方式
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; //是否把最小二乘的优化过程输出到cout
cout << "Initial x1 = "<< x1 << ", x2 = " << x2 << ", x3 = " << x3 << ", x4 = " << x4 << endl;
Solver::Summary summary; //优化信息
Solve(options, &problem, &summary); //开始优化
cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl; //简要报告
cout << summary.FullReport() << endl; //完整报告
cout << "Final x1 = " << x1 << ", x2 = " << x2 << ", x3 = " << x3 << ", x4 = " << x4 << endl;
return 0;
} 对应的CMakeLists.txt文件:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(ceres_study)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
set(SOURCE_FILES powell.cpp)
add_executable(ceres_study ${SOURCE_FILES})
target_link_libraries(ceres_study ${CERES_LIBRARIES})编译运行结果:
Initial x1 = 3, x2 = -1, x3 = 0, x4 = 1
iter cost cost_change |gradient| |step| tr_ratio tr_radius ls_iter iter_time total_time
0 1.075000e+02 0.00e+00 1.55e+02 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 1.00e+04 0 5.84e-05 1.25e-04
1 5.036190e+00 1.02e+02 2.00e+01 2.16e+00 9.53e-01 3.00e+04 1 7.50e-05 2.31e-04
2 3.148168e-01 4.72e+00 2.50e+00 6.23e-01 9.37e-01 9.00e+04 1 4.01e-05 2.84e-04
3 1.967760e-02 2.95e-01 3.13e-01 3.08e-01 9.37e-01 2.70e+05 1 3.73e-05 3.31e-04
4 1.229900e-03 1.84e-02 3.91e-02 1.54e-01 9.37e-01 8.10e+05 1 3.58e-05 3.76e-04
5 7.687123e-05 1.15e-03 4.89e-03 7.69e-02 9.37e-01 2.43e+06 1 3.09e-05 4.16e-04
6 4.804625e-06 7.21e-05 6.11e-04 3.85e-02 9.37e-01 7.29e+06 1 2.85e-05 4.51e-04
7 3.003028e-07 4.50e-06 7.64e-05 1.92e-02 9.37e-01 2.19e+07 1 2.82e-05 4.85e-04
8 1.877006e-08 2.82e-07 9.54e-06 9.62e-03 9.37e-01 6.56e+07 1 2.82e-05 5.19e-04
9 1.173223e-09 1.76e-08 1.19e-06 4.81e-03 9.37e-01 1.97e+08 1 2.93e-05 5.57e-04
10 7.333425e-11 1.10e-09 1.49e-07 2.40e-03 9.37e-01 5.90e+08 1 2.81e-05 5.91e-04
11 4.584044e-12 6.88e-11 1.86e-08 1.20e-03 9.37e-01 1.77e+09 1 3.06e-05 6.28e-04
12 2.865573e-13 4.30e-12 2.33e-09 6.02e-04 9.37e-01 5.31e+09 1 3.53e-05 6.73e-04
13 1.791438e-14 2.69e-13 2.91e-10 3.01e-04 9.37e-01 1.59e+10 1 3.40e-05 7.17e-04
14 1.120029e-15 1.68e-14 3.64e-11 1.51e-04 9.37e-01 4.78e+10 1 3.90e-05 7.66e-04
Ceres Solver Report: Iterations: 15, Initial cost: 1.075000e+02, Final cost: 1.120029e-15, Termination: CONVERGENCE
Solver Summary (v 1.13.0-eigen-(3.2.0)-lapack-suitesparse-(4.2.1)-cxsparse-(3.1.2)-openmp)
Original Reduced
Parameter blocks 4 4
Parameters 4 4
Residual blocks 4 4
Residual 4 4
Minimizer TRUST_REGION
Dense linear algebra library EIGEN
Trust region strategy LEVENBERG_MARQUARDT
Given Used
Linear solver DENSE_QR DENSE_QR
Threads 1 1
Linear solver threads 1 1
Linear solver ordering AUTOMATIC 4
Cost:
Initial 1.075000e+02
Final 1.120029e-15
Change 1.075000e+02
Minimizer iterations 15
Successful steps 15
Unsuccessful steps 0
Time (in seconds):
Preprocessor 0.000067
Residual evaluation 0.000023
Jacobian evaluation 0.000394
Linear solver 0.000071
Minimizer 0.000715
Postprocessor 0.000005
Total 0.000787
Termination: CONVERGENCE (Gradient tolerance reached. Gradient max norm: 3.642190e-11 <= 1.000000e-10)
Final x1 = 0.000146222, x2 = -1.46222e-05, x3 = 2.40957e-05, x4 = 2.40957e-05可以看到,该问题的最优结果在 x1=0,x2=0,x3=0,x4=0 ,此时目标方程结果值为0。在第十次迭代中,Ceres计算得到的结果是 4×10−12 。
Curve Fitting
直到现在,我们看到的例子都是没有数据的简单优化问题。最小二乘法和非线性最小二乘法分析的最初目的是拟合数据曲线。现在就来考虑一个这样的例子,数据是由曲线 y=e0.3x+0.1 抽样生成的,再添加标准差为 σ=0.2 的高斯误差。让我们将一些数据拟合到曲线上:
首先,定义一个模板对象来评估残差,对每一个观测值都会有一个残差。
struct ExponentialResidual {
ExponentialResidual(double x, double y)
: x_(x), y_(y) {}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const m, const T* const c, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = T(y_) - exp(m[0] * T(x_) + c[0]);
return true;
}
private:
// Observations for a sample.
const double x_;
const double y_;
};假设观测值是一个2n大小的数组,那么问题的构建就是为每个观测创建一个Cost函数。构建problem的代码:
double m = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < kNumObservations; ++i) {
CostFunction* cost_function =
new AutoDiffCostFunction1, 1, 1>(
new ExponentialResidual(data[2 * i], data[2 * i + 1]));
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL, &m, &c);
} 整个曲线拟合优化代码为:
#include 1, 1, 1>(new ExponentialResidual(x_data[i], y_data[i])),
NULL,
&m, &c);
}
cout << "Intial m = " << m << ", n = " << c << endl;
// 设定求解选项
Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 25;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
// 运行求解器
Solver::Summary summary;
Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl;
cout << "Final m = " << m << ", n = " << c << endl;
return 0;
} 对应的CMakelists.txt为:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(ceres_study)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
# ceres
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_DIRS})
set(SOURCE_FILES curve_fitting.cpp)
add_executable(ceres_study ${SOURCE_FILES})
target_link_libraries(ceres_study ${CERES_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBS})编译运行结果:
Intial m = 0, n = 0
iter cost cost_change |gradient| |step| tr_ratio tr_radius ls_iter iter_time total_time
0 1.204244e+02 0.00e+00 3.60e+02 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 1.00e+04 0 3.24e-04 3.74e-04
1 2.425961e+03 -2.31e+03 0.00e+00 8.02e-01 -1.95e+01 5.00e+03 1 3.96e-05 4.64e-04
2 2.422258e+03 -2.30e+03 0.00e+00 8.02e-01 -1.95e+01 1.25e+03 1 1.83e-05 5.08e-04
3 2.400245e+03 -2.28e+03 0.00e+00 7.98e-01 -1.93e+01 1.56e+02 1 1.49e-05 5.34e-04
4 2.210383e+03 -2.09e+03 0.00e+00 7.66e-01 -1.77e+01 9.77e+00 1 1.47e-05 5.59e-04
5 8.483095e+02 -7.28e+02 0.00e+00 5.71e-01 -6.32e+00 3.05e-01 1 1.43e-05 5.84e-04
6 3.404435e+01 8.64e+01 4.10e+02 3.12e-01 1.37e+00 9.16e-01 1 6.54e-04 1.25e-03
7 7.242644e+00 2.68e+01 1.84e+02 1.27e-01 1.11e+00 2.75e+00 1 6.11e-04 1.97e-03
8 3.933925e+00 3.31e+00 5.81e+01 3.45e-02 1.03e+00 8.24e+00 1 5.71e-04 2.64e-03
9 2.333679e+00 1.60e+00 2.52e+01 9.77e-02 9.90e-01 2.47e+01 1 3.54e-04 3.02e-03
10 1.419436e+00 9.14e-01 8.73e+00 1.16e-01 9.83e-01 7.42e+01 1 3.44e-04 3.38e-03
11 1.245322e+00 1.74e-01 1.43e+00 6.69e-02 9.89e-01 2.22e+02 1 3.45e-04 3.74e-03
12 1.237976e+00 7.35e-03 9.21e-02 1.61e-02 9.91e-01 6.67e+02 1 3.42e-04 4.10e-03
13 1.237935e+00 4.11e-05 9.96e-04 1.28e-03 9.90e-01 2.00e+03 1 3.40e-04 4.46e-03
Ceres Solver Report: Iterations: 14, Initial cost: 1.204244e+02, Final cost: 1.237935e+00, Termination: CONVERGENCE
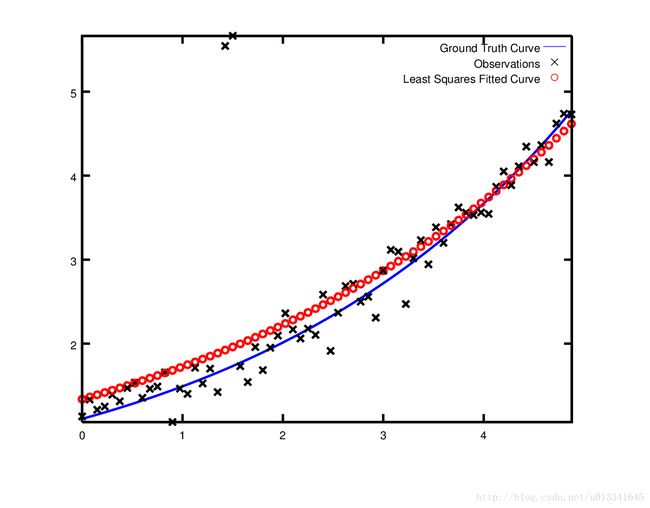
Final m = 0.301681, n = 0.0907709从参数 m=0,c=0 开始,目标方程值的结果最开始为120.424,Ceres找到的结果是 m=0.301681,n=0.0907709 ,此时目标方程值为1.2379。参数值的优化结果和原来模型的 m=0.3,c=0.1 有一点不同,但这是意料之中的。当从噪声数据中重建曲线时,我们期望看到这样的偏差。事实上,如果要评估 m=0.3,c=0.1 的目标函数,那么目标函数值为1.237935。最后的拟合曲线如下图所示:

Robust Curve Fitting
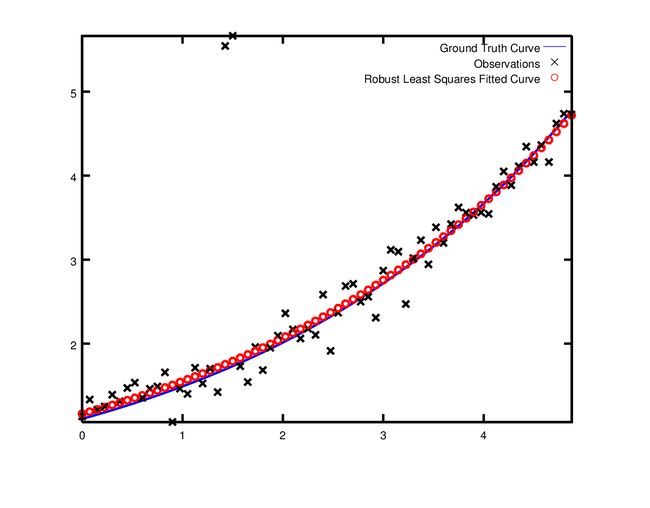
现在,假设给出的数据中含有异常点,也即有一些点并不遵从噪声模型。如果我们使用上面的代码区拟合曲线,我们将会得到下面的曲线,拟合曲线会偏离真值曲线。
为了处理异常点,标准做法是使用一个损失函数LossFunction。损失函数减少了较大残差值对残差块的影响,通常是对应于异常点。为了在残差块中使用损失函数,我们修改以下代码:
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL , &m, &c);为
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, new CauchyLoss(0.5) , &m, &c);CauchyLoss是Ceres求解器的损失函数之一。0.5指定了损失函数的大小。结果,我们可以得到下面的拟合图。注意,拟合曲线和真值曲线已经很接近了。