USACO section1.4.1
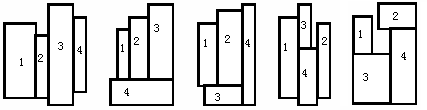
因为只有4个方块,所以枚举每个方块的选择顺序和放置方向(横放还是纵放),放置方式只有题目给出的6中基本模式,分别算出不同模式下最小的面积,更新最优解。
第4、5个在本质上其实是一样。如图,不同模式对应的最小面积如下:
设w1,w2,w3,w4表示4个方块的横长,h1,h2,h3,h4表示4个方块的纵长。w,h表示最小。
1:w=w1+w2+w3+w4;h=max(h1,h2,h3,h4)
2:w=max(w1+w2+w3,w4);h=max(h1,h2,h3)+h4
3:w=max(w1+w2,w3)+w4;h=max(h1+h3,h2+h3,h4)
4:w=w1+w2+max(w3,w4);h=max(h1,h3+h4,h2)
5:h=max(h1+h3,h2+h4)
对于w,我们细分为如下四种形式:
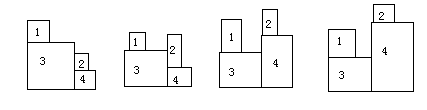
(1):h3>=h2+h4;w=max(w1,w3+w2,w3+w4)
(2):h3>h4 and h3<h2+h4;w=max(w1+w2,w2+w3,w3+w4)
(3):h4>h3 and h4<h1+h3;w=max(w1+w2,w1+w4,w3+w4)
(4):h4>=h1+h3;w=max(w2,w1+w4,w3+w4)
*:h3=h4(图中没画);w=max(w1+w2,w3+w4)
用一个数组记录最优解,最后排序输出即可。
2. 这道题真很恶心,枚举,中间还要用到dfs。还有六种情况。很复杂,直接读别人的解体报告,但是两个递归函数还是不是很明白,但是知道这个函数是做什么的,为什么会这么写还是不懂。。。等以后有时间还是要做这道题。
3. 我的代码(其实是看的官方代码,然后自己写出来的。。。。),原来写的函数总是出错,后来索性重新写了一遍,把错误的也放在上边了
/*
ID: dollar4
PROG: packrec
LANG: C++
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
//define const int INT_MAX = 10000;
struct Node
{
int x, y;
} node[4],rec;
int rst[101], rstm = 10000;
void record()
{
int m = rec.x * rec.y;
if (m < rstm)
{
rstm = m;
memset(rst, 0, sizeof(rst));
}
if (m == rstm)
{
rst[min(rec.x, rec.y)] = 1;
}
}
/*void calculate()
{
int i;
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
rec.x += node[i].x;
if (rec.y < node[i].y)
rec.y = node[i].y;
}
record();
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
rec.x = node[0].x + node[1].x + node[2].x;
if (rec.x < node[3].x)
rec.x = node[3].x;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
if (rec.y < node[i].y)
rec.y = node[i].y;
}
rec.y += node[4].y;
record();
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
rec.x = node[0].x + node[1].x;
if (rec.x < node[2].x)
rec.x = node[2].x;
rec.x += node[3].x;
int temp = node[1].y + node[0].y;
rec.y = node[2].y + node[1].y;
if (temp > rec.y)
rec.y = temp;
if (rec.y < node[3].y)
rec.y = node[3].y;
record();
rec.y = 0;
rec.x = 0;
rec.x = node[0].x + node[1].x + max(node[3].x, node[2].x);
rec.y = max(max(node[2].y + node[3].y, node[1].y), node[0].y);
record();
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
rec.y = max(node[0].y + node[2].y, node[1].y + node[3].y);
if (node[2].y >= node[1].y + node[3].y)
rec.x = max(node[0].x, max(node[2].x + node[1].x, node[2].x + node[3].x));
if (node[2].y > node[3].y && node[2].y < node[1].y + node[3].y)
rec.x = max(max(node[0].x + node[1].x, node[1].x +node[2].x), node[2].x + node[3].x);
if (node[3].y > node[2].y && node[3].y < node[0].y + node[2].y)
rec.x = max(max(node[0].x + node[1].x, node[0].x + node[3].x), node[2].x + node[3].x);
if (node[3].y >= node[0].y + node[2].y)
rec.x = max(max(node[0].x + node[1].x, node[1].x), node[2].x + node[3].x);
if (node[2].y == node[3].y)
rec.x = max(node[0].x + node[1].x, node[2].x + node[3].x);
record();
}
*/
void calculate()
{
//case 1
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
rec.x += node[i].x;
if (node[i].y > rec.y) rec.y = node[i].y;
}
record();
//case 2
rec.x = 0;
rec.y = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 4; ++i)
{
rec.x += node[i].x;
if (node[i].y > rec.y) rec.y = node[i].y;
}
if (node[0].x > rec.x) rec.x = node[0].x;
rec.y += node[0].y;
record();
//case 3
rec.x = max(node[0].x+node[1].x, node[2].x)+node[3].x;
rec.y = max(max(node[0].y, node[1].y)+node[2].y, node[3].y);
record();
//case 4, 5
rec.x = node[0].x+max(node[1].x, node[2].x)+node[3].x;
rec.y = max(max(node[0].y, node[1].y+node[2].y), node[3].y);
record();
//case 6
rec.x = node[0].x+node[1].x;
rec.y = max(node[0].y+node[2].y, node[1].y+node[3].y);
if (node[0].y < node[1].y)
rec.x = max(rec.x, node[2].x+node[1].x);
if (node[0].y+node[2].y > node[1].y)
rec.x = max(rec.x, node[2].x+node[3].x);
if (node[1].y < node[0].y)
rec.x = max(rec.x, node[0].x+node[3].x);
rec.x = max(rec.x, node[2].x);
rec.x = max(rec.x, node[3].x);
record();
}
void rota(int a)
{
if (a == 4)
calculate();
else
{
rota(a + 1);
swap(node[a].x, node[a].y);
rota(a + 1);
swap(node[a].x, node[a].y);
}
}
void pf(int a)
{
if (a == 4)
rota(0);
else
{
for (int i = a; i < 4; i++)
{
swap(node[i], node[a]);
pf(a + 1);
swap(node[i], node[a]);
}
}
}int main()
{
ofstream fout ("packrec.out");
ifstream fin ("packrec.in");
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
fin >> node[i].x >> node[i].y;
pf(0);
fout << rstm << endl;
for (i = 0; i < 101; i++)
{
if (rst[i] == 1)
fout << i << " " << rstm / i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4. 官方代码
This program is straightforward, but a bit long due to the geometry involved.
There are 24 permutations of the 4 rectangles, and for each permutation, 16 different ways to orient them. We generate all such orientations of permutations, and put the blocks together in each of the 6 different ways, recording the smallest rectangles we find.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef struct Rect Rect;
struct Rect {
int wid;
int ht;
};
Rect
rotate(Rect r)
{
Rect nr;
nr.wid = r.ht;
nr.ht = r.wid;
return nr;
}
int
max(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int
min(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
int tot;
int bestarea;
int bestht[101];
void
record(Rect r)
{
int i;
if(r.wid*r.ht < tot)
*(long*)0=0;
if(r.wid*r.ht < bestarea || bestarea == 0) {
bestarea = r.wid*r.ht;
for(i=0; i<=100; i++)
bestht[i] = 0;
}
if(r.wid*r.ht == bestarea)
bestht[min(r.wid, r.ht)] = 1;
}
void
check(Rect *r)
{
Rect big;
int i;
/* schema 1: all lined up next to each other */
big.wid = 0;
big.ht = 0;
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
big.wid += r[i].wid;
big.ht = max(big.ht, r[i].ht);
}
record(big);
/* schema 2: first three lined up, fourth on bottom */
big.wid = 0;
big.ht = 0;
for(i=0; i<3; i++) {
big.wid += r[i].wid;
big.ht = max(big.ht, r[i].ht);
}
big.ht += r[3].ht;
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[3].wid);
record(big);
/* schema 3: first two lined up, third under them, fourth to side */
big.wid = r[0].wid + r[1].wid;
big.ht = max(r[0].ht, r[1].ht);
big.ht += r[2].ht;
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[2].wid);
big.wid += r[3].wid;
big.ht = max(big.ht, r[3].ht);
record(big);
/* schema 4, 5: first two rectangles lined up, next two stacked */
big.wid = r[0].wid + r[1].wid;
big.ht = max(r[0].ht, r[1].ht);
big.wid += max(r[2].wid, r[3].wid);
big.ht = max(big.ht, r[2].ht+r[3].ht);
record(big);
/*
* schema 6: first two pressed next to each other, next two on top, like:
* 2 3
* 0 1
*/
big.ht = max(r[0].ht+r[2].ht, r[1].ht+r[3].ht);
big.wid = r[0].wid + r[1].wid;
/* do 2 and 1 touch? */
if(r[0].ht < r[1].ht)
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[2].wid+r[1].wid);
/* do 2 and 3 touch? */
if(r[0].ht+r[2].ht > r[1].ht)
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[2].wid+r[3].wid);
/* do 0 and 3 touch? */
if(r[1].ht < r[0].ht)
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[0].wid+r[3].wid);
/* maybe 2 or 3 sits by itself */
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[2].wid);
big.wid = max(big.wid, r[3].wid);
record(big);
}
void
checkrotate(Rect *r, int n)
{
if(n == 4) {
check(r);
return;
}
checkrotate(r, n+1);
r[n] = rotate(r[n]);
checkrotate(r, n+1);
r[n] = rotate(r[n]);
}
void
checkpermute(Rect *r, int n)
{
Rect t;
int i;
if(n == 4)
checkrotate(r, 0);
for(i=n; i<4; i++) {
t = r[n], r[n] = r[i], r[i] = t; /* swap r[i], r[n] */
checkpermute(r, n+1);
t = r[n], r[n] = r[i], r[i] = t; /* swap r[i], r[n] */
}
}
void
main(void)
{
FILE *fin, *fout;
Rect r[4];
int i;
fin = fopen("packrec.in", "r");
fout = fopen("packrec.out", "w");
assert(fin != NULL && fout != NULL);
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
fscanf(fin, "%d %d", &r[i].wid, &r[i].ht);
tot=(r[0].wid*r[0].ht+r[1].wid*r[1].ht+r[2].wid*r[2].ht+r[3].wid*r[3].ht);
checkpermute(r, 0);
fprintf(fout, "%d\n", bestarea);
for(i=0; i<=100; i++)
if(bestht[i])
fprintf(fout, "%d %d\n", i, bestarea/i);
exit(0);
}