Codeforces Round #822 (Div. 2)
A. Select Three Sticks
题目链接:Problem - A - Codeforces
样例输入:
4
3
1 2 3
4
7 3 7 3
5
3 4 2 1 1
8
3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6
样例输出:
2
4
1
1
题意:给定一个长度为n的数组,我们每次操作可以把数组中的一个元素的值加1或者减1,问我们至少操作多少次能使得数组中至少出现3个元素的值相同。
分析:我们直接先对元素组进行排序,然后直接暴力判断把相邻的三个数变成同一个数的代价,然后取一个最小值即可,把三个数变相同的最小代价就是把两边的数经过操作成中间的数。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a+1,a+n+1);
int ans=2e9+10;
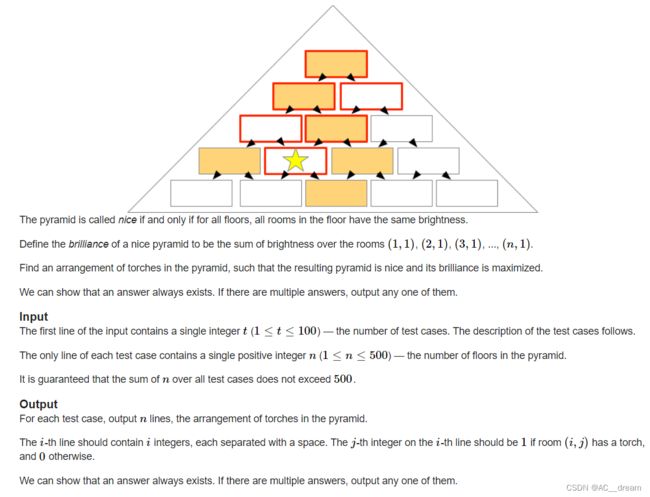
for(int i=2;i B. Bright, Nice, Brilliant
题目链接:Problem - B - Codeforces
样例输入:
3
1
2
3
样例输出:
1
1
1 1
1
1 1
1 0 1
题意不好描述,上面附有题目
分析:这个模拟一下发现直接令两斜边装有灯,其余地方不装灯即可。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
if(j==i||j==1) printf("1 ");
else printf("0 ");
puts("");
}
}
return 0;
} C. Removing Smallest Multiples
题目链接:Problem - C - Codeforces
样例输入:
6
6
111111
7
1101001
4
0000
4
0010
8
10010101
15
110011100101100
样例输出:
0
11
4
4
17
60
题意:给定一个长度为n的01串,代表我们最后要形成的目标串,第i个位置位为0代表没有i,为1代表有i,我们每次可以选择一个k,然后花费代价k消除我们剩余数组中第一个k的倍数。问我们形成目标数组所需要花费的最小代价。
分析:由贪心性质我们知道对于一个我们要删除的数x,我们肯定是用最小的k满足x%k==0且不存在我们要保留的数y
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
char s[N];
bool vis[N];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",s+1);
long long ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) vis[i]=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int j=i;
while(j<=n&&s[j]=='0')
{
if(!vis[j]) ans+=i;
vis[j]=true;
j+=i;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
} D. Slime Escape
题目链接:Problem - D - Codeforces
样例输入:
6
7 4
-1 -2 -3 6 -2 -3 -1
3 1
232 -500 -700
7 4
-1 -2 -4 6 -2 -4 -1
8 4
-100 10 -7 6 -2 -3 6 -10
8 2
-999 0 -2 3 4 5 6 7
7 3
7 3 3 4 2 1 1
样例输出:
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
简化题意:有一个长度为n的数组,每个元素都有一个值,你一开始在某个位置pos,那么你的生命值就是a[pos],你可以选择往右走,也可以选择往左走,你走到某个单元格,如果这个单元格里面的元素值为-3,那么相应的你的生命值就要-3,如果单元格里面的元素值是5,那么你的生命值就会+5,现在问你能否走出这个数组,也就是说你要么从1向左走出,要么从n向右走出,而且整个过程中你的生命值一定是一个非负数,每个单元格一旦被走过那么里面的值将不会再次起作用,可以看成变为0。
分析:其实这道题我们贪心来想就行了,我们尝试性地走,如果发现我们发现沿着这个方向没法增加血量就不走,否则就一定走。比如你先向左试探性的走,发现走了一段距离后你的生命值可以增大,而且在过程中你没有死亡,那么考虑剩余生命值最大你肯定是要走这一段的,这个时候我们继续向左走,直到我们再往左走依靠当前的生命值已经无法再继续获益,那么这个时候我们再向右走重复这个过程,直至我们两边都无法扩展那么我们直接输出NO,也或者是我们走出了这个数组直接输出YES,我们能够发现我们所试探的复杂度就是O(n)的,扩展的复杂度也是O(n)的,整体复杂度就是O(n)的。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n,pos;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&pos);
a[n+1]=a[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
long long ans=a[pos];
int l=pos,r=pos;
if(a[l]<0)
{
puts("NO");
continue;
}
bool flag=true;
while(l>=1&&r<=n)
{
bool flag1=false;
long long tans=ans;
int tl=l;
while(tans<=ans&&tans>=0&&tl>=1)
{
tans+=a[--tl];
}
if(!tl) break;//已经成功
if(tans>ans)
{
flag1=true;
ans=tans;
l=tl;
}
if(flag1) continue;//如果从左边获得价值下次就继续从左边开始
int tr;
bool flag2=true;
bool flag3=false;//标记右边界有无扩展
while(flag2)
{
flag2=false;
tans=ans;
tr=r;
while(tans<=ans&&tans>=0&&tr<=n)
{
tans+=a[++tr];
}
if(tr>n) break;
if(tans>ans)
{
flag2=true;
flag3=true;
ans=tans;
r=tr;
}
}
if(tr>n) break;
if(flag3) continue;
else
{
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}