sscanf的用法
sscanf的作用:从一个字符串中读进于指定格式相符的数据。利用它可以从字符串中取出整数、浮点数和字符串。
sscanf和scanf的区别:scanf是以键盘作为输入源,sscanf是以字符串作为输入源。
sscanf:
原型:
int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format,......);说明:
sscanf()会将参数str的字符串根据参数format字符串来转换格式并格式化数据。转换后的结果存于对应的参数内。
成功则返回参数数目,失败则返回0
举例:
1. 取指定长度的字符串
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("12345","%4s",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
} 2. 格式化时间
#include
#include
int main()
{
int year, month, day, hour, minute, second;
sscanf("2013/02/13 14:55:34","%d/%d/%d %d:%d:%d",&year, &month, &day, &hour, &minute, &second);
printf("time=%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n", year, month, day, hour, minute, second);
return 0;
}
3. 读入字符串
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("12345","%s",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
} ![]()
#include
#include
int main()
{
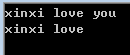
char str1[100], str2[100], str3[100];
gets(str1);
sscanf(str1,"%s%s",str2,str3);
printf("%s %s\n",str2,str3);
return 0;
}
4. %*d和%*s加了(*)表示跳过此数据不读入(也就是不把此数据读入参数中)
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("1234abcd","%*d%s",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
}
![]()
5. 取到指定字符为止的字符串。如例子所示,遇到‘+’为止的字符串。
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("1234+abc","%[^+]",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
} ![]()
遇到空格为止的字符串
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("1234+abc1234","%[^]",str);
printf("str=%s\n",str);
return 0;
}
6. 取到指定字符集为止的字符串。如遇到小写字母为止的字符串。
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("1234+abc1234","%[^a-z]",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
} 7. 取仅包含指定字符集的字符串。(取仅包含数字和小写字母的字符串,是取得连续的字符串)。
#include
#include
int main()
{
char str[100];
sscanf("123456abcdefBFRGTY7890","%[1-9a-z]",str);
printf("%s\n",str);
return 0;
} ![]()
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/hejing-swust/p/7793958.html
http://www.360doc.com/content/17/1220/22/27708084_714917039.shtml