在网络项目开发过程中经常要用到用户登录,还有权限管理,Shiro可以说是Spring的一把利器。
看懂这一篇博客需要两个要求
- 懂得SpirngMVC的基本配置和使用
- 懂得Shiro的基本配置和使用
先看一下项目结构
这个项目可以作为pull下来在作为一般项目的脚手架
POM
4.0.0
com.jk.shiroLearning
chapter5
war
1.0-SNAPSHOT
chapter5 Maven Webapp
http://maven.apache.org
2.3.0
4.2.4.RELEASE
3.1.0
javax.servlet
jstl
1.2
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
${spring-version}
org.springframework
spring-context-support
${spring-version}
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
${servlet-api-version}
provided
commons-logging
commons-logging
1.1.3
commons-collections
commons-collections
3.2.1
org.apache.shiro
shiro-core
1.2.2
org.apache.shiro
shiro-web
1.2.2
org.apache.shiro
shiro-ehcache
1.2.2
org.apache.shiro
shiro-spring
1.2.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.25
com.alibaba
druid
0.2.23
chapter5
首先要配置Web.xml
contextConfigLocation
classpath:applicationContext.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
spring
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
spring
/
shiroFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
targetFilterLifecycle
true
shiroFilter
/*
然后配置spring-servlet.xml
然后配置applicationContext.xml
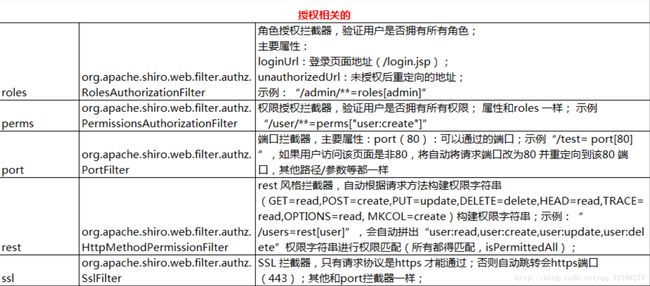
配置中重点讲解一下filterChainDefinitions,value对应的是url=权限或角色,具体如下
我们可以用一个filterChainDefinitionMap代替filterChainDefinitions
filterChainDefinitionMap
public class FilterChainDefinitionMapBuilder {
public LinkedHashMap buildFilterChainDefinitionMap(){
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap();
map.put("/login.jsp", "anon");
map.put("/shiro/login", "anon");
map.put("/shiro/logout", "logout");
map.put("/role1.jsp", "authc,roles[role1]");
map.put("/admin.jsp", "authc,roles[admin]");
map.put("/list.jsp", "user");
map.put("/**", "authc");
return map;
}
}
还有一点就是url的权限是先定义优先级越高,后定义的不会覆盖先定义的,可用/**匹配任何地址
然后再配置缓存
初始化数据库
drop database if exists shiro;
create database shiro;
use shiro;
create table users (
id bigint auto_increment,
username varchar(100),
password varchar(100),
password_salt varchar(100),
constraint pk_users primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_users_username on users(username);
create table user_roles(
id bigint auto_increment,
username varchar(100),
role_name varchar(100),
constraint pk_user_roles primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_user_roles on user_roles(username, role_name);
create table roles_permissions(
id bigint auto_increment,
role_name varchar(100),
permission varchar(100),
constraint pk_roles_permissions primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_roles_permissions on roles_permissions(role_name, permission);
insert into users(username, password, password_salt) values('jack', 'fc1709d0a95a6be30bc5926fdb7f22f4', 'jack');
insert into user_roles(username, role_name) values('jack', 'role1');
insert into user_roles(username, role_name) values('jack', 'role2');
insert into roles_permissions(role_name, permission) values('role1', 'user1:*');
insert into roles_permissions(role_name, permission) values('role1', 'user2:*');
insert into roles_permissions(role_name, permission) values('role2', 'user3:*');
再看Controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/shiro")
public class ShiroController {
@Autowired
private ShiroService shiroService;
@RequestMapping("/testShiroAnnotation")
public String testShiroAnnotation(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("key", "value12345");
try {
shiroService.testPermissionMethod();
shiroService.testRoleMethod();
}catch (UnauthorizedException e){
return "redirect:/unauthorized.jsp";
}
return "redirect:/list.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password){
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
// 把用户名和密码封装为 UsernamePasswordToken 对象
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
// 记住登录
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
// 执行登录.
currentUser.login(token);
}
// 所有认证时异常的父类.
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
System.out.println("登录失败: " + ae.getMessage());
}
}
return "redirect:/list.jsp";
}
}
可以留意到除了登录以外还有一个测试注解的方法,注解是一种比较优雅的限制执行方法权限的方法,看一下如何来使用注解
注解
public class ShiroService {
//只需满足其中一种角色就好
@RequiresRoles({"role1","admin"})
public void testRoleMethod(){
System.out.println("testMethod, time: " + new Date());
Session session = SecurityUtils.getSubject().getSession();
Object val = session.getAttribute("key");
System.out.println("Service SessionVal: " + val);
}
//只需满足其中一种权限就好
@RequiresPermissions({"user1:*","user4:*"})
public void testPermissionMethod(){
System.out.println("testMethod, time: " + new Date());
Session session = SecurityUtils.getSubject().getSession();
Object val = session.getAttribute("key");
System.out.println("Service SessionVal: " + val);
}
}
Shiro还为我们提供了SecurityUtils.getSubject().getSession()的方法来获取Session,这样就不用传requset到方法里。
Shiro还有我们提供了标签
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>
Insert title here
List Page
欢迎游客访问
已登录
已通过认证
未通过身份认证(包括记住我)
拥有角色admin
拥有角色admin或role1
不拥有角色admin
Welcome: • guest 标签:用户没有身份验证时显示相应信息,即游客访问信息:
•user 标签:用户已经经过认证/记住我登录后显示相应的信息。
• authenticated 标签:用户已经身份验证通过,即Subject.login登录成功,不是记住我登录的
• notAuthenticated 标签:用户未进行身份验证,即没有调用Subject.login进行登录,包括记住我自动登录的也属于未进行身份验证。
• pincipal 标签:显示用户身份信息,默认调用Subject.getPrincipal() 获取,即 Primary Principal。
• hasRole 标签:如果当前 Subject 有角色将显示 body 体内容:Shiro 标签
• hasAnyRoles 标签:如果当前Subject有任意一个角色(或的关系)将显示body体内容。
Shiro对一些角色和复杂的项目简直就是福音,对spring的支持也是十分友好,配置起来十分的简单