基于三轴加速度传感器的计步算法
基于三轴加速度传感器计步算法
By Sky.J 2018.08.08
概述
今天主要是想要分享利用三轴加速度传感器计步的一个算法步骤。
数据分析--->模型
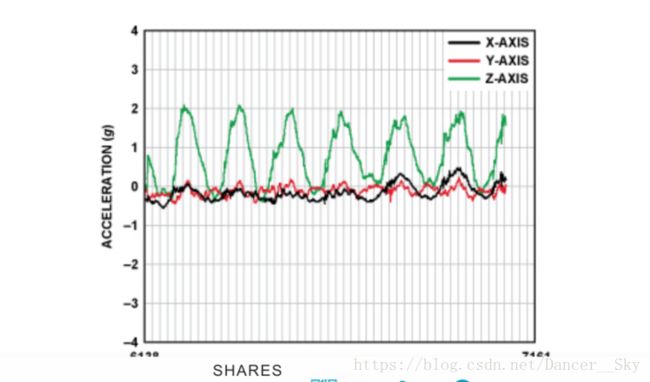
这里拿到的是ADI公司的测试数据,可以看到不管如何佩戴计步器,总有至少一个轴具有相对较大的周期性加速度变化。那么我们就可以从这里着手,进行数据分析,判断步伐。
算法
1,均值滤波器---滤波
均值滤波器实现均值滤波,其实很简单就是拿到多组x,y,z三轴数据,求平均值。最后的平均值作为输出结果,使输出结果更加平滑。完成初步滤波。
下面是伪代码
#define FILTER_CNT 4
typedef struct {
short x;
short y;
short z;
}axis_info_t;
typedef struct filter_avg{
axis_info_t info[FILTER_CNT];
unsigned char count;
}filter_avg_t;
//读取xyz数据存入均值滤波器,存满进行计算,滤波后样本存入sample,如何读取存满就不多说了。
static void filter_calculate(filter_avg_t *filter, axis_info_t *sample)
{
unsigned int i;
short x_sum = 0, y_sum = 0, z_sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < FILTER_CNT; i++) {
x_sum += filter->info[i].x;
y_sum += filter->info[i].y;
z_sum += filter->info[i].z;
}
sample->x = x_sum / FILTER_CNT;
sample->y = y_sum / FILTER_CNT;
sample->z = z_sum / FILTER_CNT;
}2,动态阈值
动态阈值: 系统持续更新3轴加速度的最大值和最小值,每采样50次更新一次。平均值(Max + Min)/2称为"动态阈值"。
对于动态阈值其实就是我们在采样过程中拿到的每个轴的最大值和最小值的平均值,它是每取50个样本就更新一次,是动态变化的。所以我们只需每50次样本,取出其中的最大最小值就行了。最大最小值,还有一个重要的功能,判断最活跃轴,因为我们最后判断步伐,也是根据哪个轴加速度变化最大认为哪个是活跃轴。
下面是动态阈值的伪代码部分
#define MAX(a,b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
#define MIN(a,b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b))
#define SAMPLE_SIZE 50
typedef struct {
axis_info_t newmax;
axis_info_t newmin;
axis_info_t oldmax;
axis_info_t oldmin;
}peak_value_t;
static void peak_value_init(peak_value_t *peak);
//在动态阈值结构体初始化时,一定要将max的值都赋值为最小值,min赋值为最大值,这样才有利于动态更新。
static void peak_update(peak_value_t *peak, axis_info_t *cur_sample)
{
static unsigned int sample_size = 0;
sample_size ++;
if (sample_size > SAMPLE_SIZE) {
/*采样达到50个,更新一次*/
sample_size = 1;
peak->oldmax = peak->newmax;
peak->oldmin = peak->newmin;
//初始化
peak_value_init(peak);
}
peak->newmax.x = MAX(peak->newmax.x, cur_sample->x);
peak->newmax.y = MAX(peak->newmax.y, cur_sample->y);
peak->newmax.z = MAX(peak->newmax.z, cur_sample->z);
peak->newmin.x = MIN(peak->newmin.x, cur_sample->x);
peak->newmin.y = MIN(peak->newmin.y, cur_sample->y);
peak->newmin.z = MIN(peak->newmin.z, cur_sample->z);
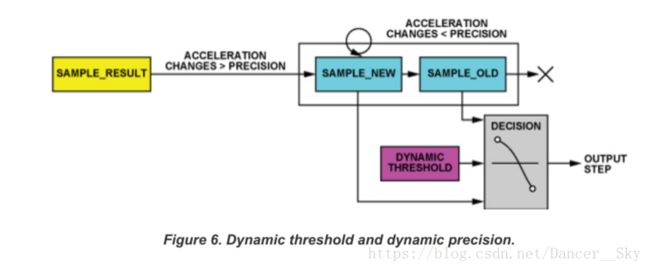
}3,动态精度
动态精度:这其实是由一个线性移位寄存器加上一个我们预设定的动态变化值来消除高频噪声。其实它的操作很简单,移位寄存器中有两个样本,一个是new_sample,一个是old_sample.只要我们采集到一个样本,当前样本cur_sample.当cur_sample到来,old_sample无条件更新为new_sample的值,但是new_sample就不是无条件更新了,假设我们设定动态精度DYNAMIC_PRECISION=10,当|cur_sample.x-new_sample.x|,如果X轴变化量大于DYNAMIC_PRECISION,那么new_sample.x就更新为cur_sample.x,否则不变。
下面是部分伪代码
#define ABS(a) (0 - (a)) > 0 ? (-(a)) : (a)
#define DYNAMIC_PRECISION 30 /*动态精度*/
/*一个线性移位寄存器,用于过滤高频噪声*/
typedef struct slid_reg{
axis_info_t new_sample;
axis_info_t old_sample;
}slid_reg_t;
static char slid_update(slid_reg_t *slid, axis_info_t *cur_sample)
{
char res = 0;
if (ABS((cur_sample->x - slid->new_sample.x)) > DYNAMIC_PRECISION) {
slid->old_sample.x = slid->new_sample.x;
slid->new_sample.x = cur_sample->x;
res = 1;
} else {
slid->old_sample.x = slid->new_sample.x;
}
if (ABS((cur_sample->y - slid->new_sample.y)) > DYNAMIC_PRECISION) {
slid->old_sample.y = slid->new_sample.y;
slid->new_sample.y = cur_sample->y;
res = 1;
} else {
slid->old_sample.y = slid->new_sample.y;
}
if (ABS((cur_sample->z - slid->new_sample.z)) > DYNAMIC_PRECISION) {
slid->old_sample.z = slid->new_sample.z;
slid->new_sample.z = cur_sample->z;
res = 1;
} else {
slid->old_sample.z = slid->new_sample.z;
}
return res;
}4,步伐判断
步伐判断:通过资料图,我们可以看到,判断为一步的条件是,先找到最活跃轴,然后最活跃轴的old_sample > 动态阈值,new_sample < 动态阈值。满足上述条件,认为走了一步。在我们运动过程,可以认为连续运动大于5步才认为是走步,这样可以过滤一些不必要的错误步数,同时资料所说的最快大约每秒5步,相当于200ms一步,我是利用每40ms取一次数据,200ms得到5组数据,滤波得到一个样本,这样可能更加准确一点。对于文档所说的时间窗口我就没有去做了,通过对比实验结果,我买的华为手环步数和我这个设备的步数基本一致,相差大约在200步以内。
下面是步伐判断伪代码:
#define MOST_ACTIVE_NULL 0 /*未找到最活跃轴*/
#define MOST_ACTIVE_X 1 /*最活跃轴X*/
#define MOST_ACTIVE_Y 2 /*最活跃轴Y*/
#define MOST_ACTIVE_Z 3 /*最活跃轴Z*/
#define ACTIVE_PRECISION 60 /*活跃轴最小变化值*/
/*判断当前最活跃轴*/
static char is_most_active(peak_value_t *peak)
{
char res = MOST_ACTIVE_NULL;
short x_change = ABS((peak->newmax.x - peak->newmin.x));
short y_change = ABS((peak->newmax.y - peak->newmin.y));
short z_change = ABS((peak->newmax.z - peak->newmin.z));
if (x_change > y_change && x_change > z_change && x_change >= ACTIVE_PRECISION) {
res = MOST_ACTIVE_X;
} else if (y_change > x_change && y_change > z_change && y_change >= ACTIVE_PRECISION) {
res = MOST_ACTIVE_Y;
} else if (z_change > x_change && z_change > y_change && z_change >= ACTIVE_PRECISION) {
res = MOST_ACTIVE_Z;
}
return res;
}
/*判断是否走步*/
static void detect_step(peak_value_t *peak, slid_reg_t *slid, axis_info_t *cur_sample)
{
static step_cnt = 0;
char res = is_most_active(peak);
switch (res) {
case MOST_ACTIVE_NULL: {
//fix
break;
}
case MOST_ACTIVE_X: {
short threshold_x = (peak->oldmax.x + peak->oldmin.x) / 2;
if (slid->old_sample.x > threshold_x && slid->new_sample.x < threshold_x) {
step_cnt ++;
}
break;
}
case MOST_ACTIVE_Y: {
short threshold_y = (peak->oldmax.y + peak->oldmin.y) / 2;
if (slid->old_sample.y > threshold_y && slid->new_sample.y < threshold_y) {
step_cnt ++;
}
break;
}
case MOST_ACTIVE_Z: {
short threshold_z = (peak->oldmax.z + peak->oldmin.z) / 2;
if (slid->old_sample.z > threshold_z && slid->new_sample.z < threshold_z) {
step_cntt ++;
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}总结
整体来说,利用三轴加速度传感器实现的算法就完成了,这也是根据ADI公司的资料来做的,整体来说效果还算OK,如果有兴趣,希望这个可以有一点参考价值。
参考资料
http://www.analog.com/en/analog-dialogue/articles/pedometer-design-3-axis-digital-acceler.html