- 基于ROS2/MoveIt!的工业机械臂控制系统开发全攻略
meslog
容器
1.系统架构设计1.1系统组成模块[VisionSystem]-->[PerceptionNode]||[GazeboSim][ROS2Control][MoveIt!Planner]||[HardwareInterface]-->[RealArm]1.2技术栈选型操作系统:Ubuntu22.04LTS;机器人框架:ROS2HumbleHawksbill;运动规划:MoveIt2+OMPL;仿真环
- vrep学习笔记_V-rep学习笔记:机器人路径规划1
weixin_39980575
vrep学习笔记
MotionPlanningLibraryV-REP从3.3.0开始,使用运动规划库OMPL作为插件,通过调用API的方式代替以前的方法进行运动规划(Theoldpath/motionplanningfunctionalityisstillfunctionalforbackwardcompatibilityandavailable,butitisrecommendednottouseitanymo
- 编译ROS1工程需要配置的环境
fttony2020
机器人算法linux开发环境笔记ROSubuntu
1.需要安装必要的依赖包$sudoaptinstall-yros-noetic-costmap-2d$sudoaptinstall-yros-noetic-ackermann-msgs$sudoaptinstall-yros-noetic-grid-map-ros$sudoaptinstall-yros-noetic-ompl$sudoapt-getinstalllibgsl-dev$sudoap
- Ubuntu18.04安装Moveit框架
dtge
ubuntulinux运维
简介Moveit是一个由一系列移动操作的功能包组成的集成化开发平台,提供友好的GUI,是目前ROS社区中使用度排名前三的功能包,Moveit包含以下三大核心功能,并集成了大量的优秀算法接口:运动学:KDL,Trac-IK,IKFast...路径规划:OMPL,CHMOP,SBPL..碰撞检测:FCL,PCD...一、更新功能包版本首先需要确保已安装的软件包为最新版本:rosdepupdatesud
- ROS Motion Planning运动规划库安装方法及进阶使用方法详细介绍
慕羽★
古月居专栏运动规划ROS运动规划库路径规划Navigation机器人自主导航C++/Python
今天偶然发现了一个优质的运动规划库:ai-winter/ros_motion_planning,比较适合从事ROS移动机器人运动规划研究领域的小伙伴学习和使用,相比于莱斯大学Kavraki实验室提供的开源的著名运动规划库OMPL、或着我之前介绍过的zhm-real开源的zhm-real/MotionPlanning和zhm-real/PathPlanning运动规划库,今天介绍的ROSMotion
- 编译volans遇到的问题
飞同学
ROSros
volans使用指导文件Couldnotfindapackageconfigurationfileprovidedby“OMPL”withanyofthefollowingnames:OMPLConfig.cmakeompl-config.cmakesudoaptinstallros-melodic-ompl*sudoaptinstalllibfcl-devlibompl-devcd/opt/ro
- 基于采样的路径规划算法RRT和代码实现
问凝
算法机器学习人工智能
文章目录前言一、概率路图法1.1采样阶段1.2搜索阶段1.3Lazycollision-checking二、快速扩展随机树2.1RRT算法流程2.2RRT算法改进2.3RRT*算法2.4KinodynamicRRT*算法2.4InformedRRT*算法三、RRT*算法代码3.1ompl库的要求3.2RRT*算法代码四、总结前言本文主要介绍快速扩展随机数算法RRT以及改进的RRT*算法,同时讲解在
- 基于ROS的OMPL库RRT*算法代码学习
陳林325
路径规划算法ROS算法c++
基于ROS的OMPL库RRT*算法代码学习过程演示ROS包主要程序文件demo_node.cpp参考引用本文是在学习路径规划算法中的一篇学习记录,由于对c++掌握粗浅,将整个代码进行了详细的梳理,由于代码中有很多是之前梳理过的《基于ROS的A*算法代码学习》中的,对本文graph_searcher.h注释可参考上一篇的Astar_searcher.h;node.h注释可参考上一篇的node.h;g
- 【OMPL.demo.1】二维点到点
HI_Forrest
学习笔记VREPmotionplanningc++动态规划
改写代码地址基于开学初用Windows下的vs2019的框架改了改,基本工程搭建过程见:vs2019+VREP基本工程框架借用vrep界面展示规划的路径,vrep主要是记录robot的轨迹,robot的位置由c++程序直接设置,vrep类的定义如下:vrep.h#pragmaonce#include"extApi.h"#include"simConst.h"#include"extApiPlatf
- Ubuntu20.04安装OMPL安装指南
Destinycjk
机器人pythonubuntu开发语言
Ubuntu20.04安装OMPL安装指南1安装说明2安装流程2.1安装文件下载2.2失败原因分析2.3安装文件修改3补充说明1安装说明项目需要想要在Ubuntu20.04安装OMPL运动规划库,官网链接安装十分简单,只需要下载安装文件运行即可。但是不知道什么原因,安装完成后缺少很多库,在Python中运行示例报错:ModuleNotFoundError:Nomodulenamed‘ompl.ba
- OOQP安装指南
野王不打野
C++OOQP安装C++库安装ubuntu
文章目录1.OOQP的github链接:2.准备工作:3.安装OOQP:4.简单使用:1.OOQP的github链接:ompl的官网网址为:https://github.com/emgertz/OOQP.git2.准备工作:OMPL有以下依赖项:blasma27或者ma571.首先创建一个文件夹my_lib(名字随意)。笔者的my_lib文件夹建在home里面,即与catkin_ws同级。2.进入
- 复现编译遇到问题(ubuntu16.04)
X uuuer.
复现ubuntulinux人工智能
1、OMPLConfig.cmakeompl-config.cmake解决方法:sudoapt-getinstallros-kinetic-ompl*2、quadrotor_msgsConfig.cmakequadrotor_msgs-config.cmake解决方法:(1)~/catkin_ws/src$gitclonegit://github.com/jchenbr/quadrotor_msg
- gazebo安装_【ROS 学习笔记】Gazebo
琦心
gazebo安装
0.简介官网镇楼:Gazebogazebosim.orgGazebo同我们常用的vrep,adams一样,都是内置物理引擎(PhysicsEngine)的动力学仿真软件,只不过ROS直接集成了Gazebo,像其他开源软件(OpenCV,OMPL)一样。Bytheway,vrep也是提供了ros接口的,不过我一般用内置的lua脚本、外部的python、甚至matlab来实现vrep仿真。先看下gaz
- MoveIt! 学习笔记10- Planning with Approximated Constraint Manifolds
HarwardWu
ROS学习历程MOVEIT
本博文转载自https://blog.csdn.net/ssw_1990/article/details/104048403;由于目前正处在学习阶段,对教程中提到的知识不是很确定含义,待以后用到的时候再添加补充。OMPL支持自定义约束,以支持遵循期望行为的规划轨迹。约束可以在关节空间和笛卡儿空间中定义,笛卡儿空间可以是基于方向的,也可以是基于位置的。在规划轨迹时,每个关节状态都需要遵循所有设置的约
- OMPL CMakeLists.txt (二)
ADHERENTS
ROS
install(FILES"${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h"DESTINATION"${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR}/ompl"COMPONENTompl)INSTALL指令安装的需要有两种,一种是从代码编译后直接makeinstall安装,一种是打包时的指定目录安装。这里需要引入一个非常有用的变量CMAKE_INSTALL_PREF
- V-rep学习笔记:机器人路径规划1
weixin_33757609
MotionPlanningLibraryV-REP从3.3.0开始,使用运动规划库OMPL作为插件,通过调用API的方式代替以前的方法进行运动规划(Theoldpath/motionplanningfunctionalityisstillfunctionalforbackwardcompatibilityandavailable,butitisrecommendednottouseitanymo
- 通过ROS控制真实世界的机械臂(4)---- MoveIt !
合工大机器人实验室
ROS学习笔记ROS实战C语言BeagleboneBlackROS机械臂
OMPL能做什么?简单说,就是提供一个运动轨迹。给定一个机器人结构(假设有N个关节),给定一个目标(比如终端移到xyz),给定一个环境,那么OMPL会提供给你一个轨迹,也就是一个完整的关节位置。沿着这个轨迹依次移动关节,就可以最终把终端移到xyz,当然,这个轨迹应当不与环境中的任何障碍发生碰撞。为什么用OMPL?运动规划的软件库和算法有很多,而OMPL由于其模块化的设计和稳定的更新,成为最流行的规
- Ompl base state space type:OMPL状态空间类型
FireFly_a
学习
namespaceompl{namespacebase{/**\briefThetypeofastatespace*/enumStateSpaceType{/**\briefUnsettype;thisisthedefaulttype*/STATE_SPACE_UNKNOWN=0,/**\briefompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace*/STATE_SPACE_REAL
- Ubuntu18.04-编译安装支持Python运动规划库OMPL
乐小树爱追逐雅克比
Ros
Ubuntu18.04-编译安装支持Python运动规划库OMPL简介开始安装1.坑1源码安装没有提及依赖项,安装文档相对简单,安装门槛较高。2.坑2ubutunapt管理源没有支持app和Pythonbinding第一步:去[官网下载源](https://ompl.kavrakilab.org/)码包:目前是1.4.2版本。第二步:去官网[拷贝安装脚本](https://ompl.kavraki
- 从零开始的OMPL库算法学习(1)RRT算法
皮卡丘的规划器
ompl
从零开始的OMPL库算法学习(1)RRT算法简介RRT算法(快速扩展随机树,rapidlyexploringrandomtree)是一种随机性算法,它可以直接应用于非完整约束系统的规划,不需进行路径转换,所以它的算法复杂度较小,尤为适用于高维多自由度的系统。缺点是得到的路径质量不是很好。其思想是快速扩张一群像树一样的路径以探索(填充)空间的大部分区域,伺机找到可行的路径。RRT的基本步骤是:1.起
- 从零开始的OMPL库算法学习(0)
皮卡丘的规划器
ompl
从零开始的OMPL库算法学习记录(0)写在开头毕设要做基于moveit的零件抓取,现在进度卡在解决place_pose_orientation的倾斜问题,所以开始学习moveit下的ompl库。希望能坚持下去,并分享给大家。本学习记录只关注算法原理,不关注程序实现。OMPLompl(TheOpenMotionPlanningLibrary)的全称是开源运动规划库,基于采样方法,包含了各种先进的路径
- 【机器人学:运动规划】OMPL开源运动规划库的安装和demo
gpeng832
【机器人学:运动规划】
开源运动规划库(OMPL)是美国莱斯大学的kavrakilab开发的,包含了当下主流的运动规划器。对于机器人方向的同学来说,无论是做移动机器人还是机械臂,这是必须要学习的工具。在ubuntu14.04环境下,安装OMPL是比较简单的。首先进入OMPL的官网http://ompl.kavrakilab.org/点击GettingStarted下的installOMPL,进入下边的页面点击“Downl
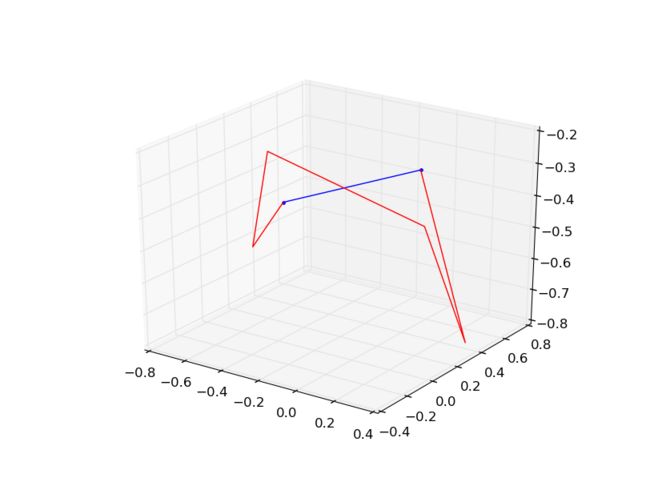
- OMPL学习笔记1
找不到工作的我
ompl
红色是ompl库中RRT搜索路径,蓝色是简化后的路径。RigidBodyPlanning.cpp#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include"boost/bind.hpp"usingnamespacestd;namespaceob=ompl::base;namespaceog=ompl::geome
- ompl示例阅读 car+dubins+reedshepp
BAleg
ompl
源码链接:http://ompl.kavrakilab.org/GeometricCarPlanning_8cpp_source.htmlOMPL入门文档:https://download.csdn.net/download/dan__ran/10797860OMPLwindows库_官方编译:https://download.csdn.net/download/dan__ran/10781563
- Could not find a package configuration file provided by "OMPL"...
weixin_45452470
编程错误集
Couldnotfindapackageconfigurationfileprovidedby“OMPL”withanyof…问题在github上下的hybridAstar的代码包,但是在编译时出现如下问题:CMakeErroratpath_planner-master/CMakeLists.txt:63(find_package):Bynotproviding“FindOMPL.cmake”in
- 基于Ubuntu 16.04和ros kinetc平台源码编译安装moveit和ompl及编译警告的解决方法
l1216766050
MoveIt
安装依赖项rosdepupdatesudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getdist-upgradesudoapt-getinstallpython-wstoolpython-catkin-toolsclang-format-3.9下载moveit的源码mkdir-p~/ws_moveit/srccd~/ws_moveitsource/opt/ros/kinetic/setup.ba
- 关于ROS中Moveit中运动规划的总结资料和相关问题
独坐寒江边
ROS
1、如果要在Moveit中配置自己的运动规划库,则需要自己用源码安装Moveit和OMPL,然后参照这个大神的资料按照步骤进行操作。或者说下载moveit代码都可以找到源码的,多项式插值之类的算法也都可以找到。要集成自己算法的话,可以参考moveit中已有的算法,也可以通过插件的形式集成,后期进行相应的尝试。2、运动规划的公开课可以参照夕法尼亚大学Coursera运动规划公开课。3、机械臂运动规划
- MoveIt!运动规划库OMPL和路径规划算法
合工大机器人实验室
ROS机械臂
运动规划(MotionPlanning):要让一个机器人实现运动规划,需要先将机器人抽象到构形空间(C-Space)。MoveIt就可以帮大家把这些工作给做了,只需提供机器人URDF模型,就可以调用几大运动规划库的规划算法(如OMPL,SBPL,CHMOP),自动生成机器人运动轨迹。之前跟着教程走的时候,很多内部结构不是很清晰,它就像是一个黑匣子,只管启动launch,就会返回机器人所需的运动路径
- 机器人路径规划 - 1
weixin_30595035
博客转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/21207-iHome/p/6049259.htmlMotionPlanningLibraryV-REP从3.3.0开始,使用运动规划库OMPL作为插件,通过调用API的方式代替以前的方法进行运动规划(Theoldpath/motionplanningfunctionalityisstillfunctionalforbackwardcompa
- ROS moveit 机械臂避障运动规划
tutu_321
机械臂moveit编程(python)moveit默认使用的运动规划库OMPL支持臂章规划,这里选用RRT算法,使用movegroup中的PlanningSceneInterface()添加障碍物,观察机械臂运动效果。程序流程:1.初始化需要控制的规划组,初始化场景;2.设置运动约束(可选);3.设置终端link;4.清理上一次运行的残留物体5.设置障碍物size和位姿,并使用scene.atta
- mondb入手
木zi_鸣
mongodb
windows 启动mongodb 编写bat文件,
mongod --dbpath D:\software\MongoDBDATA
mongod --help 查询各种配置
配置在mongob
打开批处理,即可启动,27017原生端口,shell操作监控端口 扩展28017,web端操作端口
启动配置文件配置,
数据更灵活
- 大型高并发高负载网站的系统架构
bijian1013
高并发负载均衡
扩展Web应用程序
一.概念
简单的来说,如果一个系统可扩展,那么你可以通过扩展来提供系统的性能。这代表着系统能够容纳更高的负载、更大的数据集,并且系统是可维护的。扩展和语言、某项具体的技术都是无关的。扩展可以分为两种:
1.
- DISPLAY变量和xhost(原创)
czmmiao
display
DISPLAY
在Linux/Unix类操作系统上, DISPLAY用来设置将图形显示到何处. 直接登陆图形界面或者登陆命令行界面后使用startx启动图形, DISPLAY环境变量将自动设置为:0:0, 此时可以打开终端, 输出图形程序的名称(比如xclock)来启动程序, 图形将显示在本地窗口上, 在终端上输入printenv查看当前环境变量, 输出结果中有如下内容:DISPLAY=:0.0
- 获取B/S客户端IP
周凡杨
java编程jspWeb浏览器
最近想写个B/S架构的聊天系统,因为以前做过C/S架构的QQ聊天系统,所以对于Socket通信编程只是一个巩固。对于C/S架构的聊天系统,由于存在客户端Java应用,所以直接在代码中获取客户端的IP,应用的方法为:
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
然而对于WEB
- 浅谈类和对象
朱辉辉33
编程
类是对一类事物的总称,对象是描述一个物体的特征,类是对象的抽象。简单来说,类是抽象的,不占用内存,对象是具体的,
占用存储空间。
类是由属性和方法构成的,基本格式是public class 类名{
//定义属性
private/public 数据类型 属性名;
//定义方法
publ
- android activity与viewpager+fragment的生命周期问题
肆无忌惮_
viewpager
有一个Activity里面是ViewPager,ViewPager里面放了两个Fragment。
第一次进入这个Activity。开启了服务,并在onResume方法中绑定服务后,对Service进行了一定的初始化,其中调用了Fragment中的一个属性。
super.onResume();
bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- base64Encode对图片进行编码
843977358
base64图片encoder
/**
* 对图片进行base64encoder编码
*
* @author mrZhang
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static String encodeImage(String path) {
BASE64Encoder encoder = null;
byte[] b = null;
I
- Request Header简介
aigo
servlet
当一个客户端(通常是浏览器)向Web服务器发送一个请求是,它要发送一个请求的命令行,一般是GET或POST命令,当发送POST命令时,它还必须向服务器发送一个叫“Content-Length”的请求头(Request Header) 用以指明请求数据的长度,除了Content-Length之外,它还可以向服务器发送其它一些Headers,如:
- HttpClient4.3 创建SSL协议的HttpClient对象
alleni123
httpclient爬虫ssl
public class HttpClientUtils
{
public static CloseableHttpClient createSSLClientDefault(CookieStore cookies){
SSLContext sslContext=null;
try
{
sslContext=new SSLContextBuilder().l
- java取反 -右移-左移-无符号右移的探讨
百合不是茶
位运算符 位移
取反:
在二进制中第一位,1表示符数,0表示正数
byte a = -1;
原码:10000001
反码:11111110
补码:11111111
//异或: 00000000
byte b = -2;
原码:10000010
反码:11111101
补码:11111110
//异或: 00000001
- java多线程join的作用与用法
bijian1013
java多线程
对于JAVA的join,JDK 是这样说的:join public final void join (long millis )throws InterruptedException Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die. A timeout of 0 means t
- Java发送http请求(get 与post方法请求)
bijian1013
javaspring
PostRequest.java
package com.bijian.study;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURL
- 【Struts2二】struts.xml中package下的action配置项默认值
bit1129
struts.xml
在第一部份,定义了struts.xml文件,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts
- 【Kafka十三】Kafka Simple Consumer
bit1129
simple
代码中关于Host和Port是割裂开的,这会导致单机环境下的伪分布式Kafka集群环境下,这个例子没法运行。
实际情况是需要将host和port绑定到一起,
package kafka.examples.lowlevel;
import kafka.api.FetchRequest;
import kafka.api.FetchRequestBuilder;
impo
- nodejs学习api
ronin47
nodejs api
NodeJS基础 什么是NodeJS
JS是脚本语言,脚本语言都需要一个解析器才能运行。对于写在HTML页面里的JS,浏览器充当了解析器的角色。而对于需要独立运行的JS,NodeJS就是一个解析器。
每一种解析器都是一个运行环境,不但允许JS定义各种数据结构,进行各种计算,还允许JS使用运行环境提供的内置对象和方法做一些事情。例如运行在浏览器中的JS的用途是操作DOM,浏览器就提供了docum
- java-64.寻找第N个丑数
bylijinnan
java
public class UglyNumber {
/**
* 64.查找第N个丑数
具体思路可参考 [url] http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/2541117420094245366965/[/url]
*
题目:我们把只包含因子
2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14
- 二维数组(矩阵)对角线输出
bylijinnan
二维数组
/**
二维数组 对角线输出 两个方向
例如对于数组:
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 },
slash方向输出:
1
5 2
9 6 3
13 10 7 4
14 11 8
15 12
16
backslash输出:
4
3
- [JWFD开源工作流设计]工作流跳跃模式开发关键点(今日更新)
comsci
工作流
既然是做开源软件的,我们的宗旨就是给大家分享设计和代码,那么现在我就用很简单扼要的语言来透露这个跳跃模式的设计原理
大家如果用过JWFD的ARC-自动运行控制器,或者看过代码,应该知道在ARC算法模块中有一个函数叫做SAN(),这个函数就是ARC的核心控制器,要实现跳跃模式,在SAN函数中一定要对LN链表数据结构进行操作,首先写一段代码,把
- redis常见使用
cuityang
redis常见使用
redis 通常被认为是一个数据结构服务器,主要是因为其有着丰富的数据结构 strings、map、 list、sets、 sorted sets
引入jar包 jedis-2.1.0.jar (本文下方提供下载)
package redistest;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class Listtest
- 配置多个redis
dalan_123
redis
配置多个redis客户端
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi=&quo
- attrib命令
dcj3sjt126com
attr
attrib指令用于修改文件的属性.文件的常见属性有:只读.存档.隐藏和系统.
只读属性是指文件只可以做读的操作.不能对文件进行写的操作.就是文件的写保护.
存档属性是用来标记文件改动的.即在上一次备份后文件有所改动.一些备份软件在备份的时候会只去备份带有存档属性的文件.
- Yii使用公共函数
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在网站项目中,没必要把公用的函数写成一个工具类,有时候面向过程其实更方便。 在入口文件index.php里添加 require_once('protected/function.php'); 即可对其引用,成为公用的函数集合。 function.php如下:
<?php /** * This is the shortcut to D
- linux 系统资源的查看(free、uname、uptime、netstat)
eksliang
netstatlinux unamelinux uptimelinux free
linux 系统资源的查看
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2167081
http://eksliang.iteye.com 一、free查看内存的使用情况
语法如下:
free [-b][-k][-m][-g] [-t]
参数含义
-b:直接输入free时,显示的单位是kb我们可以使用b(bytes),m
- JAVA的位操作符
greemranqq
位运算JAVA位移<<>>>
最近几种进制,加上各种位操作符,发现都比较模糊,不能完全掌握,这里就再熟悉熟悉。
1.按位操作符 :
按位操作符是用来操作基本数据类型中的单个bit,即二进制位,会对两个参数执行布尔代数运算,获得结果。
与(&)运算:
1&1 = 1, 1&0 = 0, 0&0 &
- Web前段学习网站
ihuning
Web
Web前段学习网站
菜鸟学习:http://www.w3cschool.cc/
JQuery中文网:http://www.jquerycn.cn/
内存溢出:http://outofmemory.cn/#csdn.blog
http://www.icoolxue.com/
http://www.jikexue
- 强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum
justjavac
r
原文:FluxBB Joins Forces With Flarum作者:Toby Zerner译文:强强联合:FluxBB 作者加盟 Flarum译者:justjavac
FluxBB 是一个快速、轻量级论坛软件,它的开发者是一名德国的 PHP 天才 Franz Liedke。FluxBB 的下一个版本(2.0)将被完全重写,并已经开发了一段时间。FluxBB 看起来非常有前途的,
- java统计在线人数(session存储信息的)
macroli
javaWeb
这篇日志是我写的第三次了 前两次都发布失败!郁闷极了!
由于在web开发中常常用到这一部分所以在此记录一下,呵呵,就到备忘录了!
我对于登录信息时使用session存储的,所以我这里是通过实现HttpSessionAttributeListener这个接口完成的。
1、实现接口类,在web.xml文件中配置监听类,从而可以使该类完成其工作。
public class Ses
- bootstrp carousel初体验 快速构建图片播放
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境bootstrap纵观千象
img{
border: 1px solid white;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 12px #333;
_width: expression(this.width > 600 ? "600px" : this.width + "px");
_height: expression(this.width &
- SparkSQL读取HBase数据,通过自定义外部数据源
superlxw1234
sparksparksqlsparksql读取hbasesparksql外部数据源
关键字:SparkSQL读取HBase、SparkSQL自定义外部数据源
前面文章介绍了SparSQL通过Hive操作HBase表。
SparkSQL从1.2开始支持自定义外部数据源(External DataSource),这样就可以通过API接口来实现自己的外部数据源。这里基于Spark1.4.0,简单介绍SparkSQL自定义外部数据源,访
- Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1发布
wiselyman
spring boot
Spring Boot 1.3.0.M1于6.12日发布,现在可以从Spring milestone repository下载。这个版本是基于Spring Framework 4.2.0.RC1,并在Spring Boot 1.2之上提供了大量的新特性improvements and new features。主要包含以下:
1.提供一个新的sprin