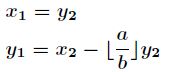- 手算逆元及手动模拟扩展欧几里得算法及思路推导
一上午的一个小推导先给出exgcd的代码吧intexgcd(inta,intb,int&x,int&y){///x,y起初不知道,是递归往上求解x,yif(b==0){x=1,y=0;returna;///两处return}intd=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);inttmp=x;x=y,y=tmp-(a/b)*y;returnd;///记得要返回d啊///【a*x+b*y=1中,x是a在模b
- 【密码学】扩展欧几里得算法例题
应付考试的写法:注意:RSA加解密、签名时:计算的是关于φ(n)的逆元不是直接关于n的逆元,d是e的逆元,φ(n)与e互素才可以有逆元已知n=pxq,计算φ(n),计算d:扩展欧几里得算法流程:题目:d·e=1mod96,e=5,求d递归(不断的做除法,辗转相除)的计算一个三元组。有两个初始的三元组:设三元组(x,y,z),x,y,z满足:因为要算5对96的逆元,一般把大的放在前面即:96*x+5
- 扩展欧几里得算法&乘法逆元
GZkx
数论之旅简单题乘法逆元
扩展欧几里得算法——exgcd主要有两个重要的用途:1.求乘法逆元(下面的例题就是)a*b%mod==1->a与b互为在mod意义下的逆元2.求二元一次线性方程exgcd(a,b,x,y)即为a,b的最大公约数,,令gcd(a,b)=a*x+b*y,则x,y也可以得出来了不懂gcd(最大公约数)的童鞋可以先了解一下哦Description给出2个数M和N(M#include#includeusin
- 扩展欧几里得算法求逆元
hesorchen
#扩展欧几里得算法#逆元
扩展欧几里得算法应该是最优的求逆元算法之一,他和费马小定理具有同样的时间复杂度O(log(n))O(log(n))O(log(n)),但是费马小定理需要模数为质数,扩展欧几里得算法则不需要。逆元定义若aaa与ppp互素,则满足(a×x)modp=1(a\timesx)modp=1(a×x)modp=1的xxx为aaa的逆元。显然,有(k×p+1)modp=1(k\timesp+1)modp=1(k
- 扩展欧几里得算法简介及代码实现
hnjzsyjyj
信息学竞赛#算法数学基础扩展欧几里得算法裴蜀定理
【扩展欧几里得算法简介】●扩展欧几里得算法(ExtendedEuclideanAlgorithm)是欧几里得算法的扩展版本,不仅能计算两个整数的最大公约数(GCD),还能找到满足贝祖等式(Bézout'sIdentity)ax+by=gcd(a,b)的整数解x和y。它在数论、密码学等领域有重要应用,例如求解模的逆元、求解线性同余方程等。●扩展欧几里得算法求ax+by=gcd(a,b)特解的方法如下
- 《夜深人静写算法》数论篇 - (10) 扩展欧几里得定理
英雄哪里出来
《夜深人静写算法》数论篇算法初等数论扩展欧几里得定理
前言 通过扩展欧几里得定理,利用扩展欧几里得算法,可以求解线性同余方程。 那么什么是线性同余方程?什么是扩展欧几里得定理?什么是扩展欧几里得算法?接下来的几篇文章会来讲解一下这几个概念。一、扩展欧几里得定理1、定理概述 对于不都为零的整数aaa和b
- AcWing 877:扩展欧几里得算法
hnjzsyjyj
信息学竞赛#算法数学基础扩展欧几里得算法裴蜀定理
【题目来源】https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/879/【题目描述】给定n对正整数ai,bi,对于每对数,求出一组xi,yi,使其满足ai×xi+bi×yi=gcd(ai,bi)。【输入格式】第一行包含整数n。接下来n行,每行包含两个整数ai,bi。【输出格式】输出共n行,对于每组ai,bi,求出一组满足条件的xi,yi,每组结果占一行。本题答案不唯一,输
- 初等数论 --- 同余、欧拉定理、费马小定理、求逆元
chstor
算法笔记
文章目录一、同余二、欧拉定理三、费马小定理四、扩展欧几里得算法4.1裴蜀定理五、一元线性同余方程六、逆元求逆元方法一、扩展欧几里得算法求逆元方法二、费马小定理加快速幂一、同余定义当两个整数a,b除以同一个正整数m,若得相同余数,则二整数同余。记为:a≡b(mod m)当两个整数a,b除以同一个正整数m,若得相同余数,则二整数同余。记为:a\equivb(\modm)当两个整数a,b除以同一个正整
- 了解倒数的概念,乘法逆元就很好理解——解析之【逆元的概念】【逆元的求解方法】
灰阳阳
算法算法裴蜀定理欧几里得算法最大公约数逆元
目录前言一、逆元的概念1、基本定义示例1:a=3,m=7a=3,m=7a=3,m=7示例2:a=2,m=5a=2,m=5a=2,m=52、乘法逆元有什么用3、相关性质二、求解逆元的方法1、费马小定理求乘法逆元定义费马小定理求逆元的方法总结模板题2、扩展欧几里得算法求逆元定义扩展欧几里得算法求逆元的方法总结模板题3、递推公式求逆元定义递推公式的推导示例总结前言首先,下面讨论的是数论相关内容。主要研究
- 【算法】数论基础——逆元的概念与应用 python
查理零世
算法python
文章目录前言一、什么是逆元?二、逆元的存在条件三、如何计算逆元?1.扩展欧几里得算法(ExtendedEuclideanAlgorithm)2.使用费马小定理(Fermat'sLittleTheorem)四、应用场景示例:求排列数和组合数前言逆元(ModularMultiplicativeInverse)在模运算中是一个非常重要的概念,特别是在需要执行除法操作时。因为在模p的情况下,直接进行除法是
- 实验一-密码学数学基础
那就摆吧
学习=进步知识密码学
实验一密码学数学基础一、实验目的掌握最大公因数的计算方法,理解其在密码学中的重要性。学习扩展欧几里得算法,能够计算乘法逆元。熟悉模幂运算的方法,了解其在加密和签名算法中的应用。二、实验原理最大公因数最大公因数(GCD)是两个整数的最大公因数,是数论中一个基本概念。在密码学中,计算GCD用于判断两个数是否互素,有以下三种常见方法:暴力穷举法通过列举所有可能的公约数来找到最大公约数。具体操作是依次检查
- 密码学----RSA算法
扬子期
密码学算法
这里写目录标题一、原理二、求解逆元相关习题一、原理参考链接:银行密码系统安全吗?质数(素数)到底有啥用?李永乐老师11分钟讲RSA加密算法二、求解逆元同时视频里还涉及到的是负数的逆元,如何转化为正数。参考链接:扩展欧几里得算法求逆元相关习题在RSA体制中,已知p=5,q=17,加密密钥e=5,请求出解密密钥d,并求出明文m=12对应的密文。
- ACM培训4
ZIZIZIZIZ()
算法笔记
学习总结--基础数论大多为模板一、GCD(最大公约数)①辗转相除法longlonggcd(longa,longb){longlongr;while(b!=0){r=a%b;a=b;b=r;}returna;}②扩展欧几里得算法intexgcd(inta,intb,int&x,int&y){if(b==0){x=1;y=0;returnaa;}intans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);intk
- 数论——扩展欧几里得算法
NOI_yzk
欧几里得&拓展欧几里得(Euclid&Extend-Euclid)欧几里得算法(Euclid)背景:欧几里德算法又称辗转相除法,用于计算两个正整数a,b的最大公约数。——百度百科代码:递推的代码是相当的简洁:intgcd(inta,intb){returnb==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);}分析:方法说了是辗转相除法,自然没有什么好介绍的了。。Fresh肯定会觉得这样递归下去会不会爆栈?实际上在
- 数学知识——欧拉函数、快速幂、扩展欧几里得算法
up-to-star
acwing算法基础课学习笔记
欧拉函数欧拉函数定义为ϕ(n)=1−n中与n互质的个数\phi(n)=1-n中与n互质的个数ϕ(n)=1−n中与n互质的个数,互质就是最大公约数是1。欧拉函数求解公式:将n分解质因数:n=p1a1+p2a2+...+pkakn=p_1^{a1}+p_2^{a2}+...+p_k^{ak}n=p1a1+p2a2+...+pkak,则ϕ(n)=n∗(1−1p1)∗(1−1p2)∗.....∗(1−1p
- 扩展欧几里得算法 exgcd 求逆元(适用于模数不为质数的情况)
Waldeinsamkeit41
算法
原理不打算自己懂。。。代码ullexgcd(ulla,ullb,ull&x,ull&y)//扩展欧几里得求模b意义下a的逆元//返回的d是a和b的最大公约数,而最终的x是a在模b意义下的逆元{if(b==0){x=1;y=0;returna;}ulld=exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);y=y-a/b*x;returnd;}exgcd(a,b,x,y);//注意最终x可能返回负数,要加上b变成正数
- 【数论】exgcd 扩展欧几里得算法
Texcavator
数论算法
参考:exgcd详解-zzt1208-博客园(cnblogs.com)exgcd(扩展欧几里得算法),用来求形如ax+by=gcd(a,b)ax+by=gcd(a,b)ax+by=gcd(a,b)(a,ba,ba,b为常数)的方程的一组整数解。(如果不确定等号右边是不是gcd,可以先当做gcd,求出来之后验证,是的话就是解,不是的话就不是解)推导见上面的链接,这篇只放个板子codeintexgcd
- 备战蓝桥杯---数学基础3
cocoack
蓝桥杯算法数学c++
本专题主要围绕同余来讲:下面介绍一下基本概念与定理:下面给出解这方程的一个例子:下面是用代码实现扩展欧几里得算法:#includeusingnamespacestd;intgcd(inta,intb,int&x,int&y){if(b==0){x=1;y=0;returna;}intd=gcd(b,a%b,y,x);y=y-b/a*x;returnd;}下面我们引进二元一次不定方程的通解:
- 逆元 与 扩展欧几里得(超级详细,c++)
海风许愿
Acm算法c++c++开发语言算法
逆元与扩展欧几里得算法(veryimportant)^-^点个赞再走吧~~^-^点个赞再走吧~~^-^点个赞再走吧~~欧几里得定理:给定任意a,b,一定存在x,y使得ax+by=gcd(a,b)公式:ax+by=gcd(a,b);1)利用欧几里得的过程给定n,对正整数ai,bi,对于每对数,求出一组xi,yi,使其满足ai*xi+bi*yi=gcd(ai,bi)推导:ax+by=d=>bx+(a%
- 扩展欧几里得
云儿乱飘
数学知识数论
877.扩展欧几里得算法-AcWing题库#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#includeusingnamespacestd;#definelllonglong#definePIIpair#defineTUP
- 笔记--扩展欧几里得算法
Die love 6-feet-under
算法笔记c++
AcWing.877.欧几里得算法给定nnn对正整数aaai,bbbi,对于每对数,求出一组xxxi,yyyi,使其满足aaai×x×x×xi+b+b+bi×y×y×yi=gcd(a=gcd(a=gcd(ai,b,b,bi)))。输入格式第一行包含整数nnn。接下来nnn行,每行包含两个整数aaai,bbbi。输出格式输出共nnn行,对于每组aaai,bbbi,求出一组满足条件的xxxi,yyyi
- RSA知识点及刷题记录
甜酒大马猴
密码学python笔记
Crypto密码学------RSARSA基础知识欧拉函数phi=(p-1)*(q-1)*(r-1)gmpy2.gcd(a,b)//欧几里得算法gmpy2.gcdext(a,b)//扩展欧几里得算法gmpy2.iroot(x,n)//x开n次根d=gmpy2.invert(e,pai)//求逆元,d*e=1(modpai)gmpy2.mpz(x)//初始化一个大整数xgmpy2.mpfr(x)//
- C++ 数论相关题目 扩展欧几里得算法(裴蜀定理)
伏城无嗔
算法笔记数论力扣算法c++
给定n对正整数ai,bi,对于每对数,求出一组xi,yi,使其满足ai×xi+bi×yi=gcd(ai,bi)。输入格式第一行包含整数n。接下来n行,每行包含两个整数ai,bi。输出格式输出共n行,对于每组ai,bi,求出一组满足条件的xi,yi,每组结果占一行。本题答案不唯一,输出任意满足条件的xi,yi均可。数据范围1≤n≤105,1≤ai,bi≤2×109输入样例:246818输出样例:-1
- C++ 数论相关题目 线性同余方程 (扩展欧几里得算法的应用)
伏城无嗔
数论力扣算法笔记算法c++
给定n组数据ai,bi,mi,对于每组数求出一个xi,使其满足ai×xi≡bi(modmi),如果无解则输出impossible。输入格式第一行包含整数n。接下来n行,每行包含一组数据ai,bi,mi。输出格式输出共n行,每组数据输出一个整数表示一个满足条件的xi,如果无解则输出impossible。每组数据结果占一行,结果可能不唯一,输出任意一个满足条件的结果均可。输出答案必须在int范围之内。
- 算法学习系列(二十九):裴蜀定理、扩展欧几里得算法
lijiachang030718
算法算法学习
目录引言一、裴蜀定理二、扩展欧几里得算法模板三、公式推导四、例题1.扩展欧几里得算法模板题2.线性同余方程引言这个扩展欧几里得算法用的还是比较多的,而且也很实用,话不多说直接开始吧。一、裴蜀定理裴蜀定理:对于任意正整数a和b,一定存在非零整数x和y,使得ax+by=gcd(a,b)裴蜀定理:对于任意正整数a和b,一定存在非零整数x和y,使得ax+by=gcd(a,b)裴蜀定理:对于任意正整数a和b
- 【数学】二元一次不定方程、裴蜀定理、扩展欧几里得算法与乘法逆元
OIer-zyh
数学#数论c++算法OI数论数学
二元一次不定方程形如ax+by=cax+by=cax+by=c的方程称为二元一次不定方程。在数论中一般研究该方程的整数解。明显原方程无整数解或有无穷多组整数解。裴蜀定理裴蜀定理:当且仅当gcd(a,b)∣c\gcd(a,b)|cgcd(a,b)∣c时,二元一次不定方程有整数解。一方面,ax+by≡0≡c(modgcd(a,b))ax+by\equiv0\equivc\pmod{\gcd(a,b
- Acwing - 算法基础课 - 笔记(数学知识 · 二)
抠脚的大灰狼
算法Acwing算法基础课算法数论
文章目录数学知识(二)欧拉函数公式法筛法欧拉定理快速幂扩展欧几里得算法中国剩余定理数学知识(二)这一小节主要讲解的内容是:欧拉函数,快速幂,扩展欧几里得算法,中国剩余定理。这一节内容偏重于数学推导,做好心理准备。欧拉函数公式法什么是欧拉函数呢?欧拉函数用ϕ(n)\phi(n)ϕ(n)来表示,它的含义是,111到nnn中与nnn互质的数的个数比如,ϕ(6)=2\phi(6)=2ϕ(6)=2,解释:1
- 数论知识及模板整理
smiling~
数论模板学习笔记算法
目录一、质数的判定1.试除法判定质数2.质因数的分解3.质数筛选法(埃氏筛法+线性筛)4.米勒罗宾素数检测法(快速判断大质数)二、约数相关(1)试除法求约数(2)求约数个数或约数之和(3)求最大公因数/最小公倍数三、欧几里得算法(1)扩展欧几里得算法(2)线性同余方程四、快速幂(1)快速幂算法(2)大数快速幂(降幂公式)(3)快速幂求逆元(费马小定理)五、欧拉函数六、组合数学七、高斯消元八、容斥原
- 数论知识学习总结(二)
Nie同学
acwing学习总结c++
文章目录一、欧拉函数1.欧拉函数2.筛法求欧拉函数(采用筛质数的线性筛法)二、快速幂1.快速幂2.快速幂求逆元三、扩展欧几里得算法1.扩展欧几里得算法2.线性同余方程四、中国剩余定理1.表达整数的奇怪方式一、欧拉函数在数论,对正整数nnn,欧拉函数是小于等于nnn的正整数中与nnn互质的数的数目.1.欧拉函数1∼N1\simN1∼N中与NNN互质的数的个数被称为欧拉函数,记为ϕ(N)\phi(N)
- 算法归纳总结(第五天)(数论、数学知识(第一部分)总结)
乘风破浪的咸鱼君
算法c++
目录一、筛质数(与试除法)1、普通筛法2、埃筛法3、线性筛法4、试除法①、试除法代码二、约数1、试除法求约数2、最大公约数①、辗转相除法(欧几里得算法)3、约数个数4、约数之和三、欧拉函数1、普通筛求欧拉函数①、欧拉函数定义②、应用公式。③、代码实现2、线性筛求欧拉函数①、线性筛法②、求欧拉函数四、快速幂与求逆元1、快速幂2、快速幂求逆元五、扩展欧几里得算法与线性同余方程1、扩展欧几里得算法①、裴
- ASM系列五 利用TreeApi 解析生成Class
lijingyao8206
ASM字节码动态生成ClassNodeTreeAPI
前面CoreApi的介绍部分基本涵盖了ASMCore包下面的主要API及功能,其中还有一部分关于MetaData的解析和生成就不再赘述。这篇开始介绍ASM另一部分主要的Api。TreeApi。这一部分源码是关联的asm-tree-5.0.4的版本。
在介绍前,先要知道一点, Tree工程的接口基本可以完
- 链表树——复合数据结构应用实例
bardo
数据结构树型结构表结构设计链表菜单排序
我们清楚:数据库设计中,表结构设计的好坏,直接影响程序的复杂度。所以,本文就无限级分类(目录)树与链表的复合在表设计中的应用进行探讨。当然,什么是树,什么是链表,这里不作介绍。有兴趣可以去看相关的教材。
需求简介:
经常遇到这样的需求,我们希望能将保存在数据库中的树结构能够按确定的顺序读出来。比如,多级菜单、组织结构、商品分类。更具体的,我们希望某个二级菜单在这一级别中就是第一个。虽然它是最后
- 为啥要用位运算代替取模呢
chenchao051
位运算哈希汇编
在hash中查找key的时候,经常会发现用&取代%,先看两段代码吧,
JDK6中的HashMap中的indexFor方法:
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
- 最近的情况
麦田的设计者
生活感悟计划软考想
今天是2015年4月27号
整理一下最近的思绪以及要完成的任务
1、最近在驾校科目二练车,每周四天,练三周。其实做什么都要用心,追求合理的途径解决。为
- PHP去掉字符串中最后一个字符的方法
IT独行者
PHP字符串
今天在PHP项目开发中遇到一个需求,去掉字符串中的最后一个字符 原字符串1,2,3,4,5,6, 去掉最后一个字符",",最终结果为1,2,3,4,5,6 代码如下:
$str = "1,2,3,4,5,6,";
$newstr = substr($str,0,strlen($str)-1);
echo $newstr;
- hadoop在linux上单机安装过程
_wy_
linuxhadoop
1、安装JDK
jdk版本最好是1.6以上,可以使用执行命令java -version查看当前JAVA版本号,如果报命令不存在或版本比较低,则需要安装一个高版本的JDK,并在/etc/profile的文件末尾,根据本机JDK实际的安装位置加上以下几行:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_25
- JAVA进阶----分布式事务的一种简单处理方法
无量
多系统交互分布式事务
每个方法都是原子操作:
提供第三方服务的系统,要同时提供执行方法和对应的回滚方法
A系统调用B,C,D系统完成分布式事务
=========执行开始========
A.aa();
try {
B.bb();
} catch(Exception e) {
A.rollbackAa();
}
try {
C.cc();
} catch(Excep
- 安墨移动广 告:移动DSP厚积薄发 引领未来广 告业发展命脉
矮蛋蛋
hadoop互联网
“谁掌握了强大的DSP技术,谁将引领未来的广 告行业发展命脉。”2014年,移动广 告行业的热点非移动DSP莫属。各个圈子都在纷纷谈论,认为移动DSP是行业突破点,一时间许多移动广 告联盟风起云涌,竞相推出专属移动DSP产品。
到底什么是移动DSP呢?
DSP(Demand-SidePlatform),就是需求方平台,为解决广 告主投放的各种需求,真正实现人群定位的精准广
- myelipse设置
alafqq
IP
在一个项目的完整的生命周期中,其维护费用,往往是其开发费用的数倍。因此项目的可维护性、可复用性是衡量一个项目好坏的关键。而注释则是可维护性中必不可少的一环。
注释模板导入步骤
安装方法:
打开eclipse/myeclipse
选择 window-->Preferences-->JAVA-->Code-->Code
- java数组
百合不是茶
java数组
java数组的 声明 创建 初始化; java支持C语言
数组中的每个数都有唯一的一个下标
一维数组的定义 声明: int[] a = new int[3];声明数组中有三个数int[3]
int[] a 中有三个数,下标从0开始,可以同过for来遍历数组中的数
- javascript读取表单数据
bijian1013
JavaScript
利用javascript读取表单数据,可以利用以下三种方法获取:
1、通过表单ID属性:var a = document.getElementByIdx_x_x("id");
2、通过表单名称属性:var b = document.getElementsByName("name");
3、直接通过表单名字获取:var c = form.content.
- 探索JUnit4扩展:使用Theory
bijian1013
javaJUnitTheory
理论机制(Theory)
一.为什么要引用理论机制(Theory)
当今软件开发中,测试驱动开发(TDD — Test-driven development)越发流行。为什么 TDD 会如此流行呢?因为它确实拥有很多优点,它允许开发人员通过简单的例子来指定和表明他们代码的行为意图。
TDD 的优点:
&nb
- [Spring Data Mongo一]Spring Mongo Template操作MongoDB
bit1129
template
什么是Spring Data Mongo
Spring Data MongoDB项目对访问MongoDB的Java客户端API进行了封装,这种封装类似于Spring封装Hibernate和JDBC而提供的HibernateTemplate和JDBCTemplate,主要能力包括
1. 封装客户端跟MongoDB的链接管理
2. 文档-对象映射,通过注解:@Document(collectio
- 【Kafka八】Zookeeper上关于Kafka的配置信息
bit1129
zookeeper
问题:
1. Kafka的哪些信息记录在Zookeeper中 2. Consumer Group消费的每个Partition的Offset信息存放在什么位置
3. Topic的每个Partition存放在哪个Broker上的信息存放在哪里
4. Producer跟Zookeeper究竟有没有关系?没有关系!!!
//consumers、config、brokers、cont
- java OOM内存异常的四种类型及异常与解决方案
ronin47
java OOM 内存异常
OOM异常的四种类型:
一: StackOverflowError :通常因为递归函数引起(死递归,递归太深)。-Xss 128k 一般够用。
二: out Of memory: PermGen Space:通常是动态类大多,比如web 服务器自动更新部署时引起。-Xmx
- java-实现链表反转-递归和非递归实现
bylijinnan
java
20120422更新:
对链表中部分节点进行反转操作,这些节点相隔k个:
0->1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9
k=2
8->1->6->3->4->5->2->7->0->9
注意1 3 5 7 9 位置是不变的。
解法:
将链表拆成两部分:
a.0-&
- Netty源码学习-DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
看DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder的API,有举例:
接收到的ChannelBuffer如下:
+--------------+
| ABC\nDEF\r\n |
+--------------+
经过DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(Delimiters.lineDelimiter())之后,得到:
+-----+----
- linux的一些命令 -查看cc攻击-网口ip统计等
hotsunshine
linux
Linux判断CC攻击命令详解
2011年12月23日 ⁄ 安全 ⁄ 暂无评论
查看所有80端口的连接数
netstat -nat|grep -i '80'|wc -l
对连接的IP按连接数量进行排序
netstat -ntu | awk '{print $5}' | cut -d: -f1 | sort | uniq -c | sort -n
查看TCP连接状态
n
- Spring获取SessionFactory
ctrain
sessionFactory
String sql = "select sysdate from dual";
WebApplicationContext wac = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
String[] names = wac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(int i=0; i&
- Hive几种导出数据方式
daizj
hive数据导出
Hive几种导出数据方式
1.拷贝文件
如果数据文件恰好是用户需要的格式,那么只需要拷贝文件或文件夹就可以。
hadoop fs –cp source_path target_path
2.导出到本地文件系统
--不能使用insert into local directory来导出数据,会报错
--只能使用
- 编程之美
dcj3sjt126com
编程PHP重构
我个人的 PHP 编程经验中,递归调用常常与静态变量使用。静态变量的含义可以参考 PHP 手册。希望下面的代码,会更有利于对递归以及静态变量的理解
header("Content-type: text/plain");
function static_function () {
static $i = 0;
if ($i++ < 1
- Android保存用户名和密码
dcj3sjt126com
android
转自:http://www.2cto.com/kf/201401/272336.html
我们不管在开发一个项目或者使用别人的项目,都有用户登录功能,为了让用户的体验效果更好,我们通常会做一个功能,叫做保存用户,这样做的目地就是为了让用户下一次再使用该程序不会重新输入用户名和密码,这里我使用3种方式来存储用户名和密码
1、通过普通 的txt文本存储
2、通过properties属性文件进行存
- Oracle 复习笔记之同义词
eksliang
Oracle 同义词Oracle synonym
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2098861
1.什么是同义词
同义词是现有模式对象的一个别名。
概念性的东西,什么是模式呢?创建一个用户,就相应的创建了 一个模式。模式是指数据库对象,是对用户所创建的数据对象的总称。模式对象包括表、视图、索引、同义词、序列、过
- Ajax案例
gongmeitao
Ajaxjsp
数据库采用Sql Server2005
项目名称为:Ajax_Demo
1.com.demo.conn包
package com.demo.conn;
import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;
//获取数据库连接的类public class DBConnec
- ASP.NET中Request.RawUrl、Request.Url的区别
hvt
.netWebC#asp.nethovertree
如果访问的地址是:http://h.keleyi.com/guestbook/addmessage.aspx?key=hovertree%3C&n=myslider#zonemenu那么Request.Url.ToString() 的值是:http://h.keleyi.com/guestbook/addmessage.aspx?key=hovertree<&
- SVG 教程 (七)SVG 实例,SVG 参考手册
天梯梦
svg
SVG 实例 在线实例
下面的例子是把SVG代码直接嵌入到HTML代码中。
谷歌Chrome,火狐,Internet Explorer9,和Safari都支持。
注意:下面的例子将不会在Opera运行,即使Opera支持SVG - 它也不支持SVG在HTML代码中直接使用。 SVG 实例
SVG基本形状
一个圆
矩形
不透明矩形
一个矩形不透明2
一个带圆角矩
- 事务管理
luyulong
javaspring编程事务
事物管理
spring事物的好处
为不同的事物API提供了一致的编程模型
支持声明式事务管理
提供比大多数事务API更简单更易于使用的编程式事务管理API
整合spring的各种数据访问抽象
TransactionDefinition
定义了事务策略
int getIsolationLevel()得到当前事务的隔离级别
READ_COMMITTED
- 基础数据结构和算法十一:Red-black binary search tree
sunwinner
AlgorithmRed-black
The insertion algorithm for 2-3 trees just described is not difficult to understand; now, we will see that it is also not difficult to implement. We will consider a simple representation known
- centos同步时间
stunizhengjia
linux集群同步时间
做了集群,时间的同步就显得非常必要了。 以下是查到的如何做时间同步。 在CentOS 5不再区分客户端和服务器,只要配置了NTP,它就会提供NTP服务。 1)确认已经ntp程序包: # yum install ntp 2)配置时间源(默认就行,不需要修改) # vi /etc/ntp.conf server pool.ntp.o
- ITeye 9月技术图书有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
ITeye
ITeye携手博文视点举办的9月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。 9月试读活动回顾:http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2118112本次技术图书试读活动的优秀奖获奖名单及相应作品如下(优秀文章有很多,但名额有限,没获奖并不代表不优秀):
《NFC:Arduino、Andro
![]() 的解。原理如下
的解。原理如下![]() ,当
,当![]() 时,
时,![]() ,此时
,此时![]() ,否则设
,否则设![]() ,所以进一步得到
,所以进一步得到![]() 和
和![]() ,要求称出质量为
,要求称出质量为![]() 的物品,要求
的物品,要求![]() 的数量
的数量![]() 和
和![]() 的数量
的数量![]() 的和
的和![]()
![]() 最小值,取
最小值,取![]() 最小的。
最小的。![]() 转化为最小正值,即
转化为最小正值,即![]() ,
,![]() ,若
,若![]() 为负值,则把
为负值,则把![]() 变正,意思就是砝码放置的位置有左右之分,可以左面的减去右面的,也可以右面
变正,意思就是砝码放置的位置有左右之分,可以左面的减去右面的,也可以右面![]() 为最小合法正值时
为最小合法正值时![]() 的解,将这两种情况比较取小的即可。
的解,将这两种情况比较取小的即可。![]() 和
和![]() ,其中
,其中![]() ,只对
,只对![]() 和
和![]() 进行加减操作,求最少需要多少步能得到1。
进行加减操作,求最少需要多少步能得到1。