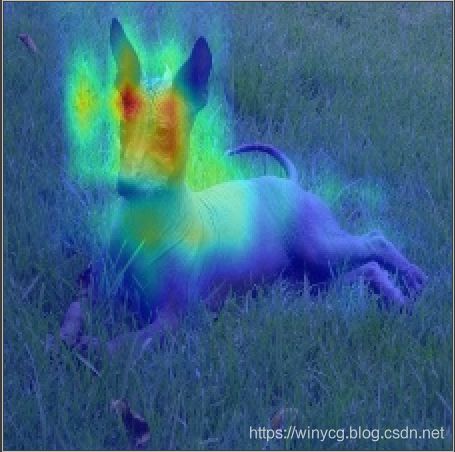
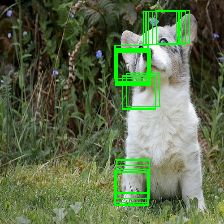
BagNet特征heatmap可视化
BagNet地址:https://github.com/wielandbrendel/bag-of-local-features-models
BagNet是ResNet的变体,显著的区别是将3x3卷积变为1x1卷积来达到构造整体网络具有某个最终的感受野(receptive field)目的。在这里主要讲解对于一张来源于ImageNet的尺寸为224x224的原始图像,如何判断其局部的image patch的重要性大小,并可视化heatmap。
获取heatmap张量
1. 读取预训练的BagNet,并读取原始图像并转化为tensor。将图像tensor输入BagNet得到维度为224x224的2D heatmap。
import bagnets.pytorchnet
from bagnets.utils import plot_heatmap, generate_heatmap_pytorch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import numpy as np
import cv2
import torch
pytorch_model = bagnets.pytorchnet.bagnet33(pretrained=True).cuda()
pytorch_model.eval()
image_path = 'val.JPEG'
raw_image = cv2.imread(image_path)
raw_image = cv2.resize(raw_image, (224,) * 2)
image = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])(raw_image[..., ::-1].copy()) # cv2库读取的为BGR通道,需将其变为RGB
image = torch.unsqueeze(image, 0) # 将单张图像维度由(3,224,224)变为(1,3,224,224)
heatmap = generate_heatmap_pytorch(pytorch_model, image, 2, 33)
np.save('heatmap.npy', heatmap) # 将heatmap张量保存用于之后可视化
generate_heatmap_pytorch函数的内容是根据(3,224,224)原始图像生成对应的2D (224,224)的heatmap,过程如下:
def generate_heatmap_pytorch(model, image, target, patchsize):
"""
Generates high-resolution heatmap for a BagNet by decomposing the
image into all possible patches and by computing the logits for
each patch.
Parameters
----------
model : Pytorch Model
This should be one of the BagNets.
image : Numpy array of shape [1, 3, X, X]
The image for which we want to compute the heatmap.
target : int
Class for which the heatmap is computed.
patchsize : int
The size of the receptive field of the given BagNet.
"""
import torch
with torch.no_grad():
# 这里采用9x9的滑动框来生成image patches,为了保证输出尺寸为224x224
# 需要pad 0
_, c, x, y = image.shape
padded_image = np.zeros((c, x + patchsize - 1, y + patchsize - 1))
padded_image[:, (patchsize-1)//2:(patchsize-1)//2 + x, (patchsize-1)//2:(patchsize-1)//2 + y] = image[0]
image = padded_image[None].astype(np.float32)
# turn to torch tensor
input = torch.from_numpy(image).cuda()
# extract patches
patches = input.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
# 这个语句负责生成patches
# patches:(1,224,224,3)
# 设num_H==num_W=(224+2*paddings)/patchsize
# patches.unfold(1, patchsize, 1):(1,num_H,224,3,patchsize)
# patches.unfold(1, patchsize, 1).unfold(2, patchsize, 1):
# (1,num_H,num_W,3,patchsize,patchsize)
patches = patches.unfold(1, patchsize, 1).unfold(2, patchsize, 1)
num_rows = patches.shape[1]
num_cols = patches.shape[2]
patches = patches.contiguous().view((-1, 3, patchsize, patchsize))
# compute logits for each patch
logits_list = []
for batch_patches in torch.split(patches, 1000):
logits = model(batch_patches)
logits = logits[:, target]
logits_list.append(logits.data.cpu().numpy().copy())
logits = np.hstack(logits_list)
return logits.reshape((224, 224))
可视化heatmap
方法一: 这里采用bagnet的方法,将原图padding之后裁剪成224* 224个小片,然后依次进入网络得到 logits值,于是得到224*224个数,直接reshape就可以得到heatmap无需插值
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import feature, transform
import cv2
def plot_heatmap(heatmap, original, ax1, ax2, ax3, cmap='RdBu_r',
percentile=99, dilation=0.5, alpha=0.25):
"""
Plots the heatmap on top of the original image
(which is shown by most important edges).
Parameters
----------
heatmap : Numpy Array of shape [X, X]
Heatmap to visualise.
original : Numpy array of shape [X, X, 3]
Original image for which the heatmap was computed.
ax : Matplotlib axis
Axis onto which the heatmap should be plotted.
cmap : Matplotlib color map
Color map for the visualisation of the heatmaps (default: RdBu_r)
percentile : float between 0 and 100 (default: 99)
Extreme values outside of the percentile range are clipped.
This avoids that a single outlier dominates the whole heatmap.
dilation : float
Resizing of the original image. Influences the edge detector and
thus the image overlay.
alpha : float in [0, 1]
Opacity of the overlay image.
"""
dx, dy = 0.05, 0.05
xx = np.arange(0.0, heatmap.shape[1], dx)
yy = np.arange(0.0, heatmap.shape[0], dy)
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = np.amin(xx), np.amax(xx), np.amin(yy), np.amax(yy)
extent = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax
cmap_original = plt.get_cmap('Greys_r')
cmap_original.set_bad(alpha=0)
# Compute edges (to overlay to heatmaps later)
original_greyscale = original if len(original.shape) == 2 else np.mean(original, axis=-1)
# dilation=0.5,图像由(224,224)缩放为(112,112),这样做的目的是找出更粗略的边缘纹理
in_image_upscaled = transform.rescale(original_greyscale, dilation, mode='constant',
multichannel=False, anti_aliasing=True)
# 找到图像的边缘纹理特征
edges = feature.canny(in_image_upscaled).astype(float)
edges[edges < 0.5] = np.nan
edges[:5, :] = np.nan
edges[-5:, :] = np.nan
edges[:, :5] = np.nan
edges[:, -5:] = np.nan
overlay = edges # 找出图像的边缘特征显示在heatmap上,便于对照原图特征
# 最大值设为99%处,若设为真正的最大值,heatmap的重要处颜色不是特别深
abs_max = np.percentile(np.abs(heatmap), percentile)
abs_min = abs_max
a1 = ax1.imshow(heatmap, extent=extent, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap, vmin=-abs_min, vmax=abs_max)
a2 = ax2.imshow(overlay, extent=extent, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap_original, alpha=alpha)
cb = fig.colorbar(a1, ax=ax1, ticks=[1, 2, 3])
cb.set_ticks([-abs_min, abs_max])
cb.set_ticklabels(['Low', 'High'])
a3 = ax3.imshow(heatmap, extent=extent, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap, vmin=-abs_min, vmax=abs_max)
ax3.imshow(overlay, extent=extent, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap_original, alpha=alpha)
heatmap = np.load('heatmap.npy')
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
image_path = 'val.JPEG'
raw_image = cv2.imread(image_path)
original_image = cv2.resize(raw_image, (224, 224))
fig, _axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
axs = _axs.flatten()
axs[0].set_title('original')
# matplotlib的imshow的RGB 3通道表示与cv2库(BGR)的顺序不同
axs[0].imshow(original_image[..., ::-1] / 255.)
axs[0].axis('off') # 不显示坐标尺寸
axs[1].set_title('heatmap')
axs[1].axis('off') # 不显示坐标尺寸
axs[2].set_title('feature canny')
axs[2].axis('off') # 不显示坐标尺寸
axs[3].set_title('heatmap+feature canny')
axs[3].axis('off') # 不显示坐标尺寸
plot_heatmap(heatmap, original_image, axs[1], axs[2], axs[3], dilation=0.5, percentile=99, alpha=.25)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()

方法二: 将global average pooling前的3D 特征图根据FC层的权值进行加权(参加CAM方法),得到2D的特征图。由于此时的分辨率是小于224* 224的,此时一般需要进行插值来resize。以下给出一个2D特征图的npy文件,将其进行可视化。
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import matplotlib.cm as cm
# 升采样map
map = cv2.resize(map, (224, 224))
image_path = 'val.JPEG'
raw_image = cv2.imread(image_path)
original_image = cv2.resize(raw_image, (224, 224))
# 标准化到[0,1]
map = (map- map.min()) / (map.max()-map.min())
# 使用jet_r映射为RGB的heatmap
heatmap3 = cm.jet_r(map)[..., :3] * 255.0
# 与原图进行结合显示
gcam = (heatmap3.astype(np.float) + original_image.astype(np.float)) / 2
cv2.imwrite('heatmap.jpg', np.uint8(gcam))
map = cv2.resize(map, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
map = (map- map.min()) / (map.max()-map.min())
heatmap = cm.jet_r(map)[..., :3] * 255.0
cv2.imwrite('heatmap.jpg', np.uint8(heatmap ))
标注重点的image patch
根据生成的heatmap对应到原始图像的image patch,并使用矩形框标注,这里使用的是33x33的框规模:
import numpy as np
import cv2
image_path = 'val.JPEG'
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = cv2.resize(image, (224,) * 2)
heatmap = np.load('heatmap.npy')
maximum = 0
pos_list = []
# 选取>99.95位置的数才标注出对应的image patch
threshold = np.percentile(heatmap, 99.95)
for i in range(heatmap.shape[0]):
for j in range(heatmap.shape[1]):
if heatmap[i, j] > threshold:
pos_list.append((i, j))
padding = 33//2
for pos in pos_list:
# 注意cv2库中的图像坐标和numpy数组中的不同
pt1 = (pos[1] - padding , pos[0] - padding)
pt2 = (pt1[0] + 33-1, pt1[1] + 33-1)
# (0, 255, 0)表示RGB中的绿色,1表示框的宽度
cv2.rectangle(image, pt1, pt2, (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.imshow('label', image)
cv2.waitKey() # 等待按键才退出
计算bbox的IOU
def IOU(bboxA, bboxB):
x1 = bboxA[0]
y1 = bboxA[1]
width1 = bboxA[2] - bboxA[0]
height1 = bboxA[3] - bboxA[1]
x2 = bboxB[0]
y2 = bboxB[1]
width2 = bboxB[2] - bboxB[0]
height2 = bboxB[3] - bboxB[1]
endx = max(x1 + width1, x2 + width2)
startx = min(x1, x2)
width = width1 + width2 - (endx - startx)
endy = max(y1 + height1, y2 + height2)
starty = min(y1, y2)
height = height1 + height2 - (endy - starty)
if width <= 0 or height <= 0:
ratio = 0 # 重叠率为 0
else:
Area = width * height # 两矩形相交面积
Area1 = width1 * height1
Area2 = width2 * height2
ratio = Area * 1. / (Area1 + Area2 - Area)
return ratio
image_path = 'val.JPEG'
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = cv2.resize(image, (224,) * 2)
pt1 = (0, 10)
pt2 = (pt1[0] + 33, pt1[1] +33)
pt3 = (20, 15)
pt4 = (pt3[0] + 33, pt3[1] + 33)
print(IOU(pt1+pt2, pt3+pt4))
cv2.rectangle(image, pt1, pt2, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.rectangle(image, pt3, pt4, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('label', image)
cv2.waitKey() # 等待按键才退出