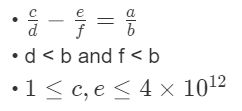2020牛客暑期多校训练营(第三场)
A. Clam and Fish
传送门
题意:
有 n 个阶段来钓鱼,每一阶段有四个状态:
(0)没有鱼,没有蛤蜊
(1)没有鱼,有一个蛤蜊
(2)有一条鱼,没有蛤蜊
(3) 有一条鱼,有一个蛤蜊
在每一阶段你可以采取以下四个操作之一:
(1)如果该阶段有一个蛤蜊,用蛤蜊制作一个鱼饵
(2)如果该阶段有一条鱼,可以直接钓(不需要鱼饵)
(3)如果还有鱼饵,不管有没有鱼,都可以使用鱼饵钓到一条鱼
(4)啥也不干
给定 n 个阶段的状态,问最多能钓多少鱼
思路:
状态2、3直接钓,状态0用鱼饵钓(如果有鱼饵的话),状态1判断当前鱼饵个数和后面没有鱼的状态的个数(即0和1),鱼饵多的话就钓鱼,鱼饵少的话就做鱼饵
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-3;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
int cn[N];
char s[N];
int main()
{
int t, n;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%d%s", &n, s);
int ans = 0, now = 0;
cn[n + 1] = 0;
for(int i = n; i >= 0; --i) {
cn[i] = cn[i + 1];
if(s[i] == '0' || s[i] == '1') cn[i]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(s[i] == '2' || s[i] == '3') ans++;
if(s[i] == '0') {
if(now) now--, ans++;
}
if(s[i] == '1') {
if(now == 0 || cn[i] > now) now++;
else now--, ans++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
B. Classical String Problem
传送门
题意:
给一个字符串和 q 个操作,操作分为两种:M操作修改当前字符串,x > 0时将字符串左边 x 个字符全部移到最后,x < 0时将字符串右边 x 个字符全部移到开头;A 操作询问当前字符串的第 x 个字符
思路:
将字符串循环一次,每次M操作修改当前字符串的起始下标并取模,A操作O(1)访问,卡cin...
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-11;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 4e6 + 5;
char s[N], tmp[N];
int main() {
char c;
int q, x, id = 0;
scanf("%s%d", s, &q);
int len = strlen(s);
strcpy(tmp, s);
strcat(s, tmp);
while(q--) {
getchar();
scanf("%c%d", &c, &x);
if(c == 'A')
printf("%c\n", s[id + x - 1]);
else {
if(x > 0) {
id += x;
id %= len;
}
else {
x *= (-1);
id += len - x;
id %= len;
}
}
}
return 0;
} C. Operation Love
传送门
题意:顺时针或逆时针给出手印各点的坐标,问是左手还是右手
思路1:找到长度为9的边和它的下一个点,由这三个点计算叉乘判断顺逆时针,然后求下一条边的长度,顺时针的话下一条边是6是右手,下一条边是8是左手;逆时针相反。
-----------------------------------------小科普时间-------------------------------------------
判断三点是顺时针还是逆时针方向:
p1 = (x1, y1); p2 = (x2, y2); p3 = (x3, y3);
求向量 p12 = (x2 - x1, y2 - y1); p23 = (x3 - x2, y3 - y2);
求叉乘 p12 × p23 = (x2 - x1) * (y3 - y2) - (y2 - y1) * (x3 - x2)
> 0,p1 - p2 - p3为逆时针
< 0,p1 - p2 - p3为顺时针
= 0,三点共线
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
由于边的大小就这么几种,判相等的时候把eps设大一点....eps小于1e-5就卡了淦 qaq
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-3;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 45;
struct point
{
double x, y;
} s[N];
double dis(point a, point b)
{
return 1.0 * sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y));
}
double axb(point A, point B, point C)
{
return (B.x-A.x)*(C.y-B.y)-(B.y-A.y)*(C.x-B.x);
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; ++i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf", &s[i].x, &s[i].y);
s[i + 20] = s[i];
}
int q1, q2, q3;
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
double disc = 1.0 * dis(s[i], s[i+1]);
if(fabs(disc - 9.0) < eps)
{
q1 = i;
q2 = i + 1;
q3 = i + 2;
break;
}
}
bool flag = 0; ///左1右0
if(axb(s[q1], s[q2], s[q3]) < 0)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; ++i)
{
double dis1 = dis(s[i], s[i+1]);
if(fabs(dis1 - 9.0) < eps)
{
double dis2 = dis(s[i + 1], s[i + 2]);
if(fabs(dis2 - 8.0) < eps)
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
double dis1 = dis(s[i], s[i+1]);
if(fabs(dis1 - 9.0) < eps)
{
double dis2 = dis(s[i + 1], s[i + 2]);
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps)
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag)
cout<<"left"<<'\n';
else
cout<<"right"<<'\n';
}
} 思路2(很笨):发现手印中只有一条长度为9的边、一条长度为8的边和一条长度为6的边,O(n)找到长度为9的边,根据这条边两点的位置关系和下一点和这条边的位置关系(在9这条边的上方还是下方)判断是顺时针还是逆时针,下面同上。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 45;
struct point
{
double x, y;
} s[N];
double dis(point a, point b)
{
return 1.0 * sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y));
}
bool judge(point a, point b, point c) ///点c和直线a,b的位置关系
{
double k = 1.0 * (a.y - b.y) / (a.x - b.x);
if((c.x - b.x) * k + b.y > c.y) ///c在直线下方
return 0;
return 1; ///c在直线上方
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; ++i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf", &s[i].x, &s[i].y);
s[i + 20] = s[i];
}
bool flag; ///左1右0
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; ++i)
{
double dis1 = dis(s[i], s[i + 1]);
if(fabs(dis1 - 9.0) < eps)
{
double dis2 = dis(s[i + 1], s[i + 2]); ///下一条边的长度 不是8就是6
if(fabs(s[i].x - s[i + 1].x) < eps) ///9与y轴平行
{
if(s[i].x > s[i + 2].x) ///下一点在左方
{
if(s[i].y < s[i + 1].y) ///9正
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 1;
else
flag = 0;
}
else ///9反
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 0;
else
flag = 1;
}
}
else ///右方
{
if(s[i].y < s[i + 1].y) ///9正
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 0;
else
flag = 1;
}
else ///9反
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 1;
else
flag = 0;
}
}
}
else
{
if(judge(s[i], s[i + 1], s[i + 2])) ///下一个点在线段上方
{
if(s[i].x < s[i + 1].x) ///9正着
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 1;
else
flag = 0;
}
else ///9反着
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 0;
else
flag = 1;
}
}
else ///下方
{
if(s[i].x < s[i + 1].x) ///9正着
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 0;
else
flag = 1;
}
else ///9反着
{
if(fabs(dis2 - 6.0) < eps) ///6
flag = 1;
else
flag = 0;
}
}
}
break;
}
}
if(flag)
cout<<"left"<<'\n';
else
cout<<"right"<<'\n';
}
return 0;
} F. Fraction Construction Problem
传送门
题意:
给定a, b,求一组c, d, e, f 满足
思路:
(原题解做法)
(1)若 gcd(a, b) != 1,取 a, b 的任意一个大于1的公因数 g,那么 a / g,b / g,1,b / g 就满足题意
(2)若gcd(a, b) == 1,如果 b 的相异质因数只有一个,无解,原因:
(3)若gcd(a, b) == 1,b的相异质因数多于1个,可以取一组 d 和 f ,使 d * f == b 且 gcd(d, f) == 1,这样就变成了求解 c * f - d * e = a,由于gcd(d, f) == 1,exgcd 求出 c * f - d * e = 1的一组 c, e 后乘以 a 即可
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
ll pri[N], tot, cn[N], bp[N]; //cn[i]:i的不同质因数的个数; bp[i]:i的一个质因数
bool vis[N];
void init() {
tot = 0;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(cn, 0, sizeof(cn));
vis[0] = vis[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; ++i) {
if(!vis[i]) {
cn[i]++;
bp[i] = i;
pri[++tot] = i;
for(int j = i + i; j < N; j += i) {
vis[j] = 1;
cn[j]++;
bp[j] = i;
}
}
}
}
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if(a == 0 && b == 0)
return -1;
if(b == 0) {
x = 1;
y = 0;
return a;
}
ll d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return d;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main() {
init();
ll t, a, b, c, d, e, f;
scanf("%lld", &t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b);
if(b == 1) {
printf("-1 -1 -1 -1\n");
continue;
}
ll gd = gcd(a, b);
if(gd > 1) {
printf("%lld %lld %lld %lld\n", a / gd + 1, b / gd, 1, b / gd);
continue;
}
if(cn[b] == 1) {
printf("-1 -1 -1 -1\n");
continue;
}
ll tmp = b;
d = 1;
while(tmp % bp[b] == 0) {
tmp /= bp[b];
d *= bp[b];
}
f = b / d;
gd = exgcd(f, d, c, e);
e = -e;
while(c < 0 || e < 0) {
c += d;
e += f;
}
c *= a;
e *= a;
printf("%lld %lld %lld %lld\n", c, d, e, f);
}
return 0;
}
L. Problem L is the Only Lovely Problem
传送门
~~~~温暖的签到
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double eps = 1e-11;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int main()
{
string s;
while(getline(cin, s))
{
if(tolower(s[0]) == 'l'
&& tolower(s[1]) == 'o'
&& tolower(s[2]) == 'v'
&& tolower(s[3]) == 'e'
&& tolower(s[4]) == 'l'
&& tolower(s[5]) == 'y')
cout<<"lovely"<<'\n';
else
cout<<"ugly"<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}