HDLBits刷题合集—20 Building Larger Circuits
HDLBits刷题合集—20 Building Larger Circuits
HDLBits-153 Exams/review2015 count1k
Problem Statement
建立一个计数器,其计数范围为0到999(含0和999),周期为1000。 复位输入是同步的,应将计数器复位到0。
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset,
output [9:0] q);
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (reset) q <= 10'b0;
else if (q == 999)
q <= 10'b0;
else q <= q + 1'b1;
end
endmodule
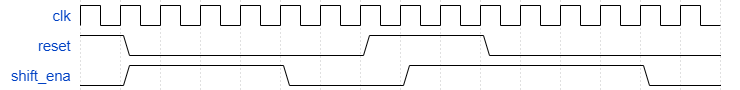
HDLBits-154 Exams/review2015 shiftcount
Problem Statement
这是由五个练习组成的系列中的第一部分,该练习从几个较小的电路中构建出一个复杂的计数器。 有关整体设计,请参见最终练习。
建立一个四位移位寄存器,该寄存器还可以用作递减计数器。 当shift_ena为1时,数据首先以最高有效位移位。当count_ena为1时,移位寄存器中当前的数字递减。
由于整个系统永远不会同时使用shift_ena和count_ena,因此如果两个控制输入均为1,则电路执行什么操作都没关系(这主要意味着,哪种情况下优先级更高没有关系)。
代码如下:
module top_module (
input clk,
input shift_ena,
input count_ena,
input data,
output [3:0] q);
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (shift_ena) q <= {q[2:0], data};
if (count_ena) q <= q - 1'b1;
end
endmodule
HDLBits-155 Exams/review2015 fsmseq
Problem Statement
这是由五个练习组成的系列中的第二部分,该练习从几个较小的电路中构建出一个复杂的计数器。 有关整体设计,请参见最终练习。
建立一个在输入比特流中搜索序列1101的有限状态机。 找到序列后,应将start_shifting永久设置为1,直到重置为止。 卡在最终状态中的目的是为尚未实现的更大FSM中的其他状态建模。 我们将在接下来的几个练习中扩展此FSM。
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
input data,
output start_shifting);
parameter S0=0, S1=1, S2=2, S3=3, S4=4;
reg [2:0] state, state_next;
always @(*) begin
case (state)
S0 : begin
if (data) state_next = S1;
else state_next = S0;
end
S1 : begin
if (data) state_next = S2;
else state_next = S0;
end
S2 : begin
if (data) state_next = S2;
else state_next = S3;
end
S3 : begin
if (data) state_next = S4;
else state_next = S0;
end
S4 : begin
state_next = S4;
end
default : state_next = S0;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (reset) state <= S0;
else state <= state_next;
end
assign start_shifting = (state == S4);
endmodule
HDLBits-156 Exams/review2015 fsmshift
Problem Statement
这是由五个练习组成的系列中的第三部分,该练习从几个较小的电路中构建出一个复杂的计数器。 有关整体设计,请参见最终练习。
作为FSM中用于控制移位寄存器的一部分,我们希望能够在检测到正确的位模式时,在4个时钟周期内使能移位寄存器(即移位寄存器在4个周期内工作)。 我们在Exams / review2015_fsmseq中处理序列检测,因此FSM的这一部分仅处理启用移位寄存器4个周期的操作。
每当FSM复位时,将shift_ena置为4个周期,然后置为0(直到复位reset)。
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
output shift_ena);
parameter S0=0, S1=1, S2=2, S3=3, S4=4;
reg [2:0] state, state_next;
always @(*) begin
case (state)
S0 : begin
if (reset) state_next <= S1;
else state_next <= S0;
end
S1 : begin
state_next <= S2;
end
S2 : begin
state_next <= S3;
end
S3: begin
state_next <= S4;
end
S4: begin
state_next <= S0;
end
default : state_next <= S0;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (reset) state <= S1;
else state <= state_next;
end
assign shift_ena = (state != S0);
endmodule
HDLBits-157 Exams/review2015 fsm
Problem Statement
这是由五个练习组成的系列中的第四部分,该练习从几个较小的电路中构建出一个复杂的计数器。 有关整体设计,请参见最终练习。
你可能希望先做:FSM: Enable shift register和FSM: Sequence recognizer 。
我们想要创建一个定时器:
1、当检测到特定模式(1101)时启动
2、再移4位以确定延迟时间,
3、等待计数器完成计数,然后
4、通知用户并等待用户确认定时器。
在此问题中,仅实现控制定时器的有限状态机。此处不包括数据路径(计数器和一些比较器)。
串行数据在数据输入引脚上可用。当接收到模式1101时,状态机必须在4个时钟周期内输出shift_ena。
此后,状态机声明输出counting以表明其正在等待计数器,并等待直到输入done_counting为高电平。
那时,状态机必须输出done,以通知用户计时器已超时,并等待直到输入ack为1才被复位以查找下一次出现的启动序列(1101)。
状态机应重置为开始搜索输入序列1101的状态。
这是预期输入和输出的示例。 “ x”状态可能会使阅读有些混乱。它们表明FSM在该周期中不应关心该特定输入信号。例如,一旦检测到1101模式,FSM将不再查看数据输入,直到在完成所有其他操作后恢复搜索为止。
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
input data,
output shift_ena,
output counting,
input done_counting,
output done,
input ack );
parameter S=4'b0000,S1=4'b0001,S11=4'b0010,S110=4'b0011,B0=4'b0100;
parameter B1=4'b0101,B2=4'b0110,B3=4'b0111,Count=4'b1000,Wait=4'b1001;
reg [3:0] state,state_next;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (reset) state <= S;
else state <= state_next;
end
always @(*) begin
case (state)
S: begin
if (data) state_next <= S1;
else state_next <= S;
end
S1: begin
if (data) state_next <= S11;
else state_next <= S;
end
S11: begin
if (data) state_next <= S11;
else state_next <= S110;
end
S110: begin
if (data) state_next <= B0;
else state_next <= S;
end
B0: begin
state_next <= B1;
end
B1: begin
state_next <= B2;
end
B2: begin
state_next <= B3;
end
B3: begin
state_next <= Count;
end
Count: begin
if (done_counting)
state_next <= Wait;
else state_next <= Count;
end
Wait: begin
if (ack) state_next <= S;
else state_next <= Wait;
end
default: state_next <= S;
endcase
end
assign shift_ena = (state==B0 | state==B1| state==B2 | state==B3);
assign counting = (state==Count);
assign done = (state==Wait);
endmodule
HDLBits-158 Exams/review2015 fancytimer
Problem Statement
这是由五个练习组成的系列中的第五部分,该练习从几个较小的电路中构建出一个复杂的计数器。 有关整体设计,请参见最终练习。
你可能希望先进行前面的四个练习(counter,sequence recognizer FSM,FSM delay和 combined FSM)。
我们想要创建一个定时器:
1、当检测到特定模式(1101)时启动
2、再移4位以确定延迟时间,
3、等待计数器完成计数,然后
4、通知用户并等待用户确认定时器。
串行数据从数据输入引脚获得。 当接收到模式1101时,电路必须随后在接下来的4位进行移位,最高有效位在前。 这4位确定定时器延迟的持续时间。 我将其称为delay [3:0]。
此后,状态机输出counting以指示其正在计数。 状态机必须精确计数(delay [3:0] + 1)* 1000个时钟周期。 例如,delay = 0表示计数1000个周期,而delay = 5表示计数6000个周期。 同时输出当前剩余时间。 这应该等于delay×1000个周期,然后等于(delay-1)×1000个周期,依此类推,直到0×1000个周期。 当电路不计数时,count [3:0]输出无关紧要(随便实现什么值)。
那时,状态机必须输出done,以通知用户计时器已超时,并等待直到输入ack为1才被复位以查找下一次出现的启动序列(1101)。
电路应重置为开始搜索输入序列1101的状态。
这是预期输入和输出的示例。 “ x”状态可能会使阅读有些混乱。 它们表明FSM在该周期中不应关心该特定输入信号。 例如,一旦读取了1101和delay [3:0],电路将不再查看数据输入,直到在完成所有其他操作后恢复搜索为止。 在此示例中,电路的计数为2000个时钟周期,因为delay [3:0]值为4’b0001。 最后几个周期以delay [3:0] = 4’b1110开始另一个计数,该计数将计数15000个周期。
参考Andy_ICer的代码如下:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
input data,
output [3:0] count,
output counting,
output done,
input ack );
parameter S=4'b0000,S1=4'b0001,S11=4'b0010,S110=4'b0011,B0=4'b0100;
parameter B1=4'b0101,B2=4'b0110,B3=4'b0111,Count=4'b1000,Wait=4'b1001;
reg[3:0] state, state_next;
reg[3:0] shift;
reg[13:0] counter;
wire done_counting;
wire shift_ena;
assign shift_ena = (state == B0) | (state == B1) | (state == B2) | (state == B3);
always @(*) begin
case (state)
S: state_next = data ? S1 : S;
S1: state_next = data ? S11 : S;
S11: state_next = data ? S11 : S110;
S110: state_next = data ? B0 : S;
B0: state_next = B1;
B1: state_next = B2;
B2: state_next = B3;
B3: state_next = Count;
Count: state_next = done_counting ? Wait : Count;
Wait: state_next = ack ? S : Wait;
default: state_next = S;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
state <= S;
else
state <= state_next;
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
shift <= 0;
else if (shift_ena)
shift <= {shift[2:0],data};
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
counter <= 0;
else
case (state)
Count: counter <= counter + 1'b1;
default: counter <= 0;
endcase
end
assign done_counting = (counter == (shift + 1) * 1000 - 1);
assign count = shift - counter/1000;
assign counting = (state == Count);
assign done = (state == Wait);
endmodule
HDLBits-159 Exams/review2015 fsmonehot
Problem Statement
给定下列具有3个输入,3个输出和10个状态的状态机:

假定使用独热码编码,得出次态逻辑方程和输出逻辑方程:(S, S1, S11, S110, B0, B1, B2, B3, Count, Wait) = (10’b0000000001, 10’b0000000010, 10’b0000000100, … , 10’b1000000000)。
编写代码生成以下方程:
● B3_next ---- next-state logic for state B3
● S_next
● S1_next
● Count_next
● Wait_next
● done – output logic
● counting
● shift_ena
代码如下:
module top_module(
input d,
input done_counting,
input ack,
input [9:0] state, // 10-bit one-hot current state
output B3_next,
output S_next,
output S1_next,
output Count_next,
output Wait_next,
output done,
output counting,
output shift_ena
); //
parameter S=0, S1=1, S11=2, S110=3, B0=4, B1=5, B2=6, B3=7, Count=8, Wait=9;
// assign B3_next = state[6];
assign B3_next = state[B2];
assign S_next = (~d & state[S]) | (~d & state[S1]) | (~d & state[S110]) | (ack & state[Wait]);
assign S1_next = d & state[S];
assign Count_next = state[B3] | (~done_counting & state[Count]);
assign Wait_next = (done_counting & state[Count]) | (~ack & state[Wait]);
assign done = state[Wait];
assign counting = state[Count];
assign shift_ena = state[B0] | state[B1] | state[B2] | state[B3];
endmodule
Note
新手一枚,主要分享博客,记录学习过程,后期参考大佬代码或思想会一一列出。欢迎大家批评指正!