ORB-SLAM2地图加载
前一篇讲了地图保存,经测试是可以使用的,现在进行之前保存地图的读取模式,但是这个代码会有几个问题,后续还得慢慢解决。
首先在Map.h加入函数的定义,Map.cc中用到SystemSetting,Map.h中需要加入SystemSetting.h,也需要添加“class SystemSetting;”后面会涉及到。
void Load( const string &filename, SystemSetting* mySystemSetting );
MapPoint* LoadMapPoint( ifstream &f );
KeyFrame* LoadKeyFrame( ifstream &f, SystemSetting* mySystemSetting );下面是加载主函数Load的构成:
void Map::Load ( const string &filename, SystemSetting* mySystemSetting )
{
cerr << "Map reading from:"<//按照保存的顺序,先读取MapPoints的数目;
unsigned long int nMapPoints;
f.read((char*)&nMapPoints, sizeof(nMapPoints));
//依次读取每一个MapPoints,并将其加入到地图中
cerr<<"The number of MapPoints:"<for ( unsigned int i = 0; i < nMapPoints; i ++ )
{
MapPoint* mp = LoadMapPoint(f);
AddMapPoint(mp);
}
//获取所有的MapPoints;
std::vector//依次读取每一关键帧,并加入到地图;
vector//读取生长树;
map<unsigned long int, KeyFrame*> kf_by_id;
for ( auto kf: mspKeyFrames )
kf_by_id[kf->mnId] = kf;
cerr<<"Start Load The Parent!"<for( auto kf: kf_by_order )
{
//读取当前关键帧的父节点ID;
unsigned long int parent_id;
f.read((char*)&parent_id, sizeof(parent_id));
//给当前关键帧添加父节点关键帧;
if ( parent_id != ULONG_MAX )
kf->ChangeParent(kf_by_id[parent_id]);
//读取当前关键帧的关联关系;
//先读取当前关键帧的关联关键帧的数目;
unsigned long int nb_con;
f.read((char*)&nb_con, sizeof(nb_con));
//然后读取每一个关联关键帧的ID和weight,并把该关联关键帧加入关系图中;
for ( unsigned long int i = 0; i < nb_con; i ++ )
{
unsigned long int id;
int weight;
f.read((char*)&id, sizeof(id));
f.read((char*)&weight, sizeof(weight));
kf->AddConnection(kf_by_id[id],weight);
}
}
cerr<<"Parent Load OVER!"<for ( auto mp: vmp )
{
if(mp)
{
mp->ComputeDistinctiveDescriptors();
mp->UpdateNormalAndDepth();
}
}
f.close();
cerr<<"Load IS OVER!"<return;
} 其过程就是根据保存的顺序依次加载地图点的数目、地图点、关键帧的数目、关键帧、生长树和关联关系。
下面是LoadMapPoints函数的构成:
MapPoint* Map::LoadMapPoint( ifstream &f )
{
//主要包括MapPoints的位姿和ID;
cv::Mat Position(3,1,CV_32F);
long unsigned int id;
f.read((char*)&id, sizeof(id));
f.read((char*)&Position.at<float>(0), sizeof(float));
f.read((char*)&Position.at<float>(1), sizeof(float));
f.read((char*)&Position.at<float>(2), sizeof(float));
//初始化一个MapPoint,并设置其ID和Position;
MapPoint* mp = new MapPoint(Position, this );
mp->mnId = id;
mp->SetWorldPos( Position );
return mp;
}从这里开始涉及到了MapPoint类的初始化问题,由于这里只有Position以及当前的Map,所以需要从新定义MapPoint的构造函数,分别加入到MapPoint的头文件和源文件中,在MapPoint.h添加定义:
MapPoint( const cv::Mat& Pos, Map* pMap );在MapPoint.cc中
MapPoint::MapPoint(const cv::Mat &Pos, Map* pMap):
mnFirstKFid(0), mnFirstFrame(0), nObs(0), mnTrackReferenceForFrame(0), mnLastFrameSeen(0), mnBALocalForKF(0), mnFuseCandidateForKF(0), mnLoopPointForKF(0), mnCorrectedByKF(0),
mnCorrectedReference(0), mnBAGlobalForKF(0), mpRefKF(static_cast(NULL)), mnVisible(1), mnFound(1), mbBad(false),
mpReplaced(static_cast(NULL)), mfMinDistance(0), mfMaxDistance(0), mpMap(pMap)
{
Pos.copyTo(mWorldPos);
mNormalVector = cv::Mat::zeros(3,1,CV_32F);
// MapPoints can be created from Tracking and Local Mapping. This mutex avoid conflicts with id.
unique_lock lock(mpMap->mMutexPointCreation);
mnId=nNextId++;
} 紧接着是LoadKeyFrame函数的构成,这里由于KeyFrame类需要的初始化信息比较多,因此定义了一个InitKeyFrame类,它通过SystemSetting进行初始化,二SystemSetting的主要作用就是读取设置文件(相机内参,ORB特征参数等),后面将给出SystemSetting和InitKeyFrame类的代码:
KeyFrame* Map::LoadKeyFrame( ifstream &f, SystemSetting* mySystemSetting )
{
//声明一个初始化关键帧的类initkf;
InitKeyFrame initkf(*mySystemSetting);
//按照保存次序,依次读取关键帧的ID和时间戳;
f.read((char*)&initkf.nId, sizeof(initkf.nId));
f.read((char*)&initkf.TimeStamp, sizeof(double));
//读取关键帧位姿矩阵;
cv::Mat T = cv::Mat::zeros(4,4,CV_32F);
std::vector<float> Quat(4);
//Quat.reserve(4);
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
f.read((char*)&Quat[i],sizeof(float));
cv::Mat R = Converter::toCvMat( Quat );
for ( int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ )
f.read((char*)&T.at<float>(i,3),sizeof(float));
for ( int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ )
for ( int j = 0; j < 3; j ++ )
T.at<float>(i,j) = R.at<float>(i,j);
T.at<float>(3,3) = 1;
// for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
// {
// for ( int j = 0; j < 4; j ++ )
// {
// f.read((char*)&T.at(i,j), sizeof(float));
// cerr<<"T.at("<(i,j)<
// }
// }
//读取当前关键帧特征点的数目;
f.read((char*)&initkf.N, sizeof(initkf.N));
initkf.vKps.reserve(initkf.N);
initkf.Descriptors.create(initkf.N, 32, CV_8UC1);
vector<float>KeypointDepth;
std::vector(NULL));
//依次读取当前关键帧的特征点和描述符;
std::vector 从文件中读取的内容同保存的一致,同时由于是通过InitKeyFrame初始化的关键帧类KeyFrame,因此这里同样需要添加构造函数以及初始化方式:
在KeyFrame.h中添加对应的函数
KeyFrame(InitKeyFrame &initkf, Map* pMap, KeyFrameDatabase* pKFDB,vector< MapPoint*>& vpMapPoints);
在对应的KeyFrame.cc中添加函数对应的定义
KeyFrame::KeyFrame(InitKeyFrame &initkf, Map *pMap, KeyFrameDatabase *pKFDB, vector &vpMapPoints):
mnFrameId(0), mTimeStamp(initkf.TimeStamp), mnGridCols(FRAME_GRID_COLS), mnGridRows(FRAME_GRID_ROWS),
mfGridElementWidthInv(initkf.fGridElementWidthInv), mfGridElementHeightInv(initkf.fGridElementHeightInv),
mnTrackReferenceForFrame(0), mnFuseTargetForKF(0), mnBALocalForKF(0), mnBAFixedForKF(0),
mnLoopQuery(0), mnLoopWords(0), mnRelocQuery(0), mnRelocWords(0), mnBAGlobalForKF(0),
fx(initkf.fx), fy(initkf.fy), cx(initkf.cx), cy(initkf.cy), invfx(initkf.invfx),
invfy(initkf.invfy), mbf(initkf.bf), mb(initkf.b), mThDepth(initkf.ThDepth), N(initkf.N),
mvKeys(initkf.vKps), mvKeysUn(initkf.vKpsUn), mvuRight(initkf.vRight), mvDepth(initkf.vDepth),
mDescriptors(initkf.Descriptors.clone()), mBowVec(initkf.BowVec), mFeatVec(initkf.FeatVec),
mnScaleLevels(initkf.nScaleLevels), mfScaleFactor(initkf.fScaleFactor), mfLogScaleFactor(initkf.fLogScaleFactor),
mvScaleFactors(initkf.vScaleFactors), mvLevelSigma2(initkf.vLevelSigma2),mvInvLevelSigma2(initkf.vInvLevelSigma2),
mnMinX(initkf.nMinX), mnMinY(initkf.nMinY), mnMaxX(initkf.nMaxX), mnMaxY(initkf.nMaxY), mK(initkf.K),
mvpMapPoints(vpMapPoints), mpKeyFrameDB(pKFDB), mpORBvocabulary(initkf.pVocabulary),
mbFirstConnection(true), mpParent(NULL), mbNotErase(false), mbToBeErased(false), mbBad(false),
mHalfBaseline(initkf.b/2), mpMap(pMap)
{
mnId = nNextId ++;
} 加载了一个关键帧之后还需要计算其BoW向量等操作,同时指定关键帧对地图点的观测。
在MapPoint.h中添加函数定义
KeyFrame* SetReferenceKeyFrame(KeyFrame* RFKF);
在MapPoint.cc中添加
KeyFrame* MapPoint::SetReferenceKeyFrame(KeyFrame* RFKF)
{
return mpRefKF = RFKF;
} 补充SystemSetting和InitKeyFrame两个类的代码。实际上,由于是通过SystemSetting来读取的相机内参以及ORB特征参数,所以就可以将Tracking.cc中关于读取内参的部分替换掉了
创建新的头文件SystemSetting.h
#ifndef SYSTEMSETTING_H
#define SYSTEMSETTING_H
#include SystemSetting.cc的函数具体实现:
#include "Loading System Parameters form:"<"Camera.width"];
height = fSettings["Camera.height"];
fx = fSettings["Camera.fx"];
fy = fSettings["Camera.fy"];
cx = fSettings["Camera.cx"];
cy = fSettings["Camera.cy"];
cv::Mat tmpK = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F);
tmpK.at<float>(0,0) = fx;
tmpK.at<float>(1,1) = fy;
tmpK.at<float>(0,2) = cx;
tmpK.at<float>(1,2) = cy;
tmpK.copyTo(K);
cv::Mat tmpDistCoef(4,1,CV_32F);
tmpDistCoef.at<float>(0) = fSettings["Camera.k1"];
tmpDistCoef.at<float>(1) = fSettings["Camera.k2"];
tmpDistCoef.at<float>(2) = fSettings["Camera.p1"];
tmpDistCoef.at<float>(3) = fSettings["Camera.p2"];
const float k3 = fSettings["Camera.k3"];
if( k3!=0 )
{
tmpDistCoef.resize(5);
tmpDistCoef.at<float>(4) = k3;
}
tmpDistCoef.copyTo( DistCoef );
bf = fSettings["Camera.bf"];
fps= fSettings["Camera.fps"];
invfx = 1.0f/fx;
invfy = 1.0f/fy;
b = bf /fx;
initialized = true;
cout<<"- size:"<"x"<cout<<"- fx:" <cout << "- fy: " << fy << endl;
cout << "- cx: " << cx << endl;
cout << "- cy: " << cy << endl;
cout << "- k1: " << DistCoef.at<float>(0) << endl;
cout << "- k2: " << DistCoef.at<float>(1) << endl;
if(DistCoef.rows==5)
cout << "- k3: " << DistCoef.at<float>(4) << endl;
cout << "- p1: " << DistCoef.at<float>(2) << endl;
cout << "- p2: " << DistCoef.at<float>(3) << endl;
cout << "- bf: " << bf << endl;
//Load RGB parameter
nRGB = fSettings["Camera.RGB"];
//Load ORB feature parameters
nFeatures = fSettings["ORBextractor.nFeatures"];
fScaleFactor = fSettings["ORBextractor.scaleFactor"];
nLevels = fSettings["ORBextractor.nLevels"];
fIniThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.iniThFAST"];
fMinThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.minThFAST"];
cout << endl << "ORB Extractor Parameters: " << endl;
cout << "- Number of Features: " << nFeatures << endl;
cout << "- Scale Levels: " << nLevels << endl;
cout << "- Scale Factor: " << fScaleFactor << endl;
cout << "- Initial Fast Threshold: " << fIniThFAST << endl;
cout << "- Minimum Fast Threshold: " << fMinThFAST << endl;
//Load others parameters, if the sensor is MONOCULAR, the parameters is zero;
//ThDepth = fSettings["ThDepth"];
//DepthMapFactor = fSettings["DepthMapFactor"];
fSettings.release();
return true;
}
} 创建 InitKeyFrame.h,并在keyframe.h中加上InitKeyFrame头文件,还需要加上“class InitKeyFrame”.
#ifndef INITKEYFRAME_H
#define INITKEYFRAME_H
#include "Thirdparty/DBoW2/DBoW2/BowVector.h"
#include "Thirdparty/DBoW2/DBoW2/FeatureVector.h"
#include "SystemSetting.h"
#include InitKeyFrame.cc的函数实现
#include "InitKeyFrame.h"
#include 在System.h中添加函数定义:
void LoadMap(const string &filename,SystemSetting* mySystemSetting);
并在对应的System.cc中添加了定义
void System::LoadMap(const string &filename,SystemSetting* mySystemSetting)
{
mpMap->Load(filename, mySystemSetting);
} 还需要在System.h中添加声明
std::string mySettingsFile;
同时添加构造函数
mySettingsFile = strSettingsFile;
如果这样读进来好像没法做定位只能显示出地图,需要在Map.cc中Load函数读入每一个关键帧后添加到KeyFrameDatabase中去,但这样需要在Map.h中加入KeyFrameDatabase的头文件,这样就可以读入地图后进行relocalisation了。
会出现什么样的问题呢?如果在重新播放之前的场景,并不能进行重定位,同一个特征点可能会被认为是不同的点,即在空间中会产生两个点。导致地图错位!但是,本篇博客主要是记载如何进行mapName.bin的地图加载,其他工作还得完善。
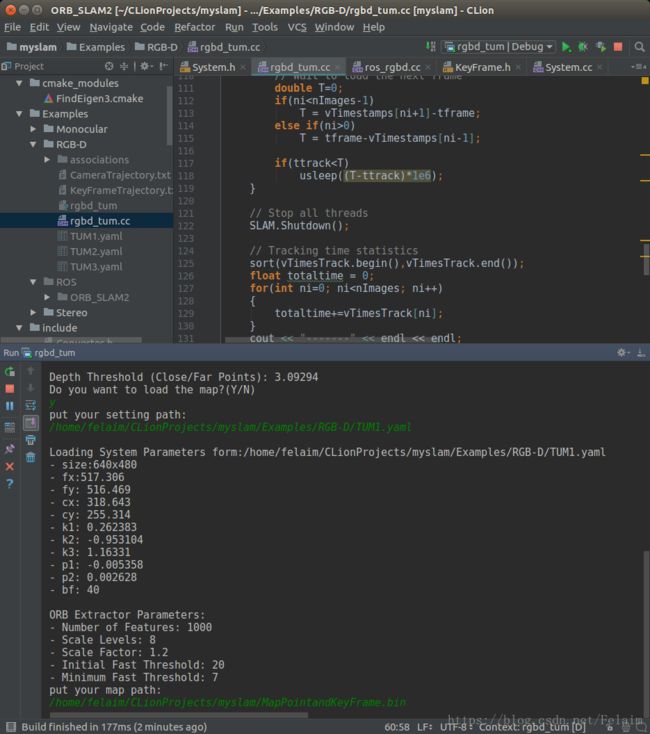
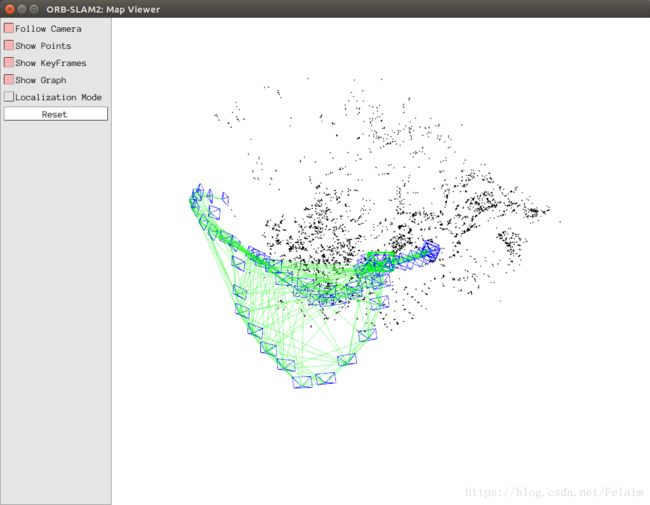
这是直接加载的之前一篇文章的地图:
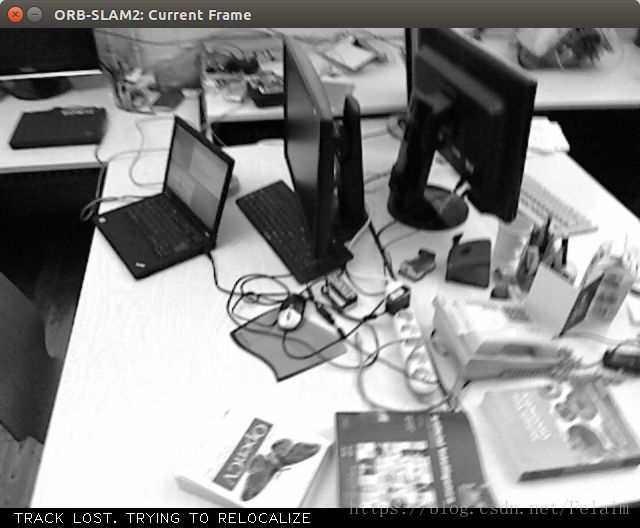
没有办法进行重定位,一直都是下图的状态:
参考博客地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/u012177641/article/details/78802315
http://www.cnblogs.com/mafuqiang/p/6972841.html