GAMES101-现代计算机图形学入门-闫令琪——Lecture 11 Geometry 2 (Curves and Surfaces) 学习笔记
Lecture 11 Geometry 2 (Curves and Surfaces)
(一)、Bézier Curves
1、Evaluating Bézier Curves (de Casteljau Algorithm)
以三点的贝塞尔曲线举例
①、Consider three points (quadratic Bezier)
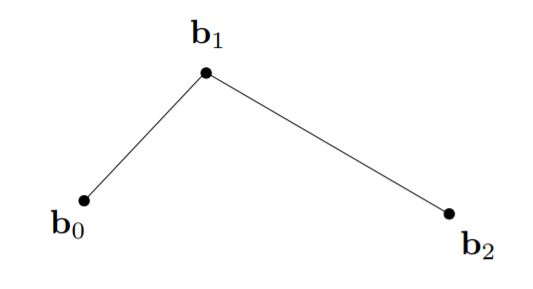
首先这条线一定要从b0开始,到b2结束。b1决定了整条线要向哪个方向弯曲。
②、Insert a point using linear interpolation

给定一个时间t,从0开始到1结束。
三个输入的点b0、b1、b2确定了两条线段b0b1、b1b2,在b0b1上认为b0是0,b1是1,那么在这个线段上,找一个点t。假设此时t=1/3,这个点记为b10。
③、Insert on both edges

同样的,在b1b2上,认为b1是0,b2是1,也找这样一个点t=1/3,这个点记为b11。
到此我们通过三个点b0、b1、b2得到了两个点b10、b11。
④、Repeat recursively

把刚刚得到的两个点b10、b11连起来,再认为这条线段又是从0到1,b10是0,b11是1,再取同样的t=1/3,这时我们找到了1个点b20,这个点即为由b0、b1、b2三点确定的一条贝塞尔曲线在时间t=1/3上的点。
⑤、Run the same algorithm for every t in [0,1]
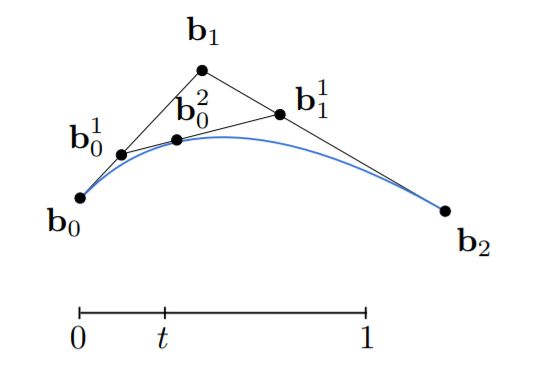
t的取值从0到1,每取一个值都重复上述步骤,然后得到了一系列点,将所有的点连起来就得到了一条贝塞尔曲线。
Four input points in total
Same recursive linear interpolations

四个点确定的一条贝塞尔曲线同理,只不过这次的操作需要先由4个点b0、b1、b2、b3组成的3条线段b0b1、b1b2、b2b3确定3个点b10、b11、b12,再由3个点b10、b11、b12确定的2条线段b10b11、b11b12确定2个点b20、b21,再由2个点b20、b21确定的1条线段b20b21确定一个点b30。
然后再对t取从0到1的所有值,重复上述步骤画出贝塞尔曲线。
2、Evaluating Bézier Curves Algebraic Formula
de Casteljau algorithm gives a pyramid of coefficients

Example: quadratic Bézier curve from three points
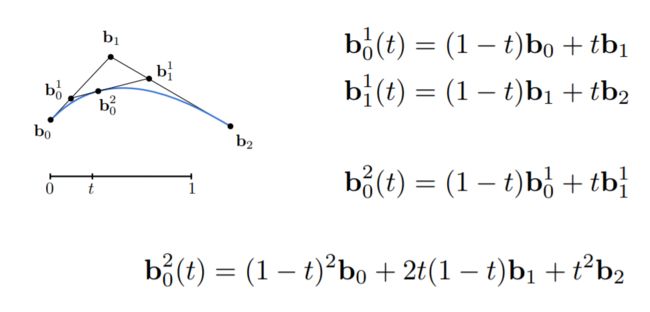
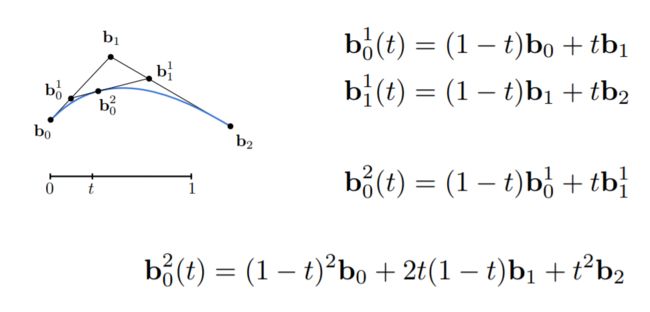
Bernstein form of a Bézier curve of order n:

(与二项展开式类似)
Example:
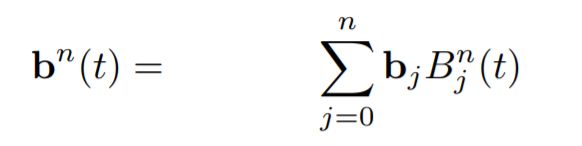
Example: assume n = 3 and we are in R3
i.e. we could have control points in 3D such as:
b0 = (0, 2, 3), b1 = (2, 3, 5), b2 = (6, 7, 9), b3 = (3, 4, 5)
These points define a Bezier curve in 3D that is a cubic polynomial in t:
bn(t) = b0(1-t)3+ b13t(1-t) 2+ b23t2(1-t)2 + b3t3
3、Properties of Bézier Curves
Interpolates endpoints
- For cubic Bézier:b(0) = b0; b(1) = b3
Tangent to end segments
- Cubic case: b‘ (0) = 3(b1-b0); b’ (1) = 3(b3 -b2)
Affine transformation property
- Transform curve by transforming control points
Convex hull property
- Curve is within convex hull of control points
4、BTW: What’s a Convex Hull
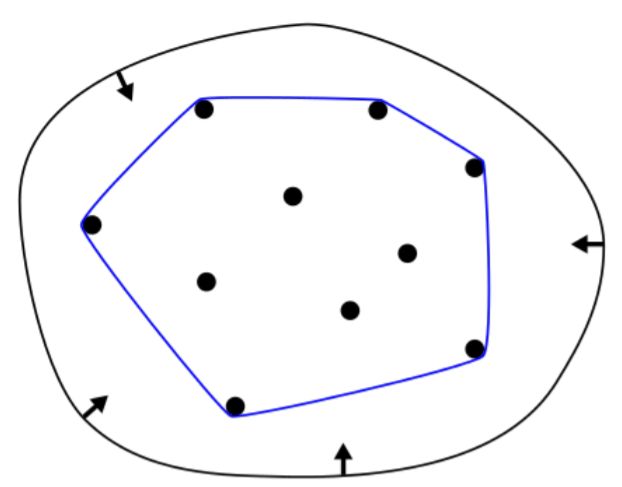
凸包:能够包围一系列给定的几何形体的最小的凸多边形
更直观来讲,如上图,在一个板子上打好多钉子,用一个橡皮筋拉大包住所有钉子后放手,让橡皮筋自然收缩,被卡在的一圈钉子组成的多边形即为凸包。
5、Piecewise Bézier Curves
Higher-Order Bézier Curves?

Very hard to control!
当控制点的数量过多,就可能导致某些地方弯曲不到我想要的程度,很难去控制局部。
Piecewise Bézier Curves
Instead, chain many low-order Bézier curve
Piecewise cubic Bézier the most common technique

将贝塞尔曲线每4个点做一次分段,其中1号和3号点是正常插入的位置点,而2号和4号则是被当做了“控制手柄”。
Piecewise Bézier Curve – Continuity
C0 continuity:an=b0
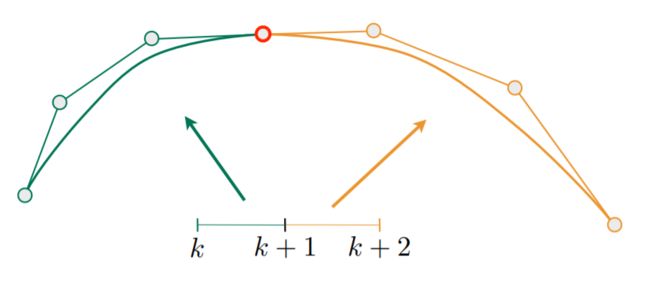
第一段的终点等于第二段的起点,这种点叫C0连续。
C1 continuity:an=b0=1/2(an-1+ b1)
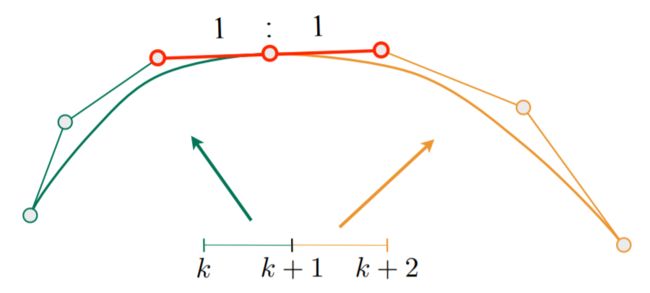
第一段的终点等于第二段的起点(公共点),且公共点相邻的左右两个控制点和这个公共点之间距离相等且三点共线(方向相反、等距、共线)。
6、Other types of splines
-
Spline
--a continuous curve constructed so as to pass through a given set of points and have a certain number of continuous derivatives.
--In short, a curve under control
-
B-splines
--Short for basis splines
--Require more information than Bezier curves
--Satisfy all important properties that Bézier curves have (i.e. superset)
(二)、Bézier Surfaces
Extend Bézier curves to surfaces
Bicubic Bézier Surface Patch
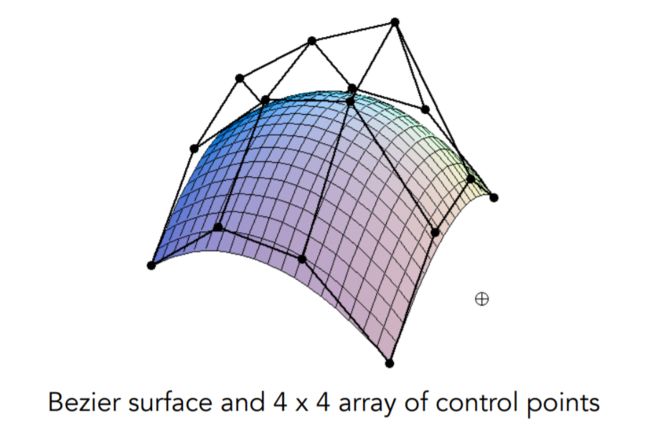
Visualizing Bicubic Bézier Surface Patch

在两个方向上分别运用贝塞尔曲线。
首先在一个方向上做贝塞尔曲线,然后把得到的点作为控制点,再做一次贝塞尔曲线即可。
Evaluating Bézier Surfaces
Evaluating Surface Position For Parameters (u,v)
For bi-cubic Bezier surface patch,
Input: 4x4 control points
Output is 2D surface parameterized by (u,v) in [0,1]2
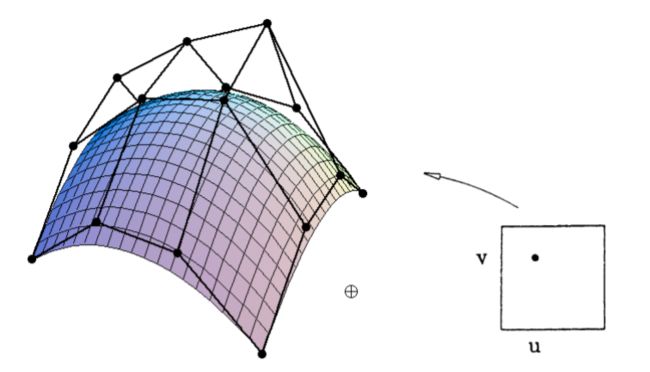
Method: Separable 1D de Casteljau Algorithm
Goal: Evaluate surface position corresponding to (u,v)
(u,v)-separable application of de Casteljau algorithm
- Use de Casteljau to evaluate point u on each of the 4 Bezier curves in u. This gives 4 control points for the “moving” Bezier curve
- Use 1D de Casteljau to evaluate point v on the “moving” curve

可以通过一个u方向和一个v方向做一个映射关系。
Method: Separable 1D de Casteljau Algorithm
