视觉slam14讲学习(四)之Ceres和G2O使用
1. 曲线拟合问题
所谓曲线拟合,就是给定一组x和y的值,它们大体上满足一条曲线方程,但受噪声影响,并不精确满足方程。在这种情况下求取曲线方程的参数。例如,给定100对x和y的值,把它们画在坐标系上如图所示:

预测模型也就是该曲线方程的形式为:
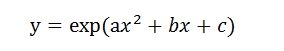
那么就可以构造一个最小二乘问题以估计其中的未知参数a、b和c。该最小二乘问题的代价函数为:

2. 利用Eigen求解
直接利用Eigen构建增量方程,再利用高斯-牛顿迭代法优化求解.
代码如下:
//author:jiangcheng
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值
double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0; // 估计参数值
int N = 100; // 数据点
double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值
cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器
vector x_data, y_data; // 数据
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = i / 100.0;
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + rng.gaussian(w_sigma));
}
// 开始Gauss-Newton迭代
int iterations = 100; // 迭代次数
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; // 本次迭代的cost和上一次迭代的cost
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
Matrix3d H = Matrix3d::Zero(); // Hessian = J^T J in Gauss-Newton
Vector3d b = Vector3d::Zero(); // bias
cost = 0;
//-----------------用GN构建增量方程,HX=g---------------------------------//
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double xi = x_data[i], yi = y_data[i]; // 第i个数据点
// start your code here
// double error = 0; // 填写计算error的表达式
double error = yi-exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // 第i个数据点的计算误差
Vector3d J; // 雅可比矩阵,3x1
J[0] = -xi*xi*exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/da,函数求倒数,-df/da
J[1] = -xi*exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce);; // de/db
J[2] = -exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce);; // de/dc
H += J * J.transpose(); // GN近似的H
b += -error * J;
// end your code here
cost += error * error;
}
// 求解线性方程 Hx=b,建议用ldlt
// start your code here
Vector3d dx;
//LDL^T Cholesky求解
// clock_t time_stt2 = clock();
dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);//Hx=b,,,H.ldlt().solve(b)
// cout<<"LDL^T分解,耗时:\n"<<(clock()-time_stt2)/(double)
// CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"ms"< 0 && cost > lastCost) {
// 误差增长了,说明近似的不够好
cout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
// 更新abc估计值
ae += dx[0];
be += dx[1];
ce += dx[2];
lastCost = cost;
cout << "total cost: " << cost << endl;
}
cout << "estimated abc = " << ae << ", " << be << ", " << ce << endl;
return 0;
}
3. 利用Ceres求解
Ceres是一个C++库,用于求解通用的最小二乘问题,因此非常适合上面介绍的曲线拟合。而且Ceres的使用也非常简单,大体上分为如下三步:
官方tutorial
- 定义代价函数;
- 构建最小二乘问题,向问题中添加误差项,此时会用到第一步的代价函数;
- 配置求解器,开始求解。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 代价函数的计算模型
struct CURVE_FITTING_COST
{
CURVE_FITTING_COST ( double x, double y ) : _x ( x ), _y ( y ) {}
// 残差的计算
template
bool operator() (
const T* const abc, // 模型参数,有3维
T* residual ) const // 残差
{
residual[0] = T ( _y ) - ceres::exp ( abc[0]*T ( _x ) *T ( _x ) + abc[1]*T ( _x ) + abc[2] ); // y-exp(ax^2+bx+c)
return true;
}
const double _x, _y; // x,y数据
};
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值
int N=100; // 数据点
double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值
cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器
double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值
vector x_data, y_data; // 数据
cout<<"generating data: "< (
new CURVE_FITTING_COST ( x_data[i], y_data[i] )
),
nullptr, // 核函数,这里不使用,为空
abc // 待估计参数
);
}
// 配置求解器
ceres::Solver::Options options; // 这里有很多配置项可以填
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; // 增量方程如何求解
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; // 输出到cout
ceres::Solver::Summary summary; // 优化信息
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
ceres::Solve ( options, &problem, &summary ); // 开始优化
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used = chrono::duration_cast>( t2-t1 );
cout<<"solve time cost = "< 4. 利用G2O求解
使用G2O拟合曲线,需要将问题抽象成图优化.只需要记住节点为优化变量,边为误差项.步骤:

#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型
class CurveFittingVertex: public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual void setToOriginImpl() // 重置
{
_estimate << 0,0,0;
}
virtual void oplusImpl( const double* update ) // 更新
{
_estimate += Eigen::Vector3d(update);
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
virtual bool read( istream& in ) {}
virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}
};
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class CurveFittingEdge: public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1,double,CurveFittingVertex>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
CurveFittingEdge( double x ): BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {}
// 计算曲线模型误差
void computeError()
{
const CurveFittingVertex* v = static_cast (_vertices[0]);
const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate();
_error(0,0) = _measurement - std::exp( abc(0,0)*_x*_x + abc(1,0)*_x + abc(2,0) ) ;
}
virtual bool read( istream& in ) {}
virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}
public:
double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement
};
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值
int N=100; // 数据点
double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值
cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器
double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值
vector x_data, y_data; // 数据
cout<<"generating data: "< > Block; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为3,误差值维度为1
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense(); // 线性方程求解器
Block* solver_ptr = new Block( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器
// 梯度下降方法,从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( solver_ptr );
// g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton( solver_ptr );
// g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg( solver_ptr );
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm( solver ); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose( true ); // 打开调试输出
// 往图中增加顶点
CurveFittingVertex* v = new CurveFittingVertex();
v->setEstimate( Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,0) );
v->setId(0);
optimizer.addVertex( v );
// 往图中增加边
for ( int i=0; isetId(i);
edge->setVertex( 0, v ); // 设置连接的顶点
edge->setMeasurement( y_data[i] ); // 观测数值
edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix::Identity()*1/(w_sigma*w_sigma) ); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆
optimizer.addEdge( edge );
}
// 执行优化
cout<<"start optimization"< time_used = chrono::duration_cast>( t2-t1 );
cout<<"solve time cost = "<estimate();
cout<<"estimated model: "< 

