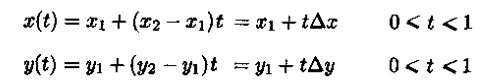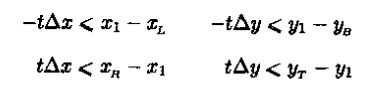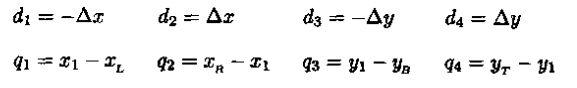图形学初步--裁剪算法之Liang-Barsky算法
一、概念
裁剪是CG中许多重要问题的基础,裁剪最典型的用途是确定场景中或画面中位于给定区域之内的部分。由于在一个典型的场景之中,需要对大量的点、线段进行裁剪,因此裁剪算法的效率十分重要。
关于裁剪有一些很常见的算法,比如说Cohen-Sutherland线段细分裁剪算法、中点分割算法、Cyrus-Beck算法、Liang-Barsky算法。这篇文章重点讲Liang-Barsky算法。剩下的那些算法有空再补。
二、Liang-Barsky算法
参考博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/keguniang/p/9688126.html
https://blog.csdn.net/pleasecallmewhy/article/details/8393445
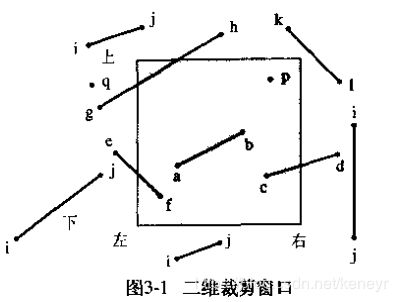
首先知道直线和裁剪框的位置关系,如下图:
可以看到直线可能完全在裁剪框的外面,也可能完全在裁剪框的里面,或者和裁剪框相交。
所以是裁剪的规则是这样的:
如果直线的两个端点都在窗口边界之内,如ab,则直线保留;
如果直线的一个端点在窗口边界之内,另一个端点在窗口边界之外,如ef,则应从直线与边界的交点处裁剪掉边界之外的线段;
如果直线的两个端点都在窗口边界之外,有两种情况:
一种情况如ij,直线全部在窗口之外,应该全部裁减掉;
另一种情况如gh,直线横穿窗口边界,应该保留相交的片段,裁减掉剩余的片段;那么怎么去判断呢? 在讲述判断步骤之前我们要了解一个基础理论,那就是编码:
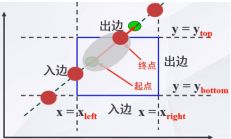
图中阴影部分是裁剪框,我们把这个区域分成了9份,采用了四位数标识线段的端点位于九个区域的哪个区域位置,从右往左数:
第一个位置为1-------如果线段端点位于窗口左侧
第二个位置为1------如果线段端点位于窗口右侧
第三个位置为1------如果线段端点为窗口下面
第四个位置为1------如果线段位于窗口上面------------------------------------------------------------------接下来是算法推导-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
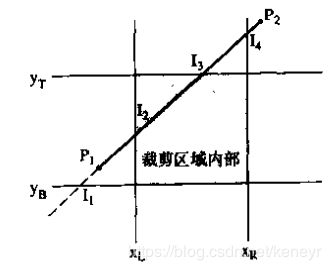
如下图所示
1.我们用方程表示直线P1P2,其中t就是直线的斜率,t∈[0,1]:
裁剪区域内部可以表达为两个不等式:
把直线方程代入得到不等式:
即
![]()
2.把直线看成是一条有方向的线段,把窗口的四条边及其延长线分成两类:入边和出边
入边:左边界和下边界------从裁剪框外向裁剪框内
出边:右边界和上边界------从裁剪框内向裁剪框外
3.分情况讨论
①d=0,q<0, 说明直线与裁剪框平行,并且位于裁剪框的外面,直线为不可见,可抛弃,直接结束
q>=0,说明直线在它所平行的窗口边界的内部,还需进一步计算确定直线是否在窗口内、外、或者相交
②d<0,说明直线是从裁剪边界的外部延伸到内部
③d>0, 说明直线是从裁剪边界的内部延伸到外部
对于d≠0,可以利用式子计算直线与边界k的交点的参数u。对于每条直线,可以计算直线位于裁剪窗口内线段的参数d1和d2
d1的值是由那些使得直线是从外部延伸到内部的窗口边界决定。对于这些边计算ri = qi/di.
d1 = max(ri,0)
d2的值是由那些使得直线是从内部延伸到窗口边界决定
d2 = min(ri,1)
如果d1>d2,这条直线完全在窗口的外面,不可见,可抛弃,否则,根据参数u的两个值,计算出裁剪后线段的端点
如果没有看懂,可以看该博主的https://blog.csdn.net/pleasecallmewhy/article/details/8393445
所以伪代码如下:
#Liang-Barsky two-dimensional clipping algorithm
#P1 and P2 are the line end points with components x1,y1,x2,y2
#tL and tU are the lower and upper parametric limits
#xL,xR,yB,yT are the left,right,bottom and top window edges
function clipt(d,q,tL,tU):
clipt performs trivial rejection tests and finds
the max of the lower set of parameter values and
the min of the upper set of parameter values
visible = true
if d=0 and q<0 then #line is outside and parallel to edge
visible = false
else if d < 0 then #looking for upper limit
t = q/d
if t>tU then #check for trivial invisible
visible = false
else if t>tL then #find the min of the max
tL = t
end if
else if d>0 then #look for the lower limit
t = q/d
if t0 then
x1 = x1+tL*deltax
y1 = y1+tL*deltay
end if
Draw P1,P2
end if
end if
end if
end if
finish 最终实现的代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
float xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax;
void myinit(void)
{
glShadeModel (GL_FLAT);
glClearColor (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
}
void myReshape(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
if (w <= h)
gluOrtho2D (0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0*(GLfloat)h/(GLfloat)w);
else
gluOrtho2D (0.0, 1.0*(GLfloat)w/(GLfloat)h, 0.0, 1.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
}
int Clip(float p,float q,float *tL,float *tU)
{
int flag=1;/*flag为标志变量0表示舍弃1表示可见*/
float r;
if (p<0.0)
{
r=q/p;
if (r>*tU)
flag=0;
else if (r>*tL) {
*tL = r;/*m取进入点最大参数值*/
}
}
else if (p>0.0) {
r=q/p;
if (r<*tL)
flag=0;
else if (r<*tU) {
*tU = r;/*n取离开点的最小值*/
}
}
else if (q<0 && p==0) //平行于边界而且在界外的线
flag=0;
return flag;
}
void myclip()
// line clipping algorithm
{
float dx, dy, x1,tL,tU, x2, y1, y2;
tL = 0, tU = 1.0;
printf("请输入线段的两个顶点坐标x1,y1,x2,y2:\n");
scanf("%f%f%f%f",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glColor4f (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glVertex2f(x1, y1); // line startpoint
glVertex2f(x2, y2); // line endpoint
glEnd();
dx=x2-x1;
if (Clip(-dx, x1 - xmin, &tL, &tU))
if (Clip(dx, xmax - x1, &tL, &tU)){
dy=y2-y1;
if (Clip(-dy, y1 - ymin, &tL, &tU))
if (Clip(dy, ymax - y1, &tL, &tU))
{
if (tU<1.0)
{
x2 = x1 + tU*dx;//通过n求得裁剪后的p2端点
y2 = y1 + tU*dy;
}
if (tL>0.0)
{
x1 = x1 + tL*dx;//通过m求得裁剪后的p1端点
y1 = y1 + tL*dy;
}
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glColor4f (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glVertex2f( x1, y1); // clipped line startpoint
glVertex2f( x2, y2); // clipped line endpoint
glEnd();
}
}
}
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
printf("请分别输入矩形的左右下上边界:\n");
scanf("%f%f%f%f",&xmin,&xmax,&ymin,&ymax);
glColor4f (1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.75);
glBegin(GL_POLYGON);
glVertex2f( xmin, ymin); // Bottom Left
glVertex2f( xmax, ymin); // Bottom Left
glVertex2f( xmax, ymax); // Bottom Right
glVertex2f( xmin, ymax); // Bottom Right
glEnd();
myclip();
glFlush();
}
/* Main Loop
* Open window with initial window size, title bar,
* RGBA display mode, and handle input events.
*/
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode (GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA);
//define size and the relative positon of the applicaiton window on the display
glutInitWindowSize (500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition (100, 100);
//init the defined window with "argv[1]" as topic showed on the top the window
glutCreateWindow (argv[0]);
// opengl setup
myinit ();
//define callbacks
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(myReshape);
//enter the loop for display
glutMainLoop();
return 1;
}
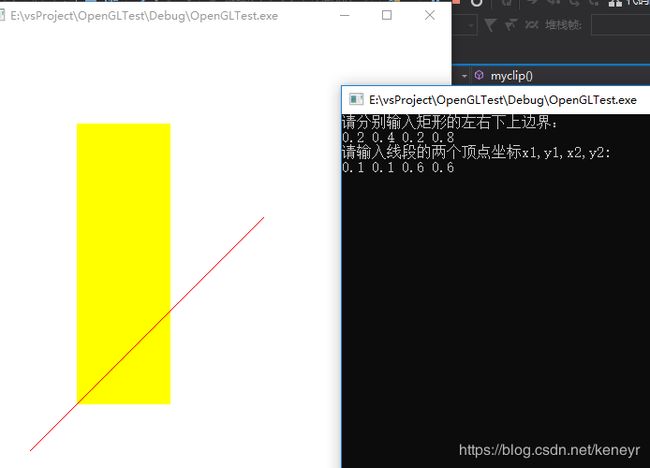
在运行该代码之前需要配置opengl环境,若没有配置,请参考该博客:https://blog.csdn.net/keneyr/article/details/83626935
代码运行结果如下: