BZOJ1180 LCT模版
此题纯模版 , 由于第一次自己实现LCT调了一会。 提一提也许初学者可能会犯的几个问题(本文不适合入门 , 入门推荐:QG博客)
LCT开始学的时候最让人迷惑的多半是“父亲”的定义。 因为这个数据结构的辅助树是Splay , 而这玩意本身就是一棵树 , 那每一个节点的父亲到底是谁呢?
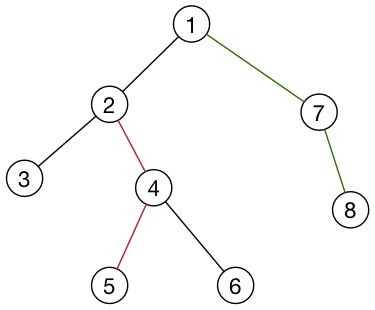
比如上图中 [2 , 4 , 5] , [1 , 7 , 8] 在两个splay里 , 那么2的父亲是谁呢? 是1么?
答案是不一定 , 如果此时2被旋转到了自己splay树的根 , 那么此时2->fa == 1 , 其他情况下2->fa等于自己splay树中对应的父亲结点。 换句话说在2的splay中 , 谁是此时的根 , 谁的父亲就是1.
当我意识到这一点时 , 我感觉很奇怪 , 这样这个图不就乱了? 我不就难得分清楚谁是谁真正的父亲了么? 后来会发现 , 其实真正的父亲是谁也没有那么重要 , 而找自己真正的父亲也不是那么难 , 伸展树可以帮你办到很多事情。
比较玄学的一点是 , 其实由于splay作为LCT的辅助树 , 所以这玩意是一个“弱相互关系”的数据结构。(这东西是我定义的) 作为对应 , 线段树可以理解为“强相互关系”的数据结构。
读Rujia的Splay板块的时候就养成了旋转操作自上而下 , 所以splay跟网上大多数版本不同:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// Lets play the LCT
const int maxn = 3e4+1e2;
inline int re() {
int n = 0, ch = getchar(); bool flag = false;
while(!isdigit(ch)) flag |= ch == '-', ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) n = n * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return flag ? -n : n;
}
struct node
{
node *fa , *ch[2];
int v , c , flip , s;
node(){ v = flip = s = 0; }
void maintain()
{
s = ch[0]->s + v + ch[1]->s;
}
void pushDown()
{
if(flip)
{
flip = 0;
ch[0]->flip ^=1;
ch[1]->flip ^=1;
if(c!=-1) c = 1-c;
swap(ch[0], ch[1]);
}
}
};
int n;
node p[maxn];
node *null = new node();
void init()
{
n = re();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
p[i].v = re();
p[i].s = p[i].v;
p[i].fa = p[i].ch[0] = p[i].ch[1] = null;
}
}
bool isRoot(node *x) { return x->fa==null || (x->fa->ch[0] != x && x->fa->ch[1] != x); }
void rotate(node *&o , int d)
{
node* k = o->ch[d^1];
k->fa = o->fa;
o->fa = k;
k->ch[d]->fa = o;
o->ch[d^1] = k->ch[d];
k->ch[d] = o;
o->maintain();
k->maintain();
o = k;
}
void _splay(node *&o)
{
o->pushDown();
if(o->c!=-1)
{
node* &o1 = o->ch[o->c];
o1->pushDown();
if(o1->c!=-1)
{
_splay(o1->ch[o1->c]);
if(o->c == o1->c) rotate(o, o->c^1); else rotate(o1, o1->c^1);
}
rotate(o, o->c^1);
}
}
void splay(node *x)
{
x->c = -1;
while(!isRoot(x))
{
if(x == x->fa->ch[0]) x->fa->c = 0;
else x->fa->c = 1;
x = x->fa;
}
_splay(x);
}
node* access(node *x)
{
node *y = null;
for(;x!=null;x = x->fa)
{
splay(x);
x->ch[1] = y;
x->maintain();
y = x;
}
for(;y->ch[0]!=null;y = y->ch[0]);
return y;
}
void makeRoot(node *x)
{
access(x);
splay(x);
x->flip ^=1;
}
bool isConnect(node *x , node *y)
{
node *r1 = access(x);
node *r2 = access(y);
return r1 == r2;
}
bool link(node *x , node *y)
{
if(isConnect(x, y)) return false;
makeRoot(x);
x->fa = y;
return true;
}
void modify(node *x , int v)
{
splay(x);
x->v = v;
x->maintain();
}
int query(node *x , node *y)
{
makeRoot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
return y->s;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
init();
int q , u , v;
cin>>q;
char s[20];
while(q--)
{
scanf("%s" , s);
u = re(); v = re();
if(s[0]=='e')
{
if(!isConnect(p+u, p+v)) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d\n" , query(p+u, p+v));
}
if(s[0]=='p') modify(p+u, v);
if(s[0]=='b')
{
if(isConnect(p+u, p+v)) puts("no");
else
{
puts("yes");
link(p+u, p+v);
}
}
}
return 0;
}