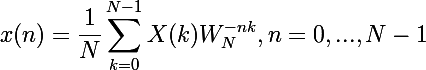FFT算法的完整DSP实现
【原文:http://blog.csdn.net/xiahouzuoxin/article/details/9790455】
傅里叶变换或者FFT的理论参考:
[1] http://www.dspguide.com/ch12/2.htm
The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing, By Steven W. Smith, Ph.D.
[2] http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6196862,可当作[1]的中文参考
[3] 任意一本数字信号处理教材,上面都有详细的推导DCT求解转换为FFT求解的过程
[4] TI文档:基于TMS320C64x+DSP的FFT实现。 使用baidu/google可以搜索到。
另外,FFT的开源代码可参考:
[1] FFTW: http://www.fftw.org/ 最快,最好的开源FFT。
[2] FFTReal: http://ldesoras.free.fr/prod.html#src_fftreal 轻量级FFT算法实现
[3] KISS FFT: http://sourceforge.net/projects/kissfft/ 简单易用的FFT的C语言实现
1. 有关FFT理论的一点小小解释
关于FFT这里只想提到两点:
(1)DFT变换对的表达式(必须记住)
![]() —— 称旋转因子
—— 称旋转因子
(2)FFT用途——目标只有一个,加速DFT的计算效率。
DFT计算X(k)需要N^2次复数乘法和N(N-1)次复数加法;FFT将N^2的计算量降为![]() 。
。
“FFT其实是很难的东西,即使常年在这个领域下打拼的科学家也未必能很好的写出FFT的算法。”——摘自参考上面提供的参考文献[1]
因此,我们不必太过纠结于细节,当明白FFT理论后,将已有的算法挪过来用就OK了,不必为闭着教材写不出FFT而郁闷不堪。
FFT的BASIC程序伪代码如下:
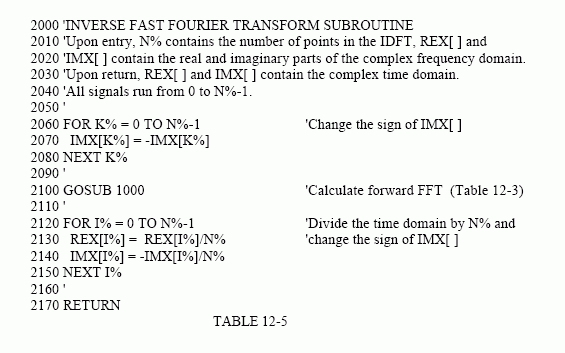
IFFT的BASIC程序伪代码如下(IFFT通过调用FFT计算):
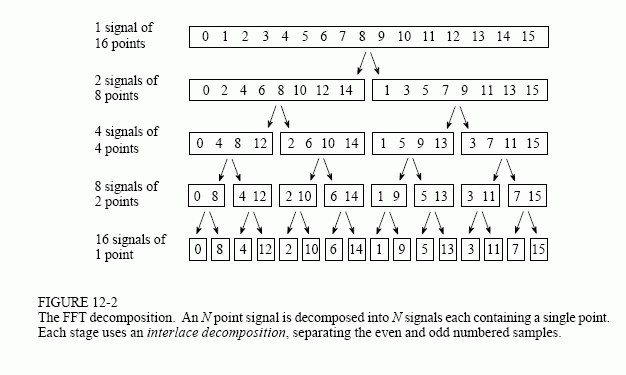
FFT算法的流程图如下图,总结为3过程3循环:
(1)3过程:单点时域分解(倒位序过程) + 单点时域计算单点频谱 + 频域合成
(2)3循环:外循环——分解次数,中循环——sub-DFT运算,内循环——2点蝶形算法
2. FFT的DSP实现
下面为本人使用C语言实现的FFT及IFFT算法实例,能计算任意以2为对数底的采样点数的FFT,算法参考上面给的流程图。
- /*
- * zx_fft.h
- *
- * Created on: 2013-8-5
- * Author: monkeyzx
- */
- #ifndef ZX_FFT_H_
- #define ZX_FFT_H_
- typedef float FFT_TYPE;
- #ifndef PI
- #define PI (3.14159265f)
- #endif
- typedef struct complex_st {
- FFT_TYPE real;
- FFT_TYPE img;
- } complex;
- int fft(complex *x, int N);
- int ifft(complex *x, int N);
- void zx_fft(void);
- #endif /* ZX_FFT_H_ */
- /*
- * zx_fft.c
- *
- * Implementation of Fast Fourier Transform(FFT)
- * and reversal Fast Fourier Transform(IFFT)
- *
- * Created on: 2013-8-5
- * Author: monkeyzx
- */
- #include "zx_fft.h"
- #include <math.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- /*
- * Bit Reverse
- * === Input ===
- * x : complex numbers
- * n : nodes of FFT. @N should be power of 2, that is 2^(*)
- * l : count by bit of binary format, @l=CEIL{log2(n)}
- * === Output ===
- * r : results after reversed.
- * Note: I use a local variable @temp that result @r can be set
- * to @x and won't overlap.
- */
- static void BitReverse(complex *x, complex *r, int n, int l)
- {
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- short stk = 0;
- static complex *temp = 0;
- temp = (complex *)malloc(sizeof(complex) * n);
- if (!temp) {
- return;
- }
- for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
- stk = 0;
- j = 0;
- do {
- stk |= (i>>(j++)) & 0x01;
- if(j<l)
- {
- stk <<= 1;
- }
- }while(j<l);
- if(stk < n) { /* 满足倒位序输出 */
- temp[stk] = x[i];
- }
- }
- /* copy @temp to @r */
- for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
- r[i] = temp[i];
- }
- free(temp);
- }
- /*
- * FFT Algorithm
- * === Inputs ===
- * x : complex numbers
- * N : nodes of FFT. @N should be power of 2, that is 2^(*)
- * === Output ===
- * the @x contains the result of FFT algorithm, so the original data
- * in @x is destroyed, please store them before using FFT.
- */
- int fft(complex *x, int N)
- {
- int i,j,l,ip;
- static int M = 0;
- static int le,le2;
- static FFT_TYPE sR,sI,tR,tI,uR,uI;
- M = (int)(log(N) / log(2));
- /*
- * bit reversal sorting
- */
- BitReverse(x,x,N,M);
- /*
- * For Loops
- */
- for (l=1; l<=M; l++) { /* loop for ceil{log2(N)} */
- le = (int)pow(2,l);
- le2 = (int)(le / 2);
- uR = 1;
- uI = 0;
- sR = cos(PI / le2);
- sI = -sin(PI / le2);
- for (j=1; j<=le2; j++) { /* loop for each sub DFT */
- //jm1 = j - 1;
- for (i=j-1; i<=N-1; i+=le) { /* loop for each butterfly */
- ip = i + le2;
- tR = x[ip].real * uR - x[ip].img * uI;
- tI = x[ip].real * uI + x[ip].img * uR;
- x[ip].real = x[i].real - tR;
- x[ip].img = x[i].img - tI;
- x[i].real += tR;
- x[i].img += tI;
- } /* Next i */
- tR = uR;
- uR = tR * sR - uI * sI;
- uI = tR * sI + uI *sR;
- } /* Next j */
- } /* Next l */
- return 0;
- }
- /*
- * Inverse FFT Algorithm
- * === Inputs ===
- * x : complex numbers
- * N : nodes of FFT. @N should be power of 2, that is 2^(*)
- * === Output ===
- * the @x contains the result of FFT algorithm, so the original data
- * in @x is destroyed, please store them before using FFT.
- */
- int ifft(complex *x, int N)
- {
- int k = 0;
- for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) {
- x[k].img = -x[k].img;
- }
- fft(x, N); /* using FFT */
- for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) {
- x[k].real = x[k].real / N;
- x[k].img = -x[k].img / N;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- /*
- * Code below is an example of using FFT and IFFT.
- */
- #define SAMPLE_NODES (128)
- complex x[SAMPLE_NODES];
- int INPUT[SAMPLE_NODES];
- int OUTPUT[SAMPLE_NODES];
- static void MakeInput()
- {
- int i;
- for ( i=0;i<SAMPLE_NODES;i++ )
- {
- x[i].real = sin(PI*2*i/SAMPLE_NODES);
- x[i].img = 0.0f;
- INPUT[i]=sin(PI*2*i/SAMPLE_NODES)*1024;
- }
- }
- static void MakeOutput()
- {
- int i;
- for ( i=0;i<SAMPLE_NODES;i++ )
- {
- OUTPUT[i] = sqrt(x[i].real*x[i].real + x[i].img*x[i].img)*1024;
- }
- }
- void zx_fft(void)
- {
- MakeInput();
- fft(x,128);
- MakeOutput();
- ifft(x,128);
- MakeOutput();
- }
程序在TMS320C6713上实验,主函数中调用zx_fft()函数即可。
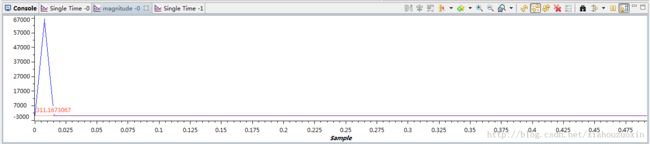
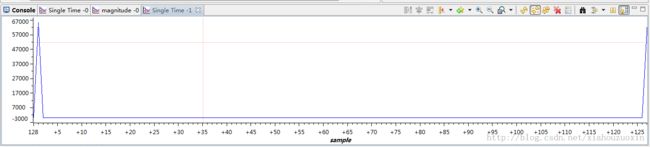
FFT的采样点数为128,输入信号的实数域为正弦信号,虚数域为0,数据精度定义FFT_TYPE为float类型,MakeInput和MakeOutput函数分别用于产生输入数据INPUT和输出数据OUTPUT的函数,便于使用CCS 的Graph功能绘制波形图。这里调试时使用CCS v5中的Tools -> Graph功能得到下面的波形图(怎么用自己琢磨,不会的使用CCS 的Help)。
输入波形
输入信号的频域幅值表示
FFT运算结果
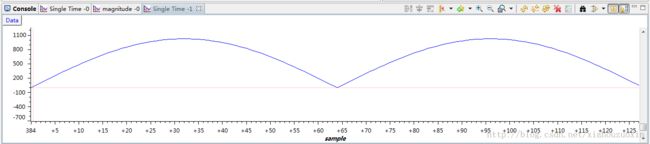
对FFT运算结果逆变换(IFFT)
如何检验运算结果是否正确呢?有几种方法:
(1)使用matlab验证,下面为相同情况的matlab图形验证代码
- SAMPLE_NODES = 128;
- i = 1:SAMPLE_NODES;
- x = sin(pi*2*i / SAMPLE_NODES);
- subplot(2,2,1); plot(x);title('Inputs');
- axis([0 128 -1 1]);
- y = fft(x, SAMPLE_NODES);
- subplot(2,2,2); plot(abs(y));title('FFT');
- axis([0 128 0 80]);
- z = ifft(y, SAMPLE_NODES);
- subplot(2,2,3); plot(abs(z));title('IFFT');
- axis([0 128 0 1]);

(2)使用IFFT验证:输入信号的FFT获得的信号再IFFT,则的到的信号与原信号相同
可能大家发现输入信号上面的最后IFFT的信号似乎不同,这是因为FFT和IFFT存在精度截断误差(也叫数据截断噪声,意思就是说,我们使用的float数据类型数据位数有限,没法完全保留原始信号的信息)。因此,IFFT之后是复数(数据截断噪声引入了虚数域,只不过值很小),所以在绘图时使用了计算幅值的方法,
C代码中:
- OUTPUT[i] = sqrt(x[i].real*x[i].real + x[i].img*x[i].img)*1024;
matlab代码中:
- subplot(2,2,3); plot(abs(z));title('IFFT');
所以IFFT的结果将sin函数的负y轴数据翻到了正y轴。另外,在CCS v5的图形中我们将显示信号的幅度放大了1024倍便于观察,而matlab中没有放大。
=================
更正 更正 。。。
=================
上面程序中的BitReverse函数由于使用了malloc函数,当要分配的n比较大时,在DSP上运行会出现一定的问题,因此改用伪代码中提供的倒位序方法更可靠。
修正后的完整FFT代码文件粘贴如下,在实际的DSP项目中测试通过,可直接拷贝复用。
- /*
- * zx_fft.h
- *
- * Created on: 2013-8-5
- * Author: monkeyzx
- */
- #ifndef _ZX_FFT_H
- #define _ZX_FFT_H
- #include "../Headers/Global.h"
- #define TYPE_FFT_E float /* Type is the same with COMPLEX member */
- #ifndef PI
- #define PI (3.14159265f)
- #endif
- typedef COMPLEX TYPE_FFT; /* Define COMPLEX in Config.h */
- extern int fft(TYPE_FFT *x, int N);
- extern int ifft(TYPE_FFT *x, int N);
- #endif /* ZX_FFT_H_ */
- /*
- * zx_fft.c
- *
- * Implementation of Fast Fourier Transform(FFT)
- * and reversal Fast Fourier Transform(IFFT)
- *
- * Created on: 2013-8-5
- * Author: monkeyzx
- *
- * TEST OK 2014.01.14
- * == 2014.01.14
- * Replace @BitReverse(x,x,N,M) by refrence to
- * <The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing>
- */
- #include "zx_fft.h"
- /*
- * FFT Algorithm
- * === Inputs ===
- * x : complex numbers
- * N : nodes of FFT. @N should be power of 2, that is 2^(*)
- * === Output ===
- * the @x contains the result of FFT algorithm, so the original data
- * in @x is destroyed, please store them before using FFT.
- */
- int fft(TYPE_FFT *x, int N)
- {
- int i,j,l,k,ip;
- static int M = 0;
- static int le,le2;
- static TYPE_FFT_E sR,sI,tR,tI,uR,uI;
- M = (int)(log(N) / log(2));
- /*
- * bit reversal sorting
- */
- l = N / 2;
- j = l;
- //BitReverse(x,x,N,M);
- for (i=1; i<=N-2; i++) {
- if (i < j) {
- tR = x[j].real;
- tI = x[j].imag;
- x[j].real = x[i].real;
- x[j].imag = x[i].imag;
- x[i].real = tR;
- x[i].imag = tI;
- }
- k = l;
- while (k <= j) {
- j = j - k;
- k = k / 2;
- }
- j = j + k;
- }
- /*
- * For Loops
- */
- for (l=1; l<=M; l++) { /* loop for ceil{log2(N)} */
- le = (int)pow(2,l);
- le2 = (int)(le / 2);
- uR = 1;
- uI = 0;
- sR = cos(PI / le2);
- sI = -sin(PI / le2);
- for (j=1; j<=le2; j++) { /* loop for each sub DFT */
- //jm1 = j - 1;
- for (i=j-1; i<=N-1; i+=le) { /* loop for each butterfly */
- ip = i + le2;
- tR = x[ip].real * uR - x[ip].imag * uI;
- tI = x[ip].real * uI + x[ip].imag * uR;
- x[ip].real = x[i].real - tR;
- x[ip].imag = x[i].imag - tI;
- x[i].real += tR;
- x[i].imag += tI;
- } /* Next i */
- tR = uR;
- uR = tR * sR - uI * sI;
- uI = tR * sI + uI *sR;
- } /* Next j */
- } /* Next l */
- return 0;
- }
- /*
- * Inverse FFT Algorithm
- * === Inputs ===
- * x : complex numbers
- * N : nodes of FFT. @N should be power of 2, that is 2^(*)
- * === Output ===
- * the @x contains the result of FFT algorithm, so the original data
- * in @x is destroyed, please store them before using FFT.
- */
- int ifft(TYPE_FFT *x, int N)
- {
- int k = 0;
- for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) {
- x[k].imag = -x[k].imag;
- }
- fft(x, N); /* using FFT */
- for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) {
- x[k].real = x[k].real / N;
- x[k].imag = -x[k].imag / N;
- }
- return 0;
- }
另外,可能还需要您在其它头文件中定义COMPLEX的复数类型
- typedef struct {
- float real;
- float imag;
- } COMPLEX;
=====================
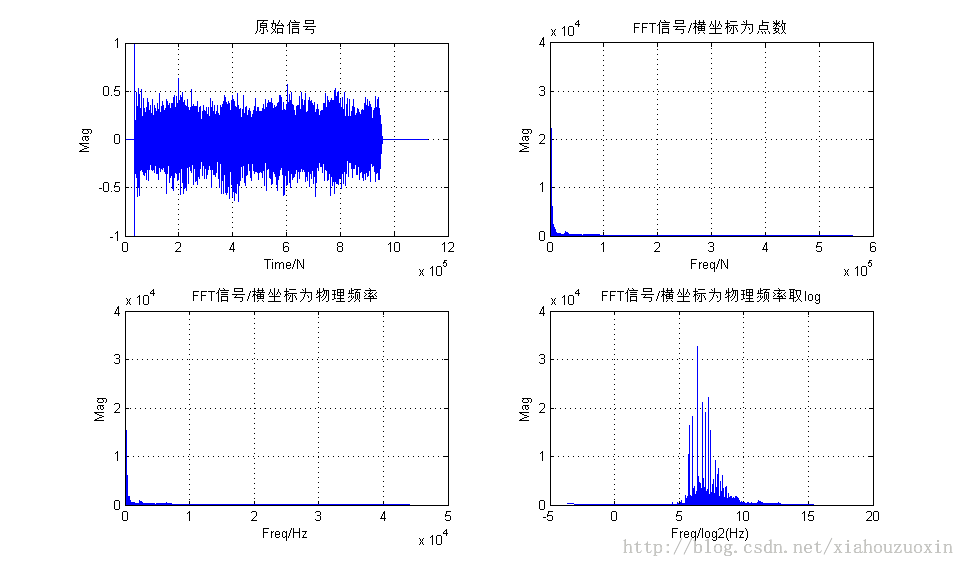
增加:FFT频谱结果显示
=====================
- clc;
- clear;
- % Read a real audio signal
- [fname,pname]=uigetfile(...
- {'*.wav';'*.*'},...
- 'Input wav File');
- [x fs nbits] = wavread(fullfile(pname,fname));
- % Window
- % N = 1024;
- N = size(x,1);
- x = x(1:N, 1);
- % FFT
- y = fft(x);
- % 频率对称,取N/2
- y = y(1:N/2);
- % FFT频率与物理频率转换
- x1 = 1:N/2;
- x2 = (1:N/2)*fs/(N/2); % /1000表示KHz
- log_x2 = log2(x2);
- % plot
- figure,
- subplot(2,2,1);plot(x);
- xlabel('Time/N');ylabel('Mag');grid on
- title('原始信号');
- subplot(2,2,2);plot(x1, abs(y));
- xlabel('Freq/N');ylabel('Mag');grid on
- title('FFT信号/横坐标为点数');
- subplot(2,2,3);plot(x2,abs(y));
- xlabel('Freq/Hz');ylabel('Mag');grid on
- title('FFT信号/横坐标为物理频率');
- subplot(2,2,4);plot(log_x2,abs(y));
- xlabel('Freq/log2(Hz)');ylabel('Mag');grid on
- title('FFT信号/横坐标为物理频率取log');
- % 更常见是将幅值取log
- y = log2(abs(y));
- figure,
- plot(x2,y);
- xlabel('Freq/Hz');ylabel('Mag/log2');grid on
- title('幅值取log2');