【文献阅读】【NMI 2022】LocalTransform :基于广义模板的有机反应性准确预测图神经网络
预测有机反应产物是有机化学的一个基本问题。基于成熟有机化学知识,化学家现在能够设计实验来制造用于不同目的的新分子。但是,它需要经验丰富的专业化学家来准确预测化学反应的结果。为了进一步帮助有机化学家并在数字化学时代实现全自动发现,机器智能可以准确预测有机反应的产物,大大加快新分子的设计过程。最近,已经提出了几种基于机器学习的方法来预测有机反应产物,但仍然需要改进反应预测模型才能达到足够的准确性,与普通有机化学家相当或更好。由于几种基于模板的方法的覆盖范围和可扩展性问题,科学家们提出了使用基于序列的模型或基于图模型的无模板方法。尽管这些方法在公共反应数据集上表现出有希望的准确性,但当前最先进的方法仍然以机械方式预测有机反应的产物,要么翻译化学语言,要么按顺序编辑分子图。相比之下,知识渊博的化学家通常通过识别反应中心并应用所学化学知识来预测有机反应性来和预测反应产物(In contrast, it is common practice for knowledgeable chemists to predict the reaction products by identifying the reaction centre and applying learnt chemistry knowledge such as named reactions to predict the organic reactivity.)。
研究人员设计了广义反应模板(GRT, generalized reaction template),一种仅描述基于原子映射的反应前后原子构型的局部变化但没有特定原子类型或官能团信息的反应模板,并提出了一个基于图机器智能的LocalTransform框架来预测反应产物。LocalTransform 通过识别反应中心以及要应用的 GRT 来预测反应产物。它通过全局注意力机制学习根据局部化学环境和选择性识别反应原子。最终反应转化由反应模板分类器预测,该分类器为预测的化学反应中心建议最可能的 GRT。
LocalTransform 在预测有机反应方面的三个重要突破:
-
GRT 在化学上是直观的和通用的。当前100 个最流行的反应模板可以描述所有训练反应的 94.6%,我们的 GRT 可以描述所有测试反应的 99.7%,从而解决了以前基于模板的方法的覆盖率和可扩展性问题。
-
证明了 LocalTransform top-k 产物预测精度,与以前的基于图的方法相比有显著改进。
-
由于模型是一种基于分类的方法,具有很强的分数-准确性相关性,它使用户能够理解不确定性并信任机器预测。(Since our model is a classification-based method with strong score–accuracy correlation, it enables the user to understand the uncertainty and trust the machine predictions. 什么意思?)
所用数据集:
USPTO: 410,000 reactions in the training set, 30,000 reactions in the validation set and 40,000 reactions in the test set.
All the reactions in the USPTO-480k dataset are atom mapped, which indicates the atom position before and after the reaction. With annotated atom mapping, we are able to track
the transformation of the atoms participating in the reaction and derive the GRTs.
USPTO是一个监督数据集,包含了反应前后的原子位置。
通过学习这种反应前后的原子位置的变化,我们能够学习到化学反应前后的原子转换规则从而推导出GRTs。
方法:
each GRT comprises a unique combination of four types of actions (ATTACK, BREAK, CHANGE or REMOTE),
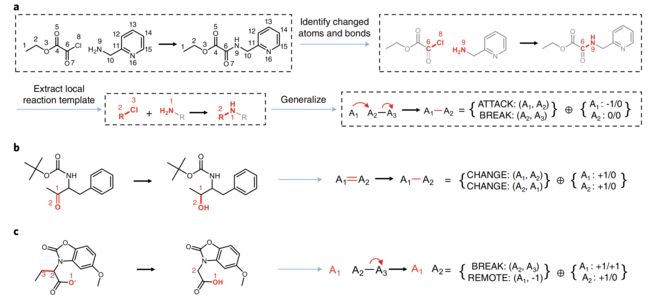
Fig1,提取过程和GRT的例子。
a、识别原子和键的改变:首先通过比较反应前后各原子电子构型(electron configuration)的变化来识别反应中心(reaction centre)。
提取局部反应模板:接下来通过关注反应中心的原子并为其分配新的编号来导出局部反应模板 。
生成:然后,我们通过移除原子类型信息(removing the atom type information)并将其描述为四个动作actions( ATTACK, BREAK, CHANGE,REMOTE)和反应中心氢/电荷变化的附加信息(changes in hydrogen/charges at the reaction centre)的组合来概括局部反应模板,从而完成 GRT 的推导。
这里显示的例子是取代反应(substitution reaction),其中酰基上的氯被伯胺取代,反应后形成仲酰胺。攻击动作(ATTACK)被标记为从伯胺到亲电碳(从 A 1 到 A 2 )。 BREAK 动作被标记为从受攻击的碳到离开的氯(从 A 2 到 A 3 )。
b,羰基还原反应(reduction reaction),其中酮基团转化为仲醇基团。 CHANGE 动作在酮的碳原子和氧原子之间(A 1 和 A 2 之间)进行双向标记。
c,负电荷引发的原子A1 还原反应(reduction reaction)。 BREAK 操作从剩余碳到离开碳(从 A2 到 A3 )进行标记,REMOTE 操作从原子 A1 进行标记其中负电荷在反应后转移到其相邻原子(在动作中用虚拟标记 -1 标记,并且 A 1 的电荷变化为 +1)。
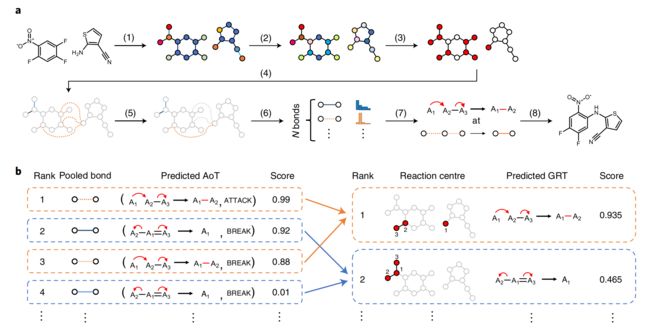
Fig. 2 | The overall prediction pipeline of LocalTransform. a, The model architecture of LocalTransform.
(1) molecular graph building:The reactants are transformed into molecular graphs by using the python package DGL-Life22. The atoms and nodes of reactants are represented by the nodes and edges in the graphs. Atom and bond features such as atom symbols and bond types are encoded in the graphs.
(2) local message passing:The features of atoms are updated by their local chemical environment
through an MPNN23.
(3) global atom attention:Atoms seek possible interactions with all the other atoms in the reactants through a distance-aware atom-wise global attention.
(4) bond feature constriction and reactive pooling:Bond features in the reactants are encoded by concatenating the atom features. Next, bonds having the top-N highest reactivity are pooled for the next stage of computation, where N is set to be the number of atoms in the reactants.
(5) global bond attention:Bonds are further sent to a bond-wise global attention to rank the reactivity of each potential reactive bonds and relate the bond relations before the final prediction of AoTs.
(6) AoT classification:Each pooled bond is classified into a probability distribution of AoTs derived from the training set by multi-class classifiers.
(7) AoT ranking and collection:The predicted AoTs are ranked by their prediction scores and collected to identify the reaction centre for the predicted GRT.
(8) product completion:Finally, we apply the predicted GRT on the predicted reaction centres to obtain the final products.
b, A more detailed scheme of step 7, that is, collecting the predicted bonds and AoTs to complete the reaction centres and GRTs. The predicted
bonds and AoTs are ranked by their predicted scores and collected on by one until the required actions of the predicted GRT are fulfilled. The reaction
centre of the predicted GRT is identified automatically by looking up the predicted bonds of the collected AoTs.
a、LocalTransform的模型架构。 (1) 使用python包DGL-Life 22 将反应物转化为分子图。反应物的原子和节点由图中的节点和边表示。原子和键特征(例如原子符号和键类型)在图中进行编码。 (2) 原子的特征通过 MPNN 23 根据其局部化学环境进行更新。 (3) 原子通过距离感知的原子全局注意力来寻求与反应物中所有其他原子可能的相互作用。 (4) 反应物中的键特征通过连接原子特征来编码。接下来,汇集具有前 N 个最高反应性的键以用于下一阶段的计算,其中 N 被设置为反应物中的原子数。 (5) 在最终预测 AoT 之前,键被进一步发送到键级全局注意力,对每个潜在反应键的反应性进行排名并关联键关系。 (6) 每个池化债券被多类分类器分类为从训练集导出的 AoT 概率分布。 (7) 预测的 AoT 按预测分数排序并收集,以确定预测的 GRT 的反应中心。 (8) 最后,我们将预测的 GRT 应用于预测的反应中心以获得最终产品。 b,步骤7的更详细方案,即收集预测的键和AoT以完成反应中心和GRT。预测的债券和 AoT 按其预测分数进行排名,并按 1 进行收集,直到满足预测的 GRT 所需的操作为止。通过查找收集的 AoT 的预测键,自动识别预测 GRT 的反应中心。
LocalTransform 预测反应的流程包含7步:
(1) molecular graph building
(2) local message passing
(3) global atom attention
(4) bond feature constriction and reactive pooling
(5) global bond attention
(6) AoT classification
(7) AoT ranking and collection
(8) product completion
Nature子刊:机器学习助力化学家精准预测有机反应结果
Nat. Mach. Intel. | 基于广义模板的图形神经网络用于准确的有机反应性预测