【C++第二阶段】运算符重载-【+】【cout】【++|--】
你好你好!
以下内容仅为当前认识,可能有不足之处,欢迎讨论!
文章目录
- 运算符重载
-
- 加法运算符重载
- 重载左移运算符
- 递增|减运算符重载
运算符重载
加法运算符重载
What
普通的加减乘除,只能应付C++中已给定的数据类型的运算,对其重载,使得满足多种多样的运算。
对已有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型。
注意
①对于内置的数据类型表达式的运算符是不可能改变的。
②不要滥用运算符重载。
对于①,基本的运算符运算不改变,int+int = int , float + float = float.
对于②,重写相加,就写相加,名副其实。如果重写了加法运算符,里面却写➖或者×÷,代码可读性会变差。
代码
成员函数重载加法运算符
#include运行结果
可以看到,将两人的身高和体重在加法运算符重载之后进行了求和。
全局函数重载加法运算符
#include运行结果
重载左移运算符
场景:
想要cout直接输出类里面的各种属性,简单地使用``cout<
How
考虑到加法运算符的重载,使用成员函数重载左移运算符。
但此时,有两个问题:①函数返回值是什么数据类型?②如何调用?
回答问题①
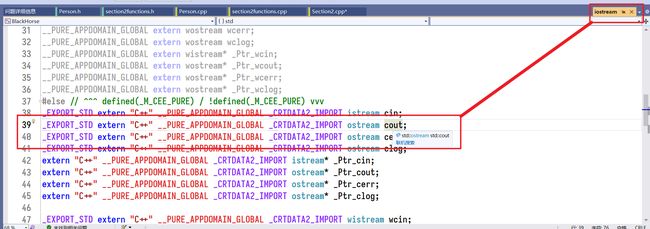
通过点击cout右键后,选择转到定义。
接着出现:
可以看到,cout属于的类是ostream输出流对象。
所以,如果想链式调用函数,可以将返回值设置为ostream。同时,只能用引用方式传递,因为全局只能有一个。
成员函数重载左移运算符:
#include运行结果为:
但是不想要person<person.operator<<(cout);这样的写作方式,而是要重载后的输出方式cout<
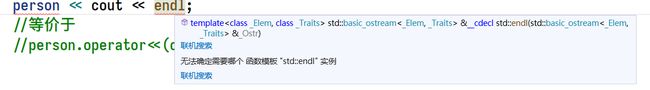
如果现在加上<
这个方式实际上是链式调用函数出错出现的问题,可以更改返回值为对应的ostream &引用来解决。
比如,以上代码中的成员函数改为:
class Person {
private :
int weight;
double height;
public:
Person(int weight, double height);
//返回值由void 改为ostream &
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout);
};
Person::Person(int weight, double height) {
this->weight = weight;
this->height = height;
}
//返回值由void 改为ostream
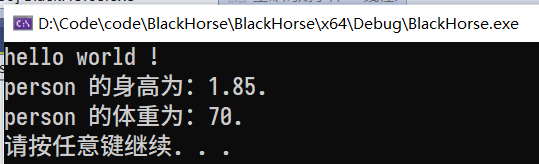
ostream& Person::operator<<(ostream &cout) {
cout << "person 的身高为:" << this->height << "." << endl;
cout << "person 的体重为:" << this->weight << "." << endl;
return cout;
}
void test_0208_1() {
int weight = 70;
double height = 1.85;
Person person(weight, height);
person << cout<<endl;//添加endl后不会报错
//等价于
//person.operator<<(cout);
}
运行结果为
但仍没有解决想要使用cout<
原因在于,如果用成员函数重载,则person只能出现在左侧,cout出现在右侧。所以,更换为使用全局函数。
全局函数重载左移运算符
#includeoperator<<(cout,person)运行结果:
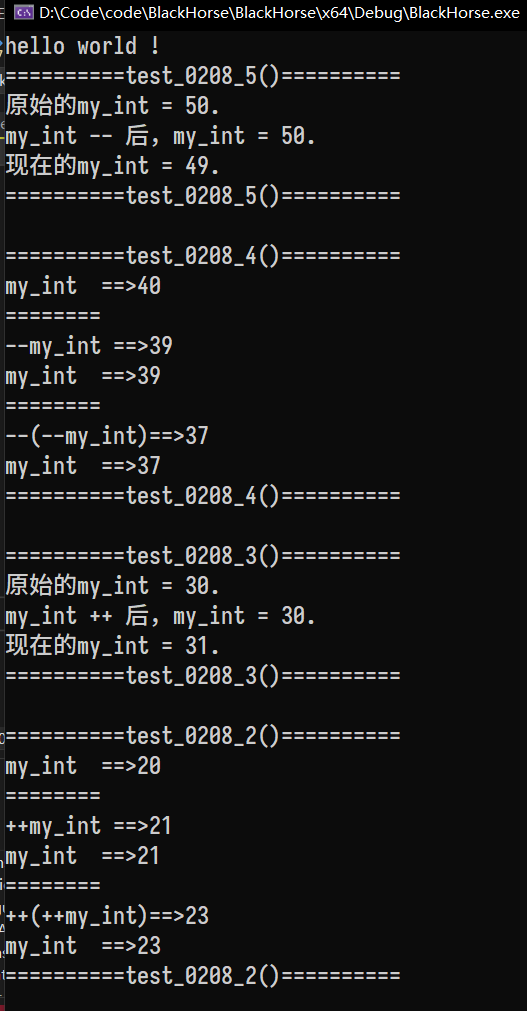
递增|减运算符重载
目的
想要达到一个自定义的整数类实现前置递增或后置递增的操作。
How
分为前置递增运算符和后置递增运算符。
对于前置递增运算符,返回值需要是MyInt类型的,因为cout已经重写,所以最好是这种类型。
返回值是指针,因为是对于当前的类进行的加减操作。
对于后置递增运算符,需要在参数中写入占位符,编译器明白这是后置运算符。
#include运行结果
以上是我的学习笔记,希望对你有所帮助!
如有不当之处欢迎指出!谢谢!
![]()