Leetcode题解-算法-搜索(python版)
文章目录
- 1、BFS
- 1.1 将一个数分解为整数的平方和
- 1.2 最短单词路径
- 1.3 K 站中转内最便宜的航班
- 1.4 课程表
- 2、DFS
- 2.1 查找最大的连通面积
- 2.2 矩阵中的连通分量数目
- 2.3 朋友圈的数量
- 2.4 填充封闭的区域
- 2.5 能到达的太平洋和大西洋的区域
- 2.6 收集树上所有苹果的最少时间
- 3 Backtracking
- 3.1 电话号码的字母组合
- 3.2 复原IP地址
1、BFS
1.1 将一个数分解为整数的平方和
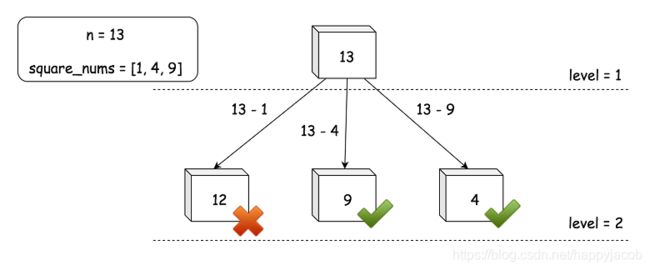
279. 完全平方数(Medium)
给定一个 N 元树,其中每个节点表示数字 n 的余数减去一个完全平方数的组合,我们的任务是在树中找到一个节点,该节点满足两个条件:
- 首先,我们准备小于给定数字 n 的完全平方数列表(即 square_nums)
- queue 保存所有剩余项在每个级别的枚举
- 每次迭代,检查余数是否是一个完全平方数,是完全平方的余数就找到了答案,如果余数不是一个完全平方数,就用其中一个完全平方数减去它,得到一个新余数,然后将新余数添加到 next_queue 中,以进行下一级的迭代
注意:在典型的 BFS 算法中,queue 通常是列表类型。这里使用 set 类型,以消除同一级别中的剩余项的冗余。
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
square_nums = [i * i for i in range(1, int(n ** 0.5) + 1)]
queue = {n}
step = 0
while queue:
step += 1
next_queue = set()
for remainder in queue:
for squ_num in square_nums:
if squ_num == remainder:
return step
elif squ_num > remainder:
break
else:
next_queue.add(remainder - squ_num)
queue = next_queue
return step
1.2 最短单词路径
127. 单词接龙(Medium)
算法中最重要的步骤是找出相邻的节点,也就是只差一个字母的两个单词。为了快速的找到这些相邻节点,我们对给定的 wordList 做一个预处理,将单词中的某个字母用 * 代替。

对于每个单词遍历查看是否只差一个字母将花费很多时间。这步预处理找出了单词表中所有单词改变某个字母后的通用状态,可以更快的找到相邻节点。
利用广度优先搜索搜索从 beginWord 到 endWord 的路径。
- 对给定的 wordList 做预处理,找出所有的通用状态。将通用状态记录在字典中,键是通用状态,值是对应的单词,例如 ‘*ot’: [‘hot’, ‘dot’, ‘lot’], ‘h*t’: [‘hot’], ‘ho*’: [‘hot’]
- 将包含 beginWord 和 1 的元组放入队列中,1 代表节点的层次
- 为了防止出现环,使用访问数组记录,beginWord : True 表示 beginWord 已经访问过了
- 当队列中有元素的时候,取出第一个元素,记为 current_word
- 找到 current_word 的所有通用状态,并找出这些通用状态的单词映射,直接在字典 all_comb_dict 中查询
- 从 all_combo_dict 获得的所有单词,和 current_word 都只差一个字母相连,如果就是目标单词直接返回 step + 1 即可,
- 如果不是目标单词,继续查找,前面没有访问过,向队列中加入元素 (word, step + 1) 其中 step 是 current_word 的层次,并将访问状态设为 True
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList or not beginWord or not endWord or not wordList:
return 0
word_len = len(beginWord)
all_comb_dict = defaultdict(list)
for word in wordList:
for i in range(word_len):
all_comb_dict[word[:i] + "*" + word[i+1:]].append(word)
queue = [(beginWord, 1)]
visited = {beginWord : True}
while queue:
cur_word, step = queue.pop(0)
for i in range(word_len):
intermediate_word = cur_word[:i] + "*" + cur_word[i+1:]
for word in all_comb_dict[intermediate_word]:
if word == endWord:
return step + 1
if word not in visited:
visited[word] = True
queue.append((word, step + 1))
all_comb_dict[intermediate_word] = []
return 0
1.3 K 站中转内最便宜的航班
bfs,广度优先搜索,先处理数据,以出发点为 key,到达站和价格为 value 构建字典,对处理好的数据进行 bfs。队列中保存的数据是站的位置,中转次数,从出发点到达此站的价格。
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n, flights, src, dst, K):
from collections import defaultdict, deque
flights_dict = defaultdict(list)
for flight in flights:
flights_dict[flight[0]].append((flight[1], flight[2]))
queue = deque()
queue.appendleft((src, 0, 0))
min_cost = float("inf")
while queue:
start, counter, cur_cost = queue.pop()
for end, price in flights_dict[start]:
if end == dst and counter <= K:
min_cost = min(min_cost, cur_cost + price)
if counter <= K and cur_cost + price <= min_cost:
queue.appendleft((end, counter+1, cur_cost + price))
return min_cost if min_cost != float("inf") else -1
1.4 课程表
207. 课程表(Medium)
如果一个节点没有入边,就是没有任何的先修课程要求。当我们将一个节点加入答案中后,我们就可以移除它的所有出边,代表着它的相邻节点少了一门先修课程的要求。如果某个相邻节点变成了「没有任何入边的节点」,那么就代表着这门课可以开始学习了。按照这样的流程,我们不断地将没有入边的节点加入答案,直到答案中包含所有的节点或者图中包含环。
我们使用一个队列来进行广度优先搜索。
- 初始时,所有入度为 0 的节点都被放入队列中
- 取出队首的节点 cur_course,移除 cur_course 的所有出边,也就是将 cur_course 的所有相邻节点的入度减少 1。如果某个相邻节点的入度变为 0,就放入队列中。
class Solution(object):
def canFinish(self, numCourses, prerequisites):
edges = collections.defaultdict(list)
enter_num = [0] * numCourses
for info in prerequisites:
edges[info[1]].append(info[0])
enter_num[info[0]] += 1
q = collections.deque([u for u in range(numCourses) if enter_num[u] == 0])
have_learn = 0
while q:
have_learn += 1
cur_course = q.popleft()
for next_course in edges[cur_course]:
enter_num[next_course] -= 1
if enter_num[next_course] == 0:
q.append(next_course)
return have_learn == numCourses
2、DFS
2.1 查找最大的连通面积
695. 岛屿的最大面积(Medium)
深度优先搜索,求网格中每个连通形状的面积,然后取最大值。
- 对于存在陆地的地方,向 4 个方向探索与之相连的每一个土地,经过的土地总数将是该连通形状的面积。
- 每经过一块土地时,将其置为 0,这样不会多次访问同一土地,同一连通区域只访问一次
class Solution:
def dfs(self, grid, cur_x, cur_y):
if cur_x < 0 or cur_y < 0 or cur_x >= len(grid) or cur_y >= len(grid[0]) or grid[cur_x][cur_y] == 0:
return 0
area = 1
grid[cur_x][cur_y] = 0
for next_x, next_y in [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]:
area += self.dfs(grid, cur_x + next_x, cur_y + next_y)
return area
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(grid) == 0 or len(grid[0]) == 0:
return 0
max_area = 0
row, col = len(grid), len(grid[0])
for x in range(row):
for y in range(col):
if grid[x][y] == 1:
max_area = max(max_area, self.dfs(grid, x, y))
return max_area
2.2 矩阵中的连通分量数目
200. 岛屿数量(Medium)
扫描整个二维网格。如果一个位置为 11,则以其为起始节点开始进行深度优先搜索。在深度优先搜索的过程中,每个搜索到的 1都会被重新标记为 0。最终岛屿的数量就是深度优先搜索的次数。
class Solution:
def dfs(self, grid, cur_x, cur_y):
if cur_x < 0 or cur_y < 0 or cur_x >= len(grid) or cur_y >= len(grid[0]) or grid[cur_x][cur_y] == '0':
return
grid[cur_x][cur_y] = '0'
for next_x, next_y in [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]:
self.dfs(grid, cur_x + next_x, cur_y + next_y)
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if len(grid) == 0 or len(grid[0]) == 0:
return 0
row, col = len(grid), len(grid[0])
num = 0
for x in range(row):
for y in range(col):
if grid[x][y] == '1':
self.dfs(grid, x, y)
num += 1
return num
2.3 朋友圈的数量
547. 朋友圈(Medium)
遍历每个人,如果没有访问过,以此人为节点进行深度优先搜索,将所有的直接,间接朋友找出,并做标记,表示已经访问过。搜索的次数就是朋友圈的个数。
class Solution:
def dfs(self, M, students, cur_pos):
if students[cur_pos] == 1:
return
students[cur_pos] = 1
for i in range(len(M)):
if M[cur_pos][i] == 1 and students[i] == 0:
self.dfs(M, students, i)
def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(M) == 0:
return 0
stu_num = len(M)
students = [0] * stu_num
fri_cir_num = 0
for i in range(stu_num):
if students[i] == 0:
self.dfs(M, students, i)
fri_cir_num += 1
return fri_cir_num
2.4 填充封闭的区域
130. 被围绕的区域(Medium)
本题要求将所有被字母 X 包围的字母 O都变为字母 X ,但很难判断哪些 O 是被包围的,哪些 O 不是被包围的。
我们从四边出发,寻找不被包围的 O,也就是从边界上的 O 为起点进行深度优先搜索,将其标记为字母 T。搜索完成后,剩下的 O 就是被包围的,将其改为 X,再将刚才搜索过程中改为 T 的改为 O 即可
class Solution:
def dfs(self, board, cur_x, cur_y):
if cur_x < 0 or cur_x >= len(board) or cur_y < 0 or cur_y >= len(board[0]) or board[cur_x][cur_y] != 'O':
return
board[cur_x][cur_y] = 'T'
for next_x, next_y in [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]:
self.dfs(board, cur_x + next_x, cur_y + next_y)
def solve(self, board):
if len(board) == 0 or len(board[0]) == 0:
return
row, col = len(board), len(board[0])
for x in range(row):
self.dfs(board, x, 0)
self.dfs(board, x, col-1)
for y in range(col):
self.dfs(board, 0, y)
self.dfs(board, row-1, y)
for x in range(row):
for y in range(col):
if board[x][y] == 'O':
board[x][y] = 'X'
elif board[x][y] == 'T':
board[x][y] = 'O'
2.5 能到达的太平洋和大西洋的区域
417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题(Medium)
我们从各边界开始逆流进行搜索。分别记录从太平洋和大西洋可以到达的地方,分别用二维数组记录下来,两个二组数中都记录的都可到达的地方就是结果
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.row = 0
self.col = 0
def valid_area(self, cur_x, cur_y):
return 0 <= cur_x < self.row and 0 <= cur_y < self.col
def dfs(self, matrix, visited, cur_x, cur_y):
visited[cur_x][cur_y] = 1
for next_x, next_y in [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]:
if self.valid_area(cur_x+next_x, cur_y+next_y) and visited[cur_x+next_x][cur_y + next_y] == 0 and matrix[cur_x+next_x][cur_y + next_y] >= matrix[cur_x][cur_y]:
self.dfs(matrix, visited, cur_x + next_x, cur_y + next_y)
def pacificAtlantic(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
if len(matrix) == 0 or len(matrix[0]) == 0:
return res
self.row = len(matrix)
self.col = len(matrix[0])
visit_pa = [[0 for _ in range(self.col)] for _ in range(self.row)]
visit_at = [[0 for _ in range(self.col)] for _ in range(self.row)]
for i in range(self.row):
self.dfs(matrix, visit_pa, i, 0)
self.dfs(matrix, visit_at, i, self.col-1)
for i in range(self.col):
self.dfs(matrix, visit_pa, 0, i)
self.dfs(matrix, visit_at, self.row-1, i)
for x in range(self.row):
for y in range(self.col):
if visit_pa[x][y] and visit_at[x][y]:
res.append([x, y])
return res
2.6 收集树上所有苹果的最少时间
1443. 收集树上所有苹果的最少时间(Medium)
哪些节点需要走呢,如果它自己有苹果,或者它的所有子树有苹果,我们就需要走这条路。
由于题目中并不一定按[parent, child]的顺序给edg(比如[[0, 2], [1, 2]]),我们用visited来去重。
对于每一个节点,最短时间为「它每个子树收集苹果的最短时间的和,加上到子树根节点的时间」。我们首先要走到那个节点,这要花费2秒的时间。
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def minTime(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], hasApple: List[bool]) -> int:
visited = [0 for _ in range(n)]
visited[0] = 1
adj_list = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in edges:
adj_list[u].append(v)
adj_list[v].append(u)
def dfs(root):
if root == None:
return 0
total = 0
for child in adj_list[root]:
if visited[child] == 1:
continue
visited[child] = 1
child_sum = dfs(child)
if hasApple[child] == True or child_sum != 0:
total += 2 + child_sum
return total
return dfs(0)
3 Backtracking
3.1 电话号码的字母组合
17. 电话号码的字母组合(Medium)
回溯是一种通过穷举所有可能情况来找到所有解的算法。如果一个候选解最后被发现并不是可行解,回溯算法会舍弃它,并在前面的一些步骤做出一些修改,并重新尝试找到可行解。
给出如下回溯函数 backtrack(combination, next_digits) ,它将一个目前已经产生的组合 combination 和接下来准备要输入的数字 next_digits 作为参数。
如果没有更多的数字需要被输入,那意味着当前的组合已经产生好了。
如果还有数字需要被输入,遍历下一个数字所对应的所有映射的字母,将当前的字母添加到组合最后,也就是 combination = combination + letter
class Solution:
def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]:
phone = {'2': ['a', 'b', 'c'],
'3': ['d', 'e', 'f'],
'4': ['g', 'h', 'i'],
'5': ['j', 'k', 'l'],
'6': ['m', 'n', 'o'],
'7': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's'],
'8': ['t', 'u', 'v'],
'9': ['w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
}
def backtrack(combination, next_digit):
if len(next_digit) == 0:
output.append(combination)
else:
for letter in phone[next_digit[0]]:
backtrack(combination + letter, next_digit[1:])
output = []
if digits:
backtrack('', digits)
return output
3.2 复原IP地址
93. 复原IP地址(Medium)
使用递归,对所有可能的字符串分隔方式进行搜索。
设题目中给出的字符串为 s。递归函数为 dfs(seg_id, seg_start) 表示从 s[seg_start] 位置开始,搜索 IP 地址中的第 seg_id 段,其中 s e g _ i d ∈ { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 } seg\_id \in \{0, 1, 2, 3\} seg_id∈{0,1,2,3} 。IP 地址的每一段必须是 [0, 255] 的整数,因此我们从 seg_start 开始,从小到大依次枚举当前这一段 IP 地址的结束位置 seg_end。如果满足要求,就递归地进行下一段搜索,调用递归函数 dfs(seg_id+1,seg_end+1)。
特别地,由于 IP 地址的每一段不能有前导零,因此如果 s[seg_start] 等于字符 ‘0’,那么 IP 地址的第 seg_id 段只能为 0
在递归搜索的过程中,如果我们已经得到了全部的 4 段 IP 地址,并且遍历完了整个字符串,那么就复原出了一种 IP 地址,我们将其加入答案。在其它的时刻,如果提前遍历完了整个字符串,就需要结束搜索,回溯到上一步。
class Solution:
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
SEG_COUNT = 4
ans = list()
segments = [0] * SEG_COUNT
def dfs(seg_id, seg_start):
# 如果找到了 4 段 IP 地址并且遍历完了字符串,就是一种答案
if seg_id == SEG_COUNT:
if seg_start == len(s):
ip_addr = '.'.join(str(seg) for seg in segments)
ans.append(ip_addr)
return
# 如果还没有找到 4 段 IP 地址就已经遍历完了字符串,那么提前回溯
if seg_start == len(s):
return
# 由于不能有前导零,如果当前数字为 0,那么这一段 IP 地址只能为 0
if s[seg_start] == '0':
segments[seg_id] = 0
dfs(seg_id + 1, seg_start + 1)
# 一般情况,枚举每一种可能性并递归
addr = 0
for seg_end in range(seg_start, len(s)):
addr = addr * 10 + (ord(s[seg_end]) - ord('0'))
if 0 < addr <= 255:
segments[seg_id] = addr
dfs(seg_id + 1, seg_end + 1)
else:
break
dfs(0, 0)
return ans