20182333 2019-2020-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》 哈夫曼编码实践报告
实践内容
设有字符集:S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n.o.p.q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z}。
给定一个包含26个英文字母的文件,统计每个字符出现的概率,根据计算的概率构造一颗哈夫曼树。
并完成对英文文件的编码和解码。
要求:
(1)准备一个包含26个英文字母的英文文件(可以不包含标点符号等),统计各个字符的概率
(2)构造哈夫曼树
(3)对英文文件进行编码,输出一个编码后的文件
(4)对编码文件进行解码,输出一个解码后的文件
(5)撰写博客记录实验的设计和实现过程,并将源代码传到码云
(6)把实验结果截图上传到云班课
哈夫曼树基本原理
1.哈夫曼树:给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
2.路径: 树中一个结点到另一个结点之间的分支构成这两个结点之间的路径。
3.路径长度:路径上的分枝数目称作路径长度。
4.树的路径长度:从树根到每一个结点的路径长度之和。
5.结点的带权路径长度:在一棵树中,如果其结点上附带有一个权值,通常把该结点的路径长度与该结点上的权值之积称为该结点的带权路径长度(weighted path length)
6.树的带权路径长度:如果树中每个叶子上都带有一个权值,则把树中所有叶子的带权路径长度之和称为树的带权路径长度。
代码解读
public class HuffmanNode implements Comparable>{
private T name;
private double length;
private HuffmanNode left;
private HuffmanNode right;
String code;
public HuffmanNode(T name, double length){
this.name = name;
this.length = length;
code = "";
}
public T getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(T name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public HuffmanNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HuffmanNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HuffmanNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HuffmanNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public String getCode(){
return code;
}
public void setCode(String str){
code = str;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "name:"+this.name+";length:"+this.length+";编码为: "+this.code;
}
@Override
//确定位置
public int compareTo(HuffmanNode other) {
if(other.getLength() > this.getLength()){
return 1;
}
if(other.getLength() < this.getLength()){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
} - 所需实现代码的方法和要实现Comparable接口,比较权重,好确定放的位置(编码是0还是1)。
public HuffmanNode createTree(List> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(nodes);
HuffmanNode left = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 2);
left.setCode(0 + "");
HuffmanNode right = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
right.setCode(1 + "");
HuffmanNode parent = new HuffmanNode(null, left.getLength() + right.getLength());
parent.setLeft(left);
parent.setRight(right);
nodes.remove(left);
nodes.remove(right);
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
} - 创建树,当还有结点时,对结点进行排序,然后左孩子为数组中的个数-2的结点,右孩子为数组中的个数-1的结点(用数组实现树的那一章说过左右孩子在数组中的索引),赋予左孩子的编码为0,右孩子的编码为1,双亲结点则为左右孩子相加的权重(也就是左右孩子的概率和),把双亲结点加入链表中,从链表中把旧的左右孩子删除,直至链表中的结点只剩一个(也就是根结点)。
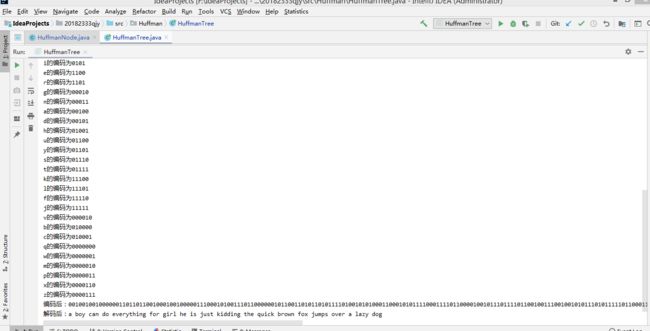
public List breadth(HuffmanNode root) {
List list = new ArrayList();
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque();
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
root.getLeft().setCode(root.getCode() + "0");
root.getRight().setCode(root.getCode() + "1");
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
list.add(queue.peek());
HuffmanNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.getLeft() != null)
node.getLeft().setCode(node.getCode() + "0");
if (node.getRight() != null)
node.getRight().setCode(node.getCode() + "1");
if (node.getLeft() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getLeft());
}
if (node.getRight() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getRight());
}
}
return list;
} - 得到相应字符的编码值
for (int n = 0;n < result.length; n++){
for (int i = 0; i < 27; i++){
if (result[n].equals(list.get(i))){
number[i] += 1;
}
}
}- 得到每个字符(包括空格)出现的次数(类似于累加的形式)
List nodeList = new ArrayList();
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat( "0.0000000");
double wei;
double sum = result.length;
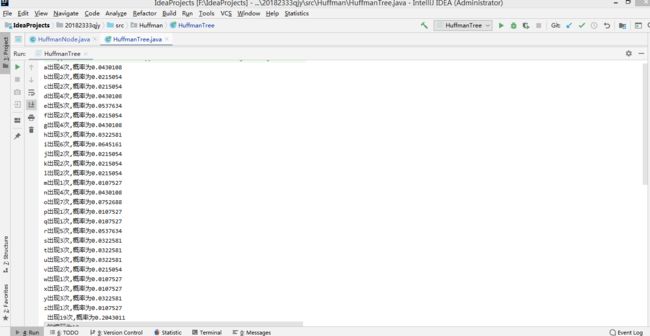
for(int i = 0;i<27;i++){
wei = ((double) number[i]/sum);
System.out.println(list.get(i) + "出现" + number[i] + "次,概率为" + df.format(wei));
nodeList.add(new HuffmanNode(list.get(i),number[i]));
}