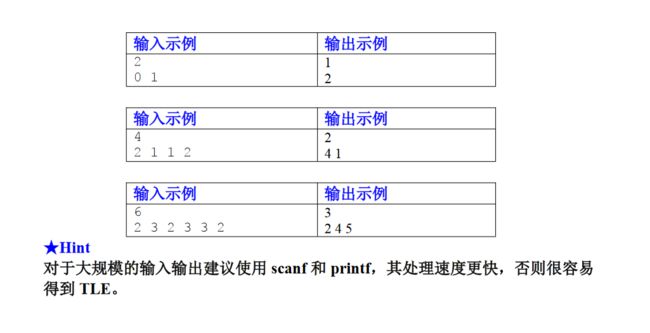
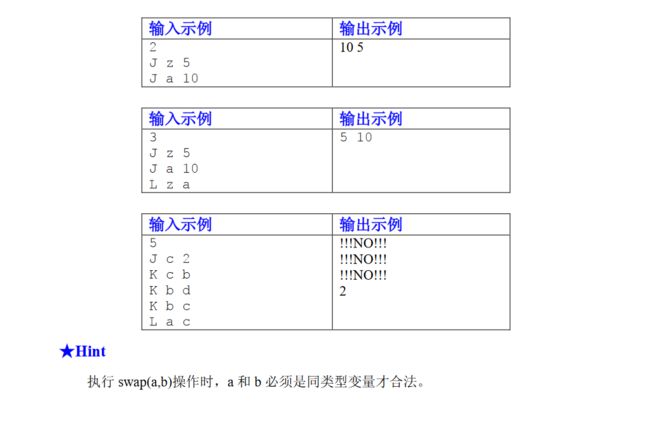
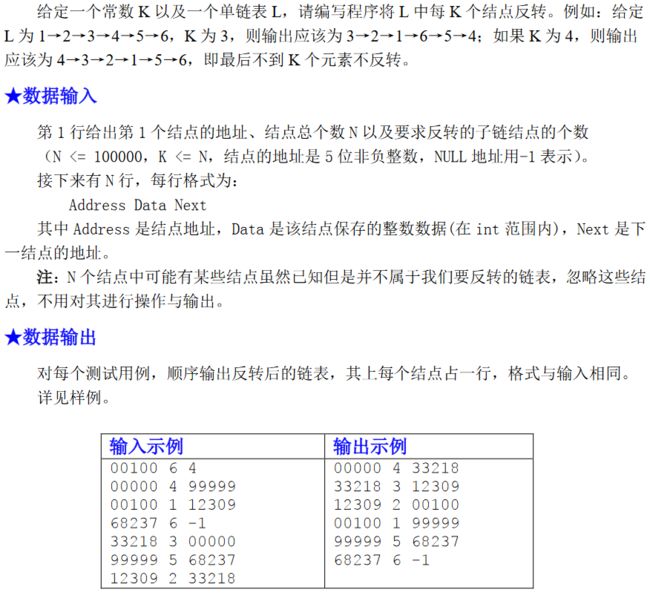
第三章
3.1 OCD
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int arr[5050];
char cha[5050][150];
int n;
int re()
{
int min = 15000;
int minid = -1;
int k;
for(k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
if(arr[k] < min)
{
min = arr[k];
minid = k;
}
}
arr[minid] = 900000;
return minid;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
string s;
int num;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
num = 0;
cin >> s;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
num +=s[i];
cha[j][i] = s[i];
}
arr[j] = num;
}
int now = 0;
for(int m = 0; m < n ; m++)
{
now = re();
for(int k = 0; cha[now][k]!=0; k++)
cout << cha[now][k];
cout <<endl;
}
return 0;
} #include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
bool check[1000010];
int arr[1000010];
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
if(arr[i] > max) max = arr[i];
}
printf("%d\n",max);
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(arr[j] < max)//bad monkey
check[j] = true;
}
int num = 0;
for(int p = 0 ; p < n; p++)
{
if(check[p] && p > num) num = p;
}
for(int k = 1; k < n; k++)
{
if(arr[(num+k)%n] == max)
printf("%d ",(num+k)%n+1);
}
return 0;
} #include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
char cha[200];
int num[200];
bool flag[200]; //int型为false
int i,j;
int main()
{
int len = 0;
int n;
cin >> n;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char op;
cin >> op;
if(op == 'J') //当操作是J时
{
len++;
cin >> cha[len] >> num[len];
flag[len] = false;
for(j = 1;j < len;j++)
if(cha[j] == cha[len]) //变量名不重复
{
cout<<"!!!NO!!!" << endl;
len--;
}
}
char c;
bool check1 = true;
bool check2 = false;
if(op == 'K') //当操作是K时
{
len++;
cin >> cha[len] >> c;
flag[len] = true;
for(j = 1;j < len;j++) //变量名不重复
if(cha[j] == cha[len])
check1 = false;
for(j = 1;j < len;j++)
{
if(cha[j]==c) //指针所指向的变量存在
{
num[len] = num[j];
check2 = true;
break;
}
}
if((check1==false)||(check2==false))
{
cout<<"!!!NO!!!" << endl;
len--;
}
}
char c1,c2;
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
if(op == 'L') //当操作是L时
{
cin >> c1 >> c2;
for(int k = 1; k <= len; k++)
{
if(cha[k] == c1) index1 = k;
if(cha[k] == c2) index2 = k;
}
if(index1&&index2&&(flag[index1]==flag[index2])) //变量存在于数组中且类型相同
{
int temp;
temp = num[index1];
num[index1] = num[index2];
num[index2] = temp;
}
else
cout <<"!!!NO!!!" << endl;
}
else if(op!='J'&&op!='K'&&op!='L') //操作不合法
{
cout <<"!!!NO!!!" << endl;
}
}
//根据字典序冒泡排序
for(i = 1; i<=len ;i++)
{
for( j = i+1 ;j <= len ;j++)
{
if(cha[i] > cha[j])
{
int t;
t = num[i];
num[i] = num[j];
num[j] = t;
}
}
}
//非指针型变量输出
for(i = 1; i<=len ;i++)
if(!flag[i])
cout <<num[i]<<" ";
return 0;
} 3.4 cut_in_line_2
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct cutline
{
int index;
int angry;
bool iscut;
cutline *next;
};
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
cutline *head = new cutline;
cutline *p1 = new cutline;
cutline *p2;
//初始化p1
cin >>p1->iscut;
p1->index = 1;
p1->angry = 0;
p1->iscut = false;
head->next = p1;
p1->next = NULL;
int op;
int angrysum = 0;
cutline *before;
cutline *now;
//创建链表
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
p2 = new cutline;
p2->index = i;
p2->angry = 0;
p2->next = NULL;
cin >> op;
int x,y;
//排队
if(op == 0)
{
p2->iscut = false;
p1->next = p2;
p1 = p2;//p1在链表尾
}
//插队
else if(op == 1)
{
cin >> x >> y;
p2->iscut = true;
bool cut = false;
for(before = head,now = head->next;now!=NULL;)
{
//插队位置之后每个+angry值
if(cut)
{
now->angry += y;
angrysum += y;
}
//插队操作
if(!cut && now->index == x)
{
cut = true;
before->next = p2;
p2 ->next = now;
before = p2;
continue;
}
before = now;
now = now->next;
}
//找不到所插入的编号
if(!cut)
{
p1->next = p2;
p1 = p2;
}
}
p1->next = NULL;
//超过阈值
if(angrysum > m)
{
angrysum = 0;
for(before = head,now = head->next;now!=NULL;)
{
now->angry = 0;
if(now->iscut)
{
before->next = now->next;
delete(now);
now = before->next;
continue;
}
before = now;
now = now->next;
}
}
}
//遍历链表输出index
now = head->next;
before = head;
cout << now->index;
delete(before);
before = now;
now = now->next;
for(;now!=NULL;)
{
cout <<" "<< now->index;
before = now;
now = now->next;
delete(before);
}
cout << endl;
cout << angrysum <<endl;
return 0;
} #include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct number
{
int address;
int data;
int next;
}num1[100010],num2[100010];
int arr[100010];
void reserve(number *p, int k)
{
for(int t = 0; t < k/2; t++)
{
swap(*(p+t),*(p+k-t-1));
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j = 0;
int address0;
int address;
int n,k;
cin >> address0 >> n >> k;
//读入n组数据,arr[address]=第几个输入数据
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> num1[i].address >> num1[i].data >> num1[i].next;
arr[num1[i].address] = i;
}
//num1为输入的乱序
//num2为按地址链表顺序
num2[0] = num1[arr[address0]];
int count = 0;
//从num2[0]开始找,num2[].next为下一个的address,在arr中找到这个位置,找到这个位置的num1赋给顺序num2
while(num2[count].next != -1)
{
num2[count+1] = num1[arr[num2[count].next]];
count++;
}
//翻转
while(j+k-1 <= count)
{
reserve(&num2[j],k);
j += k;
}
//顺序输出
for(i = 0; i < count; i++)
printf("%05d %d %05d\n",num2[i].address,num2[i].data,num2[i+1].address);
printf("%05d %d -1\n",num2[count].address,num2[count].data);
return 0;
}