剑指Offer题解——链表
文章目录
- 剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
- 利用栈
- 逆向输入数组
- 剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
- 解法
- 剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
- 快慢指针
- 剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
- 解法
- 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
- 解法
- 剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
- 解法
- 推荐阅读
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
利用栈
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (head != null) {
stack.offerFirst(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] res = new int[size];
int index = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res[index++] = stack.pollFirst();
}
return res;
}
}
逆向输入数组
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode curHead = head;
int size = 0;
while (curHead != null) {
curHead = curHead.next;
size++;
}
int[] res = new int[size];
for (int i = size - 1; i >=0; i--) {
res[i] = head.val;
head = head.next;
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
返回删除后的链表的头节点。
注意:此题对比原题有改动
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 1
输出: [4,5,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
说明:
题目保证链表中节点的值互不相同
若使用 C 或 C++ 语言,你不需要 free 或 delete 被删除的节点
解法
用前一个节点进行比较,可以直接删除节点。还可以用一个哑巴节点做头结点,这样就不用单独判断第一个节点了。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode pre = head;
if (head.val == val) {
pre = head.next;
head.next = null;
return pre;
}
while (pre.next != null) {
if (pre.next.val == val) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
return head;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
return null;
}
}
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (k-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newHead.next;
newHead.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
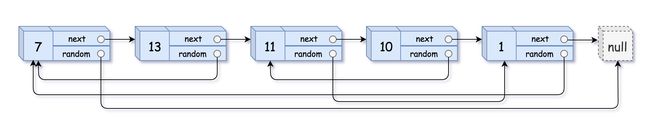
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
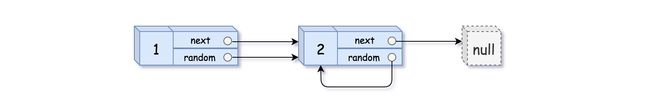
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
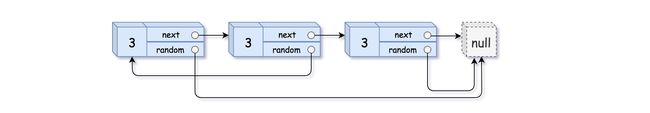
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
解法
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node ptr = head;
// 将原链表每个节点旁边增加一个节点
while (ptr != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(ptr.val);
newNode.next = ptr.next;
ptr.next = newNode;
ptr = newNode.next;
}
ptr = head;
// 将复制链表的random指向对应的位置
while (ptr != null) {
ptr.next.random = (ptr.random != null) ? ptr.random.next : null;
ptr = ptr.next.next;
}
// 将复制链表的next指向对应的位置
Node ptrOld = head, ptrNew = head.next, newHead = head.next;
while (ptrOld != null) {
ptrOld.next = ptrOld.next.next;
ptrNew.next = (ptrNew.next != null) ? ptrNew.next.next : null;
ptrOld = ptrOld.next;
ptrNew = ptrNew.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}
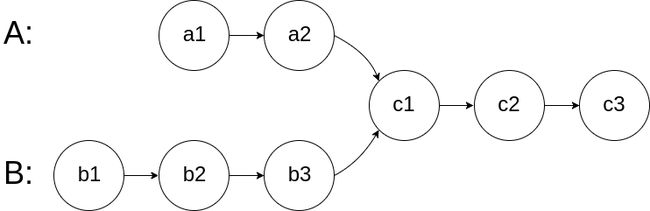
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
[剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点)
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
示例 1:
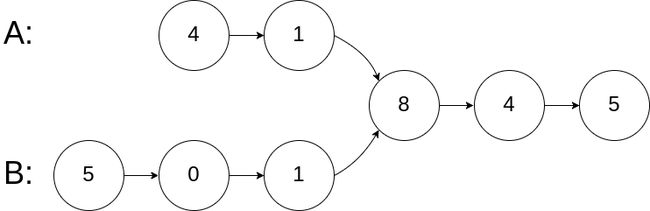
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
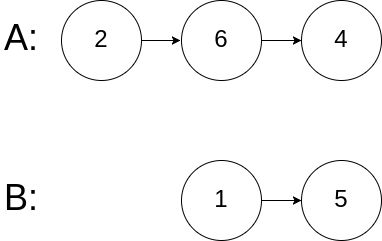
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
解法
A和B两个链表长度可能不同,但是A+B和B+A的长度是相同的,所以遍历A+B和遍历B+A一定是同时结束。 如果A,B相交的话A和B有一段尾巴是相同的,所以两个遍历的指针一定会同时到达交点 如果A,B不相交的话两个指针就会同时到达A+B(B+A)的尾节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode l1 = headA, l2 = headB;
while (l1 != l2) {
l1 = (l1 == null) ? headB : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? headA : l2.next;
}
return l1;
}
}
推荐阅读
- 机器学习资料汇总
- 吴恩达《机器学习》视频、作业、源码
- 106页《Python进阶》中文版正式发布
- 李航《统计学习方法》第二版完整课件
- 机器学习数学全书,1900页PDF下载
![]()