Tensorflow实战(一)
Tensorflow实战(一)
- tensorflow常用方法
- 计算图
- Tensorflow训练线性回归模型
- 1.生成样本
- 2.训练线性回归模型
- 3.得到模型
tensorflow常用方法
#创建变量
w = tf.Variable([[0.5,1.0]])
x = tf.Variable([[2.0],[1.0]])
#乘法 加法
y = tf.matmul(w,x)
y = tf.add(y,b)
#打印结果
print(y.eval())
#创建常量
tensor = tf.zeros([3,4],int32)#常用于b的初始化
tensor = tf.ones([3,4],int32)
tensor = tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5,6])
tensor = tf.condtant(1,shape = [2,3])
#切片式常量
tensor = tf.linspace(10.0,12.0,3, name = "linspace") #10.0到12.0之间取三个数
tensor = tf.range(3,18,3)#3到18每3个数取一个值
#高斯分布
norm = tf.random_normal([2,3],mean = -1,stddev = 4) #初始化W
#洗牌操作
shuff = tf.random_shuffle(x)
#赋值操作
update = tf.assign(state, value)
#初始化变量
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#按行取最大
tf.argmax(actv,1)
#按列取最大
tf.argmax(actv,0)
#判断两个张量是否相等,相等返回Ture,不等返回False
pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(actv, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
#转换数据类型
accur = tf.cast(pred, "float")
#求平均
accr = tf.reduce_mean(accur)
#将numpy转换成tensor
import numpy as np
a = np.zeros((3,3))
ta = tf.convert_to_tensor(a)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(ta))
arr = np.array([[31, 23, 4, 24, 27, 34],
[18, 3, 25, 0, 6, 35],
[28, 14, 33, 22, 20, 8],
[13, 30, 21, 19, 7, 9],
[16, 1, 26, 32, 2, 29],
[17, 12, 5, 11, 10, 15]])
#打印数组维度
tf.rank(arr).eval()
#打印数组的形状
tf.shape(arr).eval()
#构建网络
#初始化参数
w_c1 = tf.Variable(w_alpha*tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 32]))
b_c1 = tf.Variable(b_alpha*tf.random_normal([32]))
#卷积层,"SAME"的意思时卷积之后尺寸不变
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(x, w_c1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c1))
#池化层
conv1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv1 = tf.nn.dropout(conv1, keep_prob)
#全连接层
dense = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(dense, w_d), b_d))
#在构建神经网络模型时占位
image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=shape)
output = net(image)
#得到结果需要feed_dict
features = output.eval(feed_dict={image: input_image_pre})
计算图
TensorFlow是一个通过计算图的形式来表述计算的编程系统;
基于TensorFlow这个编程系统中的每一个计算都是计算图上的一个节点,而节点与节点之间的连线则代表计算之间的依赖关系。
计算图工作的一个小栗子:
#一个值不断加一
#定义变量
state = tf.Variable(0)
new_value = tf.add(state, tf.constant(1))
update = tf.assign(state, new_value)
#构建图
with tf.Session() as sess:
#初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#必须run一下才能打印出来
print(sess.run(state))
for _ in range(3):
sess.run(update)
print(sess.run(state))
Tensorflow训练线性回归模型
1.生成样本
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
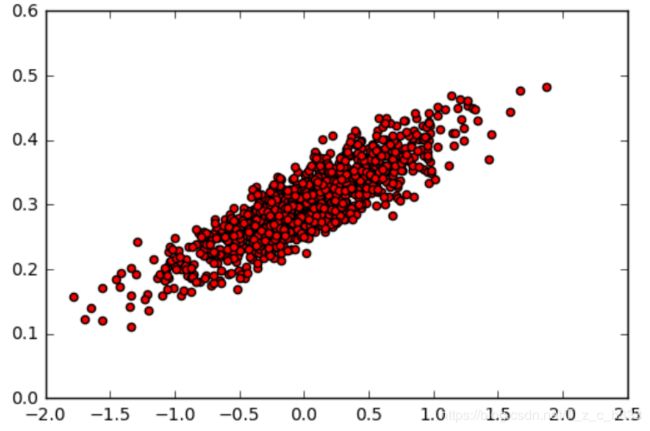
#随机生成1000个点,围绕在y=0.1x+0.3的直线周围
num_points = 1000
vectors_set = []
for i in range(num_points):
x1 = np.random.normal(0.0, 0.55)
y1 = x1 * 0.1 + 0.3 + np.random.normal(0.0, 0.03)
vectors_set.append([x1, y1])
#生成一些样本
x_data = [v[0] for v in vectors_set]
y_data = [v[1] for v in vectors_set]
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data,c='r')
plt.show()
2.训练线性回归模型
#生成1维的W矩阵,取值是[-1,1]之间的随机数
with tf.name_scope('weight'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], -1.0, 1.0), name='W')
#生成1维的b矩阵,初始值是0
with tf.name_scope('bias'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]), name='b')
#经过计算得出预估值y
with tf.name_scope('y'):
y = W * x_data + b
#以预估值y和实际值y_data之间的均方误差作为损失
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data), name='loss')
#采用梯度下降法来优化参数
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
#训练的过程就是最小化这个误差值
train = optimizer.minimize(loss, name='train')
sess = tf.Session()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
#初始化的W和b是多少
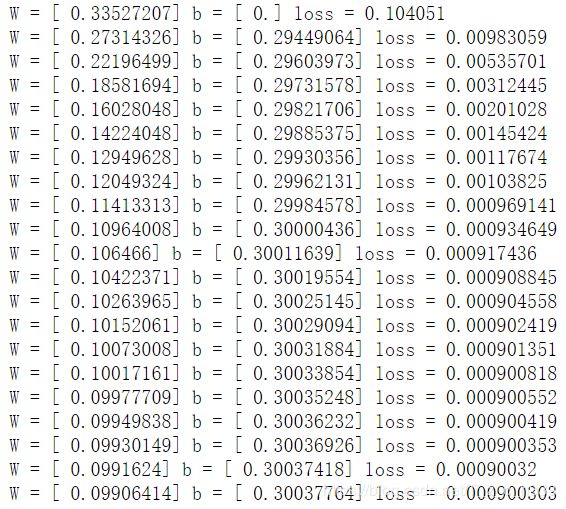
print ("W =", sess.run(W), "b =", sess.run(b), "loss =", sess.run(loss))
#执行20次训练
for step in range(20):
sess.run(train)
# 输出训练好的W和b
print ("W =", sess.run(W), "b =", sess.run(b), "loss =", sess.run(loss))
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter("logs/", sess.graph)
3.得到模型
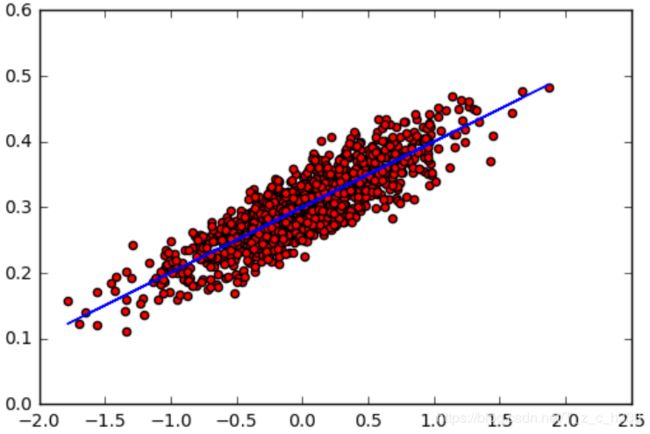
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data,c='r')
plt.plot(x_data,sess.run(W)*x_data+sess.run(b))
plt.show()