暑假集训第二周——递推 汉诺塔系列问题
/先说汉若塔I(经典汉若塔问题),有三塔,A塔从小到大从上至下放有N个盘子,现在要搬到目标C上,
规则小的必需放在大的上面,每次搬一个,求最小步数。这个问题简单,DP:a[n]=a[n-1]+1+a[n-1],先把
上面的n-1个放在B上,把最大的放在目标C上,再把N-1个放回到C上即可
Description
Gardon是个怕麻烦的人(恩,就是爱偷懒的人),很显然将64个圆盘逐一搬动直到所有的盘子都到达第三个柱子上很困难,所以Gardon决定作个小弊,他又找来了一根一模一样的柱子,通过这个柱子来更快的把所有的盘子移到第三个柱子上。下面的问题就是:当Gardon在一次游戏中使用了N个盘子时,他需要多少次移动才能把他们都移到第三个柱子上?很显然,在没有第四个柱子时,问题的解是2^N-1,但现在有了这个柱子的帮助,又该是多少呢?
Input
Output
Sample Input
1
3
12
Sample Output
1
5
81
动态规划,转移是
g[n]=min{g[n-k]+g[n-k]+f[k]}(1<=k<n)其中f[n]是三个柱子时候的汉诺塔
f[n]=f[n-1]+f[n-1]+1;----->f[n]=2^n-1;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { int n,i,k,f[65],m; f[1]=1,f[2]=3; for(i=3;i<=65;i++) { m=99999999; for(k=1;k<i;k++) if(2*f[k]+pow(2,i-k)-1<m) m=2*f[k]+(int)pow(2,i-k)-1; f[i]=m; } while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) printf("%d\n",f[n]); return 0; }
汉若塔III hdu2064
Description
现在我们改变游戏的玩法,不允许直接从最左(右)边移到最右(左)边(每次移动一定是移到中间杆或从中间移出),也不允许大盘放到下盘的上面。
Daisy已经做过原来的汉诺塔问题和汉诺塔II,但碰到这个问题时,她想了很久都不能解决,现在请你帮助她。现在有N个圆盘,她至少多少次移动才能把这些圆盘从最左边移到最右边?
Input
Output
Sample Input
1
3
12
Sample Output
2
26
531440
在经典汉若塔问题的条件改为,每次只能移动到附近塔上,求把A塔所有的移动C塔最小次数。
a[n]=a[n-1]+1+a[n-1]+1+a[n-1]:先把上面的N-1个移动到C(必然有这个状态),在把最大的移到B,再把N-1移到到A,把最大的移到C,再把N-1个移到C。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; unsigned long long a[65]; int main() { a[1]=2; for(int i=2;i<36;i++) { a[i]=3*a[i-1]+2; } int n; while(cin>>n) { cout<<a[n]<<endl; } return 0; }
汉若塔IV HDU 2077
Description
Input
每组数据有一个正整数n(1 <= n <= 20),表示有n个盘子。
Output
Sample Input
2 1 10
Sample Output
2 19684
分析:
A,B,C三个塔,方程:a[n]=ab[n-1]+1+1+bc[n-1]. (ab表示a到b)
DP思路:先把n-1个搬到b,再用俩步般最大的到C,再把n-1个从B到C。这里又要求出ac[n]和bc[n]:求其递推方程:bc[n]=bc[n-1]+1+ac[n-1],
会发现bc[]方程和ab[n]一样的。所以总方程a[n]=2*ab[n-1]+2.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; long long ac[23],bc[23],a[23]; int main() { ac[1]=a[1]=2,bc[1]=1,a[2]=4; int i,t,n; for(i=2;i<22;i++) { ac[i]=3*ac[i-1]+2; bc[i]=bc[i-1]+1+ac[i-1]; } for(i=3;i<22;i++) a[i]=2*bc[i-1]+2; cin>>t; while(t--) { cin>>n; cout<<a[n]<<endl; } return 0; }
Description
发生错移产生的系列就增加了,这种错误是放错了柱子,并不会把大盘放到小盘上,即各柱
子从下往上的大小仍保持如下关系 :
n=m+p+q
a1>a2>...>am
b1>b2>...>bp
c1>c2>...>cq
计算所有会产生的系列总数.
Input
目N<30.
Output
Sample Input
3 1 3 29
Sample Output
3 27 68630377364883
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int t,n,i; long long a[30]; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { a[0]=1; scanf("%d",&n); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=3*a[i-1]; printf("%lld\n",a[n]); } return 0; }
汉若塔VI HDU1995
在经典汉若塔问题上附加问题:求出N个盘子时,第K号盘子的移动次数。
思路,一想就是二维DP,DP[n][i]=dp[n-1][i]*2(1=<i<n),dp[n][n]=1;
最大盘只移动一次,上面盘子先移到B塔,一次,最后由B到目标C又一次,思路清晰,分分钟KO。
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; unsigned long long dp[62][62]; int main() { dp[1][1]=1;dp[2][1]=2;dp[2][2]=1; for(int i=3;i<61;i++) { for(int j=1;j<i;j++) { dp[i][j]=2*dp[i-1][j]; } dp[i][i]=1; } int t; int n,m; cin>>t; while(t--) { cin>>n>>m; cout<<dp[n][m]<<endl; } return 0; }
汉若塔VII HDU1996
在经典汉若塔问题上,求一共有多少个状态(包括所有可能移到到的状态),一个排列组合问题,
答案:求和( C(k1,n)*C(k2,n-k1))其中n>=k1>=0,n-k1>=K2>=0,从中挑出K1个从小到大放在A塔,再从剩下的
挑出K2个放在B塔,剩余的放在C塔即可。数据非大数。
其他巧妙方法:每个盘从小到大每个都有3种选择,共3^n。
#include<iostream> using namespace std; unsigned long long a[32]; long long C(int m,int n) //M>=N { if(m==0||n==0)return 1; int i; long long c=1,s=1; if(n>m-n) { n=m-n; } for(i=m;i>=m-n+1;i--) { c=c*i; } for(i=n;i>1;i--) { s*=i; } c=c/s; return c; } int main() { for(int i=1;i<30;i++) { for(int k1=0;k1<=i;k1++) { for(int k2=0;k2<=i-k1;k2++) { a[i]+=C(i,k1)*C(i-k1,k2); } } } int t; int n,m; cin>>t; while(t--) { cin>>n; cout<<a[n]<<endl; } return 0; }
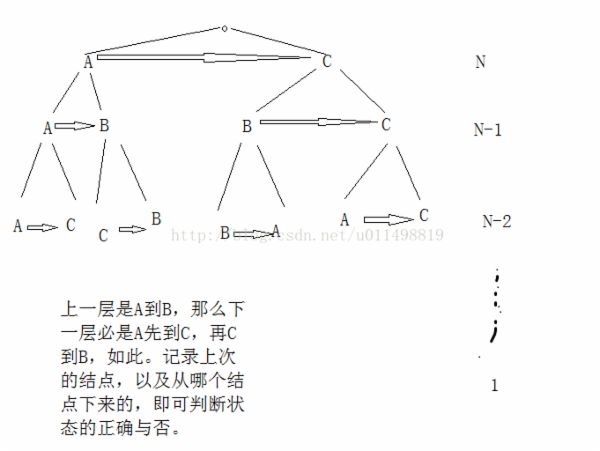
汉诺塔VII hdu1997 在经典汉若塔问题上,给出任意一个状态(移到过程中),判断该状态是否在正确的(最小移到情况)状态
中。
思路:做到这题,汉若塔就很清晰了,有几步、几个状态、状态的正确性、每个盘子的移到情况,都了如指掌。说说该题思路:
n号塔必然是A->C,那么N-1号塔, 若n在A,则n-1 在A或B,
见图:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; char get[68]; //保存I号盘子在哪个塔 bool over=0; bool tf=1; //是否结束,true_or_false是否为假 void dfs(char fl,char fr, char cur,int now) // dfs ,上面一层(now)左边和右边的塔,已经从哪个塔“下来的”(上面一层是哪个塔) { if(over)return; if(now==1){over=1;return;} //出口 int temp; if(fl=='A'&&fr=='B'||fl=='B'&&fr=='A')temp='C'; else if(fl=='A'&&fr=='C'||fl=='C'&&fr=='A')temp='B'; else temp='A'; now--; if(cur==fl) //若上一层是左边的塔 { if(get[now]==fr){over=1;tf=0;return;} //不可能是fr else { dfs(fl,temp,get[now],now); } } else if(cur==fr) { if(get[now]==fl){over=1;tf=0;return;} else { dfs(temp,fr,get[now],now); } } } int main() { int T; cin>>T; while(T--) { int n,m,p,q,tx; cin>>n; cin>>m; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { cin>>tx;get[tx]='A'; } cin>>p; for(int i=0;i<p;i++) { cin>>tx;get[tx]='B'; } cin>>q; for(int i=0;i<q;i++) { cin>>tx;get[tx]='C'; } tf=1; over=0; if(get[n]=='B') { cout<<"false"<<endl;continue; } dfs('A','C',get[n],n); if(tf==1)cout<<"true"<<endl; else cout<<"false"<<endl; } return 0; }