【python VS powershell对比学习】 python入门学习(基本数据类型)
参考课程: MOOC Python语言基础与应用 陈斌
算是对已有ps知识的查漏补缺,顺便深入学习python。
hello world
python:
pirnt(" hello world ")
powershell
“hello world”
一段随便的点餐代码
模板
python:
import random
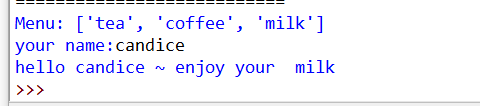
menu = ["tea","coffee","milk"]
print("Menu:", menu)
name = input("your name:")
drink = random.choice(menu)
print("hello", name,"~ enjoy your ", drink)
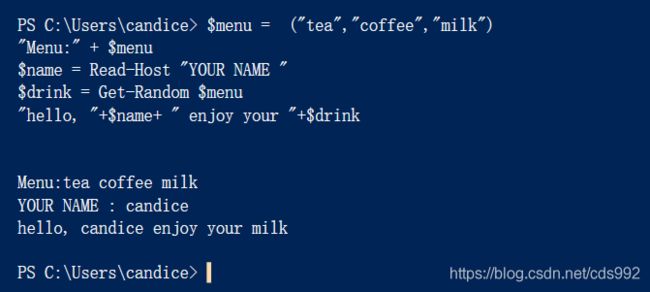
$menu = ("tea","coffee","milk")
"Menu:" + $menu
$name = Read-Host "YOUR NAME "
$drink = Get-Random $menu
"hello, "+$name+ " enjoy your "+$drink
关于日期的计算
用于判断某天处于这一年的第几天
python:
import datetime
dtstr = input("enter the datetime:")
dt = datetime.datetime.strptime(dtstr, "%Y%m%d")
a_dtstr = dtstr[:4] + '0101'
a_dt = datetime.datetime.strptime(a_dtstr, "%Y%m%d")
print(int((dt - a_dt).days) + 1)
$format = "yyyyMMdd"
$formatProvider = [Globalization.CultureInfo]::InvariantCulture
$dtstr = Read-Host "enter the datetime"
$dt = [datetime]::ParseExact($dtstr,$format,$formatProvider)
" #下面可以直接输出结果"
$dt.DayOfYear
$a_dtstr = $dtstr.Substring(0,4)+"0101"
$a_dt = [datetime]::ParseExact($a_dtstr,$format,$formatProvider)
" #两日期相减也可以得到计算结果"
($dt - $a_dt).Days +1

python与powershell的日期格式差距比较大
ps的时间转换(字串->datetime)有涉及c#
python的datetime计算略不友好,限制较多,感觉要回到解放前
字串处理
python:
import string
s = input('input a string')
letter = 0
space = 0
digit = 0
other = 0
for c in s:
if c.isalpha():
letter+=1
elif c.isspace():
space+=1
elif c.isdigit():
digit+=1
else:
other+=1
print('ther are %d letters, %d spaces, %d digits \
and %d other characters in your string.'\
%(letter,space,digit,other))
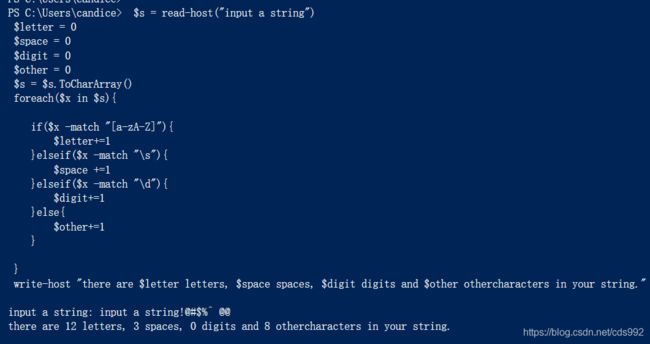
$s = read-host("input a string")
$letter = 0
$space = 0
$digit = 0
$other = 0
$s = $s.ToCharArray()
foreach($x in $s){
if($x -match "[a-zA-Z]"){
$letter+=1
}elseif($x -match "\s"){
$space +=1
}elseif($x -match "\d"){
$digit+=1
}else{
$other+=1
}
}
write-host "there are $letter letters, $space spaces, $digit digits and $other othercharacters in your string."
注意5.0的write-host可以用write-infomation 取代
算法- 归并排序
python:
import random #导入模块
def merge_sort(data_list):
if len(data_list) <=1:
return data_list
middle = int(len(data_list)/2)
left = merge_sort(data_list[:middle])
right = merge_sort(data_list[middle:])
merged = []
while left and right:
merged.append(left.pop(0) if left[0] <= right[0] else right.pop(0)) #pop用于移除一个元素
merged.extend(right if right else left)
return merged
data_list = [random.randint(1,100) for _ in range(50)]
print(merge_sort(data_list))
由于调用深度溢出,脚本失败。
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidOperation: (0:Int32) [],ParentContainsErrorRec
ordException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : CallDepthOverflow
数据类型
python:
#int
divmod(m,n) #返回两个数值,整数和小数
m **n
abs(m)
m == n
m > n
m >= n
m < n
m <= n
7 > 3 >= 3
367
0b1001000111
0o771
0x16f
#float 受到17位有效数字限制 进制转换有误差
#支持复数 ,只能比较是否相等
True, False #严格区分大小写
1 and 3 or 6
not True
a = "hello world"
>>> a[0]
'h'
>>> '''a
ddfdfdfd
dfdfdfd'''
'a\nddfdfdfd\ndfdfdfd'
#转义字符前面加反斜杠\
type(a) #查看数据类型
str = "hello world"
"hello "*5+" test "
"h" in "hello" #感觉有点像匹配的意思
str.strip
str.lstrip
str.rstrip
str.isalpha
str.isdigit
str.isalnum
powershell
$m / $n #只返回一个数
$m -eq $n
$m -gt $n
$m -ge $n
$m -lt $n
$m -le $n
7 -eq 3 -gt 2
(1tb+2gb+3mb+1kb)/1tb
367
#没有二进制表示
#没有8进制表示
0x16f
# 有效数字14位,第15位四舍五入
0.1234567890123
#不支持复数
$true, $false
1 -and 3 -or 6
-not 1 -eq 2
$a = "hello world"
$a[0]
#换行的文本可以写在文本中
"aaaa
aaaa
"
"a" -match "baseic"
$str = "14fffdfa335;455"
$str.Length
#判断类型可以直接用正则