计算机图形学:颜色模型、图像基本知识、Phong光照模型
颜色模型、图像基本知识、Phong光照模型
1.颜色模型
1.1 RGB Color Space
The reason why we pick red, green, and blue?
- essentially because of the structure of our visual system
- Our visual system is sensitive to those three colors
缺陷
Unfortunately ,Some colors cannot be written as combinations of RGB triples, because some parts of the red curve is negative
1.2 CMY
Cyan(青), magenta(品红) , and yellow
It’s called subtractive primaries(减色系统)
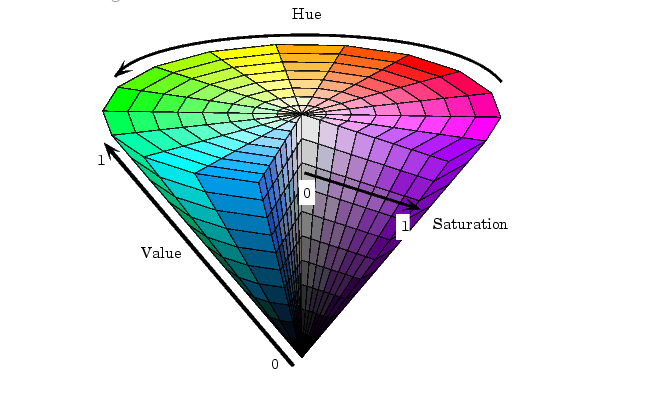
1.3 HSV Color space
RGB 不是很直观,HSV比较易于理解
- Hue (色调) means the base color, which is a main factor indicates difference between colors.
- Saturation(饱和度) is for purity of color (decrease = adding white)
- Value of brightness(亮度) Luminance of lights,(decrease = adding black)
2.图像基本知识
2.1 Image & Pixel
- Image could be treated as a 2-dimensional
discrete function f(x,y) - each discrete grid is called pixel
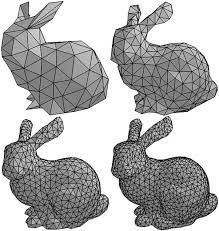
2.2 Triangle Mesh
Contains a list of faces F, and a list of vertices V
- A list of faces F = (f1,f2,…,fn), Each face is a triangle
- A list of vertices V = (v1,v2,…,vn), Each face in F is a list of indices in V
e.g.
f1–(v1,v2,v3 ), f2 --(v4,v5,v6 ),
f3–(v7,v8,v9 ), …
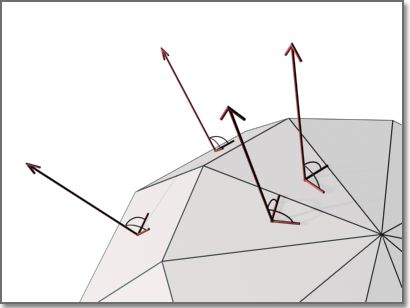
2.3 Normal
2.3.1 Face Normal
Each face has a normal direction to define the orientation
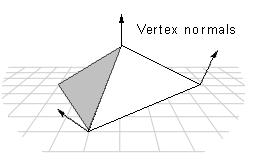
2.3.2 Vertex Normal
Each vertex is shared by m faces
计算方法
- 直接平均:Compute normal by Interpolation Nv= (Nf1+Nf2 … + Nfm)/m
- 面积加权平均:or by area based Interpolation Nv= (|F1|*Nf1+|F2|*Nf2 … + |Fm|*Nfm)/(|F1|+|F2|+…|Fm|)
- 角度加权平均:or by angle based Interpolation Nv= (|A1|*Nf1+|A2|*Nf2 … + |Am|*Nfm)/(|A1|+|A2|+…|Am|)
3.光照模型
Local Lighting
- Concerned with how objects are directly illuminated by light sources
Global Lighting
- Includes shadow effects
- Includes lighting effects from locations other than light sources, such as reflections, refractions
3.1 History of Lighting
- In 1967, Wylie: first added lighting effects into rendering
- Intensity is inverse of the distance to the light
- In 1970, Bouknight: introduced the first lighting
model:- Lambert diffuse reflection(漫发射) + ambient (No specular lighting)(环境光)
- In 1971, Gourand: gourand shading
- Lambert diffuse + Bicentric interpolation
- In 1975, Phong: proposed extended the model by further considering specular:
- Diffuse(漫发射) + ambient(环境光,模拟全局光照效果) + specular(高光)
- The most influenced lighting model
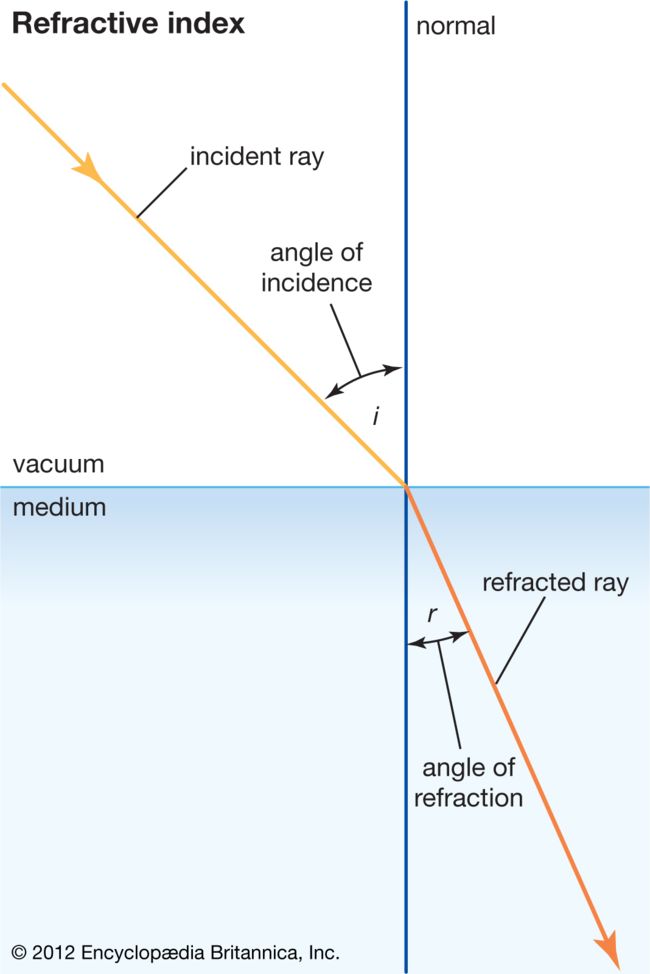
3.2折射向量的计算
-
i n c i d e n c e _ r a y incidence\_ray incidence_ray: 入射角(单位向量)
-
n o r m a l _ v e c normal\_vec normal_vec = Vector(0, 0, 1) //法向量
-
r e f r a c t i v e _ i n d e x refractive\_index refractive_index: 介质密度比(空气/水)
cos θ i = − i n c i d e n c e _ r a y . d o t ( n o r m a l _ v e c ) cos θ r = 1 − r e f r a c t i v e _ i n d e x 2 ∗ ( 1 − cos θ i 2 ) ( 大 于 0 时 ) r e f r a c t e d _ r a y = ( n o r m a l _ v e c ∗ cos θ i + i n c i d e n c e _ r a y ) ∗ r e f r a c t i v e _ i n d e x − n o r m a l _ v e c ∗ cos θ r \cos\theta_{i} = -incidence\_ray.dot(normal\_vec)\\ \cos \theta _{r} = \sqrt{1 - refractive\_index^{2} * (1 - {\cos \theta_{i}}^{2})}\ \ (大于0时)\\ refracted\_ray = (normal\_vec * \cos\theta_{i} + incidence\_ray) * refractive\_index - normal\_vec * \cos \theta _{r} cosθi=−incidence_ray.dot(normal_vec)cosθr=1−refractive_index2∗(1−cosθi2) (大于0时)refracted_ray=(normal_vec∗cosθi+incidence_ray)∗refractive_index−normal_vec∗cosθr
3.3 Measure of light
- Solid Angle(立体角) :
- How big an object appears to an observer at point P
- Max Vaule: 4π
d w = d s r 2 dw = \frac{ds}{r^2} dw=r2ds
- Irradiance (辉度) E
- E defined as: light energy per unit time arrived at per unit area (ds)
- Radiance (发光强度) I
- I defined as: irradiance per unit solid angle
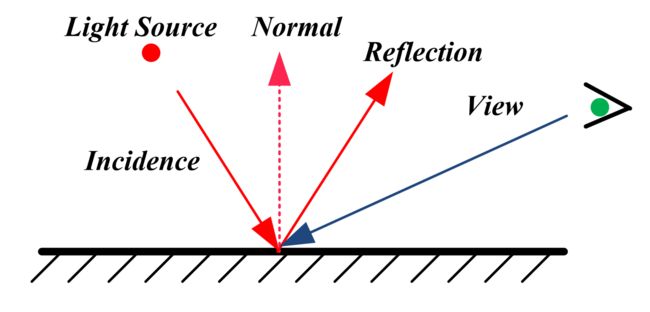
3.4 Phong Lighting Model
3.4.1 Diffuse reflection
- 漫反射光的传播是各向同性的(isotropic)
- The intensity of diffuse reflection is defined as:
I d = I i K d ∗ ( L ⋅ N ) I_d = I_iK_d*(L \cdot N) Id=IiKd∗(L⋅N)
- k d k_d kdis the diffuse reflection constant ( k d r , k d g , K d b ) (k_{dr},k_{dg},K_{db}) (kdr,kdg,Kdb)
- k d k_d kdimplies the base color of the model
3.4.2 Specular reflection
- The intensity of specular reflection is defined as:
I s = I i K s ∗ ( R ⋅ V ) n I_s = I_iK_s*(R \cdot V)^n Is=IiKs∗(R⋅V)n
- k s k_s ksis the specular reflection constant ;
- and n is the shininess constant, which decides how shiny the surface is. n越大,高光越集中
3.4.3 Ambient reflection
- To approximate global illuminations (including indirect lighting, indirect reflection…)
- The intensity of ambient reflection is defined as:
I a = I i K a I_a = I_iK_a Ia=IiKa
- K a K_a Kais the ambient reflection constant
3.4.4 最终结果
The reflection intensity is the sum of diffuse reflection, specular reflection and ambient reflection:
I = I i K a + I i K s ∗ ( R ⋅ V ) n + I i K d ∗ ( L ⋅ N ) I = I_iK_a + I_iK_s*(R \cdot V)^n + I_iK_d*(L \cdot N) I=IiKa+IiKs∗(R⋅V)n+IiKd∗(L⋅N)
3.5 Blinn-Phong Lighting Model
H = L + V 2 I s = I i K s ∗ ( N ⋅ H ) n H=\frac{L+V}{2}\\ I_s = I_iK_s*(N \cdot H)^n H=2L+VIs=IiKs∗(N⋅H)n