【Lightoj 1026 B Critical Links】& 桥
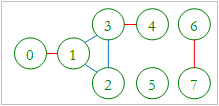
In a computer network a link L, which interconnects two servers, is considered critical if there are at least two servers A and B such that all network interconnection paths between A and B pass through L. Removing a critical link generates two disjoint sub-networks such that any two servers of a sub-network are interconnected. For example, the network shown in figure 1 has three critical links that are marked red: 0 - 1, 3 - 4 and 6 - 7 in figure 2.
Figure 1: Original Graph
Figure 2: The Critical Links
It is known that:
- The connection links are bi-directional.
- A server is not directly connected to itself.
- Two servers are interconnected if they are directly connected or if they are interconnected with the same server.
- The network can have stand-alone sub-networks.
Write a program that finds all critical links of a given computer network.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 15), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a blank line. The next line will contain n (0 ≤ n ≤ 10000) denoting the number of nodes. Each of the next n lines will contain some integers in the following format:
u (k) v1 v2 … vk
Where u is the node identifier, k is the number of adjacent nodes; v1, v2 … vk are the adjacent nodes of u. You can assume that there are at most 100000 edges in total in a case. Dataset is huge, so use faster i/o methods.
Output
For each case, print the case number first. Then you should print the number of critical links and the critical links, one link per line, starting from the beginning of the line, as shown in the sample output below. The links are listed in ascending order according to their first element and then second element. Since the graph is bidirectional, print a link u v if u < v.
Sample Input
3
8
0 (1) 1
1 (3) 2 0 3
2 (2) 1 3
3 (3) 1 2 4
4 (1) 3
7 (1) 6
6 (1) 7
5 (0)
0
2
0 (1) 1
1 (1) 0
Sample Output
Case 1:
3 critical links
0 - 1
3 - 4
6 - 7
Case 2:
0 critical links
Case 3:
1 critical links
0 - 1
Hint
Dataset is huge, use faster I/O methods.
题意 : 找“桥”的个数,桥:关键路径,去掉该边将导致原本相连的点不在联通
思路 : 据说是个模板题(QAQ)
AC代码:
#include