第十四周项目6 判断是否为二叉排序树
/* * Copyright (c)2015,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院 * All rights reserved. * 文件名称:项目4.cbp * 作 者:朱希康 * 完成日期:2015年12月14日 * 版 本 号:v1.0 * 问题描述:构造二叉排序树,替换一个元素后判断是否为二叉排序树 * 输入描述:无 * 程序输出:判断是否为二叉排序树 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int KeyType; //定义关键字类型
typedef char InfoType;
typedef struct node //记录类型
{
KeyType key; //关键字项
InfoType data; //其他数据域
struct node *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
} BSTNode;
int path[MaxSize]; //全局变量,用于存放路径
void DispBST(BSTNode *b); //函数说明
int InsertBST(BSTNode *&p,KeyType k) //在以*p为根节点的BST中插入一个关键字为k的节点
{
if (p==NULL) //原树为空, 新插入的记录为根节点
{
p=(BSTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
p->key=k;
p->lchild=p->rchild=NULL;
return 1;
}
else if (k==p->key)
return 0;
else if (k<p->key)
return InsertBST(p->lchild,k); //插入到*p的左子树中
else
return InsertBST(p->rchild,k); //插入到*p的右子树中
}
BSTNode *CreatBST(KeyType A[],int n)
//由数组A中的关键字建立一棵二叉排序树
{
BSTNode *bt=NULL; //初始时bt为空树
int i=0;
while (i<n)
InsertBST(bt,A[i++]); //将A[i]插入二叉排序树T中
return bt; //返回建立的二叉排序树的根指针
}
void DispBST(BSTNode *bt)
//以括号表示法输出二叉排序树bt
{
if (bt!=NULL)
{
printf("%d",bt->key);
if (bt->lchild!=NULL || bt->rchild!=NULL)
{
printf("(");
DispBST(bt->lchild);
if (bt->rchild!=NULL) printf(",");
DispBST(bt->rchild);
printf(")");
}
}
}
/*
int JudgeBST(BSTNode *bt)为判断一个树是否为排序二叉树设计的算法的实现
*/
KeyType predt=-32767; //predt为全局变量,保存当前节点中序前趋的值,初值为-∞
int JudgeBST(BSTNode *bt) //判断bt是否为BST
{
int b1,b2;
if (bt==NULL)
return 1; //空二叉树是排序二叉树
else
{
b1=JudgeBST(bt->lchild); //返回对左子树的判断,非排序二叉树返回0,否则返回1
if (b1==0 || predt>=bt->key) //当左子树非排序二叉树,或中序前趋(全局变量)大于当前根结点时
return 0; //返回“不是排序二叉树”
predt=bt->key; //记录当前根为右子树的中序前趋
b2=JudgeBST(bt->rchild); //对右子树进行判断
return b2;
}
}
int main()
{
BSTNode *bt;
int a[]= {43,91,10,18,82,65,33,59,27,73},n=10;
printf("创建排序二叉树:");
bt=CreatBST(a,n);
DispBST(bt);
printf("\n");
printf("bt%s\n",(JudgeBST(bt)?"是一棵BST":"不是一棵BST"));
bt->lchild->rchild->key = 30; //搞个破坏!
printf("修改后的二叉树:");
DispBST(bt);
printf("\n");
printf("bt%s\n",(JudgeBST(bt)?"是一棵BST":"不是一棵BST"));
return 0;
}
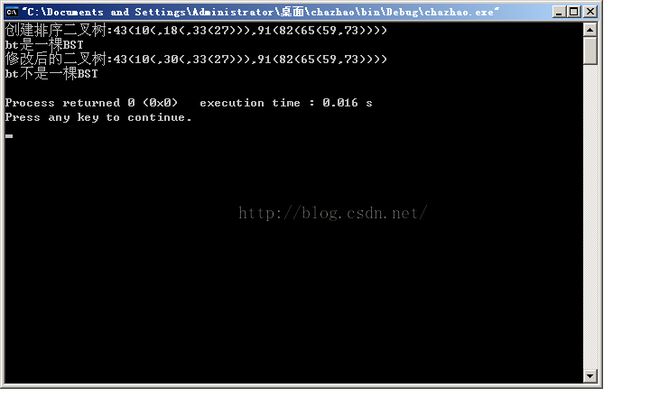
运行结果:
知识点总结:
判断是否为二叉树即判断该节点为左孩子还是右孩子,再和其根节点进行比较。