vs2015 + opencv3 双目摄像头标定(C++实现)
参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/datase/article/details/77587357
以前在本科的时候,做智能小车发现一个问题,当摄像头镜头视角越大,摄像头成像的照片出现变形的现象越严重,当时我们的解决办法是:使用小视角的镜头。今天学到摄像头标定之后,我发现,我们可以不用换小视角的镜头来解决这个问题,而是通过标定来解决这个问题。标定的目的:获得获取摄像机的内参和外参矩阵,通过这两个矩阵来矫正变形的图片,而内参矩阵指代:摄像头本身的畸变参数,外参矩阵指代:描述了如何把点从世界坐标系转换到摄像机坐标系。
对于标定的方法,网上资料很多,有通过Matlab标定,有通过c++标定,我个人比较推荐c++标定。下面我将一一介绍“张正友标定”流程:
1. 准备标定板
本人因为是自学双目摄像头而且又比较穷,所以没有钱买标定板,也没有钱打印标定板,所以想了一个简单粗暴的办法,直接将电脑的显示器当标定板来用,
2.保存样本图片
在标定过程中,我们需要拍照一些图片,其内容必须得包含整幅标定板,用来求摄像机的内参和外参矩阵。由于我们标定的摄像头是双目,所以需要保存两份图片(左摄像头和右摄像头)
3.对每一张标定图片,提取角点信息
使用到的函数为:findChessboardCorners,但要注意一个问题,它提取的内角点,对于上面的标定板,每行9个角点数,每列6个角点数
Size board_size = Size(9, 6); /* 标定板上每行、列的角点数 */
Mat imageInput = imread(filename);
vector> image_points_seq; /* 保存检测到的所有角点 */
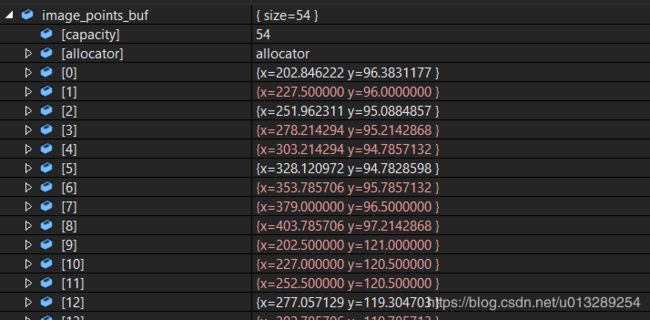
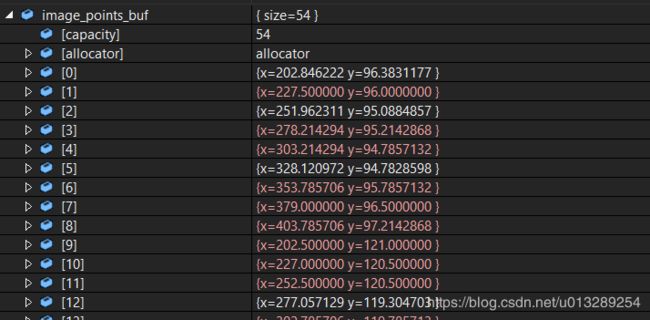
findChessboardCorners(imageInput, board_size, image_points_buf)
4.对粗提取的角点进行精确化
使用到函数为:find4QuadCornerSubpix,其中Size(5,5)是角点搜索窗口的尺寸,相对于上面的结果,有些角点值被精确化了,可以对比上下两张图片的内容。
Mat view_gray;
cvtColor(imageInput, view_gray, CV_RGB2GRAY);
/* 亚像素精确化 */
find4QuadCornerSubpix(view_gray, image_points_buf, Size(5, 5)); //对粗提取的角点进行精确化
5.将内角点可视化
使用到的函数为:drawChessboardCorners
drawChessboardCorners(view_gray, board_size, image_points_buf, false); //用于在图片中标记角点
6.相机标定
使用到函数为:calibrateCamera
vector> object_points; /* 保存标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
vector> image_points_seq; /* 保存检测到的所有角点 */
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
vector tvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的旋转向量 */
vector rvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的平移向量 */
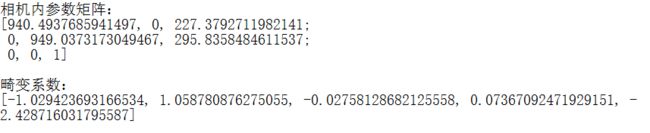
calibrateCamera(object_points, image_points_seq, image_size, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecsMat, tvecsMat, 0); 在相机标定之后,我们可以得到相机内参数矩阵与畸变系数
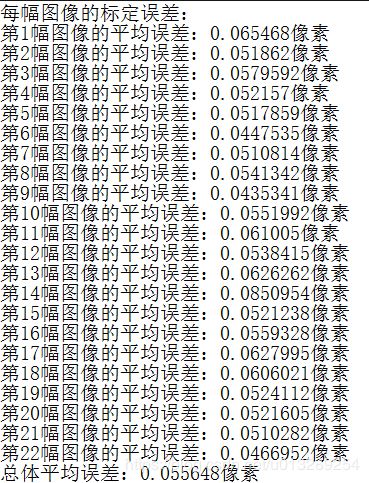
7.对标定结果进行评价
对标定结果进行评价的方法是通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到空间三维点在图像上新的投影点的坐标,计算投影坐标和亚像素角点坐标之间的偏差,偏差越小,标定结果越好,使用到的函数为:projectPoints
vector image_points2; /* 保存重新计算得到的投影点 */
/* 通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到新的投影点 */
projectPoints(tempPointSet, rvecsMat[i], tvecsMat[i], cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, image_points2); 亚像素角点坐标:
计算投影坐标:
经过循环计算,可以统计出所有的误差:
8.利用标定结果对棋盘图进行矫正
左边为矫正后的图片,右边为原始图片,效果还是不错的。
以下完整的工程代码(代码重复运行两次分别得到左右摄像头的内参和外参)
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void main()
{
ifstream fin("calibdata_right.txt"); /* 标定所用图像文件的路径 */
ofstream fout("caliberation_right_result.txt"); /* 保存标定结果的文件 */
//读取每一幅图像,从中提取出角点,然后对角点进行亚像素精确化
cout << "开始提取角点………………";
int image_count = 0; /* 图像数量 */
Size image_size; /* 图像的尺寸 */
Size board_size = Size(9, 6); /* 标定板上每行、列的角点数 */
vector image_points_buf; /* 缓存每幅图像上检测到的角点 */
vector> image_points_seq; /* 保存检测到的所有角点 */
string filename;
int count = -1;//用于存储角点个数。
while (getline(fin, filename))
{
image_count++;
// 用于观察检验输出
cout << "image_count = " << image_count << endl;
/* 输出检验*/
cout << "-->count = " << count;
Mat imageInput = imread(filename);
if (image_count == 1) //读入第一张图片时获取图像宽高信息
{
image_size.width = imageInput.cols;
image_size.height = imageInput.rows;
cout << "image_size.width = " << image_size.width << endl;
cout << "image_size.height = " << image_size.height << endl;
}
/* 提取角点 */
if (0 == findChessboardCorners(imageInput, board_size, image_points_buf))
{
cout << "can not find chessboard corners!\n"; //找不到角点
exit(1);
}
else
{
Mat view_gray;
cvtColor(imageInput, view_gray, CV_RGB2GRAY);
/* 亚像素精确化 */
find4QuadCornerSubpix(view_gray, image_points_buf, Size(5, 5)); //对粗提取的角点进行精确化
//cornerSubPix(view_gray,image_points_buf,Size(5,5),Size(-1,-1),TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS+CV_TERMCRIT_ITER,30,0.1));
image_points_seq.push_back(image_points_buf); //保存亚像素角点
/* 在图像上显示角点位置 */
drawChessboardCorners(view_gray, board_size, image_points_buf, false); //用于在图片中标记角点
imshow("Camera Calibration", view_gray);//显示图片
waitKey(500);//暂停0.5S
}
}
int total = image_points_seq.size();
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
int CornerNum = board_size.width*board_size.height; //每张图片上总的角点数
for (int ii = 0; ii 第 " << j << "图片的数据 --> : " << endl;
}
if (0 == ii % 3) // 此判断语句,格式化输出,便于控制台查看
{
cout << endl;
}
else
{
cout.width(10);
}
//输出所有的角点
cout << " -->" << image_points_seq[ii][0].x;
cout << " -->" << image_points_seq[ii][0].y;
}
cout << "角点提取完成!\n";
//以下是摄像机标定
cout << "开始标定………………";
/*棋盘三维信息*/
Size square_size = Size(10, 10); /* 实际测量得到的标定板上每个棋盘格的大小 */
vector> object_points; /* 保存标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
/*内外参数*/
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
vector point_counts; // 每幅图像中角点的数量
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
vector tvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的旋转向量 */
vector rvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的平移向量 */
/* 初始化标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
int i, j, t;
for (t = 0; t tempPointSet;
for (i = 0; i image_points2; /* 保存重新计算得到的投影点 */
cout << "\t每幅图像的标定误差:\n";
fout << "每幅图像的标定误差:\n";
for (i = 0; i tempPointSet = object_points[i];
/* 通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到新的投影点 */
projectPoints(tempPointSet, rvecsMat[i], tvecsMat[i], cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, image_points2);
/* 计算新的投影点和旧的投影点之间的误差*/
vector tempImagePoint = image_points_seq[i];
Mat tempImagePointMat = Mat(1, tempImagePoint.size(), CV_32FC2);
Mat image_points2Mat = Mat(1, image_points2.size(), CV_32FC2);
for (int j = 0; j < tempImagePoint.size(); j++)
{
image_points2Mat.at(0, j) = Vec2f(image_points2[j].x, image_points2[j].y);
tempImagePointMat.at(0, j) = Vec2f(tempImagePoint[j].x, tempImagePoint[j].y);
}
err = norm(image_points2Mat, tempImagePointMat, NORM_L2);
total_err += err /= point_counts[i];
std::cout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的平均误差:" << err << "像素" << endl;
fout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的平均误差:" << err << "像素" << endl;
}
std::cout << "总体平均误差:" << total_err / image_count << "像素" << endl;
fout << "总体平均误差:" << total_err / image_count << "像素" << endl << endl;
std::cout << "评价完成!" << endl;
//保存定标结果
std::cout << "开始保存定标结果………………" << endl;
Mat rotation_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 保存每幅图像的旋转矩阵 */
fout << "相机内参数矩阵:" << endl;
fout << cameraMatrix << endl << endl;
fout << "畸变系数:\n";
fout << distCoeffs << endl << endl << endl;
for (int i = 0; i> imageFileName;
filePath += imageFileName;
filePath += ".jpg";
Mat imageSource = imread(filePath);
Mat newimage = imageSource.clone();
//另一种不需要转换矩阵的方式
//undistort(imageSource,newimage,cameraMatrix,distCoeffs);
remap(imageSource, newimage, mapx, mapy, INTER_LINEAR);
StrStm.clear();
filePath.clear();
StrStm << i + 1;
StrStm >> imageFileName;
imageFileName += "_d.jpg";
imwrite(imageFileName, newimage);
}
std::cout << "保存结束" << endl;
return;
}
9.利用左右摄像头的内参和外参进行双目标定
代码如下(记得将第8步得到的左右摄像头的内参和外参分别填到cameraMatrixL、distCoeffL、cameraMatrixR和distCoeffR):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#include
//#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//摄像头的分辨率
const int imageWidth = 640;
const int imageHeight = 360;
//横向的角点数目
const int boardWidth = 9;
//纵向的角点数目
const int boardHeight = 6;
//总的角点数目
const int boardCorner = boardWidth * boardHeight;
//相机标定时需要采用的图像帧数
const int frameNumber = 10;
//标定板黑白格子的大小 单位是mm
const int squareSize = 10;
//标定板的总内角点
const Size boardSize = Size(boardWidth, boardHeight);
Size imageSize = Size(imageWidth, imageHeight);
Mat R, T, E, F;
//R旋转矢量 T平移矢量 E本征矩阵 F基础矩阵
vector rvecs; //R
vector tvecs; //T
//左边摄像机所有照片角点的坐标集合
vector> imagePointL;
//右边摄像机所有照片角点的坐标集合
vector> imagePointR;
//各图像的角点的实际的物理坐标集合
vector> objRealPoint;
//左边摄像机某一照片角点坐标集合
vector cornerL;
//右边摄像机某一照片角点坐标集合
vector cornerR;
Mat rgbImageL, grayImageL;
Mat rgbImageR, grayImageR;
Mat intrinsic;
Mat distortion_coeff;
//校正旋转矩阵R,投影矩阵P,重投影矩阵Q
Mat Rl, Rr, Pl, Pr, Q;
//映射表
Mat mapLx, mapLy, mapRx, mapRy;
Rect validROIL, validROIR;
//图像校正之后,会对图像进行裁剪,其中,validROI裁剪之后的区域
/*事先标定好的左相机的内参矩阵
fx 0 cx
0 fy cy
0 0 1
*/
Mat cameraMatrixL = (Mat_(3, 3) << 940.4937685941497, 0, 227.3792711982141,
0, 949.0373173049467, 295.8358484611537,
0, 0, 1);
//获得的畸变参数
Mat distCoeffL = (Mat_(5, 1) << -1.029423693166534, 1.058780876275055, -0.02758128682125558, 0.07367092471929151, -2.428716031795587);
/*事先标定好的右相机的内参矩阵
fx 0 cx
0 fy cy
0 0 1
*/
Mat cameraMatrixR = (Mat_(3, 3) << 1196.466071813248, 0, 386.9366034567681,
0, 1210.35406268507, 306.5246050041429,
0, 0, 1);
Mat distCoeffR = (Mat_(5, 1) << -1.58519463079371, 0.08628154897902529, -0.05737733624491874, -0.07915841018512512, 10.62054373440436);
/*计算标定板上模块的实际物理坐标*/
void calRealPoint(vector>& obj, int boardWidth, int boardHeight, int imgNumber, int squareSize)
{
vector imgpoint;
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < boardHeight; rowIndex++)
{
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < boardWidth; colIndex++)
{
imgpoint.push_back(Point3f(rowIndex * squareSize, colIndex * squareSize, 0));
}
}
for (int imgIndex = 0; imgIndex < imgNumber; imgIndex++)
{
obj.push_back(imgpoint);
}
}
void outputCameraParam(void)
{
/*保存数据*/
/*输出数据*/
FileStorage fs("intrisics.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
fs << "cameraMatrixL" << cameraMatrixL << "cameraDistcoeffL" << distCoeffL << "cameraMatrixR" << cameraMatrixR << "cameraDistcoeffR" << distCoeffR;
fs.release();
cout << "cameraMatrixL=:" << cameraMatrixL << endl << "cameraDistcoeffL=:" << distCoeffL << endl << "cameraMatrixR=:" << cameraMatrixR << endl << "cameraDistcoeffR=:" << distCoeffR << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Error: can not save the intrinsics!!!!" << endl;
}
fs.open("extrinsics.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
fs << "R" << R << "T" << T << "Rl" << Rl << "Rr" << Rr << "Pl" << Pl << "Pr" << Pr << "Q" << Q;
cout << "R=" << R << endl << "T=" << T << endl << "Rl=" << Rl << endl << "Rr" << Rr << endl << "Pl" << Pl << endl << "Pr" << Pr << endl << "Q" << Q << endl;
fs.release();
}
else
{
cout << "Error: can not save the extrinsic parameters\n";
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mat img;
int goodFrameCount = 0;
while (goodFrameCount < frameNumber)
{
char filename[100];
/*读取左边的图像*/
sprintf_s(filename, "E:\\c_pp_project\\opencv_test\\test\\test\\image_left_%d.jpg", goodFrameCount + 5);
rgbImageL = imread(filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
imshow("chessboardL", rgbImageL);
cvtColor(rgbImageL, grayImageL, CV_BGR2GRAY);
/*读取右边的图像*/
sprintf_s(filename, "E:\\c_pp_project\\opencv_test\\test\\test\\image_right_%d.jpg", goodFrameCount + 5);
rgbImageR = imread(filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
cvtColor(rgbImageR, grayImageR, CV_BGR2GRAY);
bool isFindL, isFindR;
isFindL = findChessboardCorners(rgbImageL, boardSize, cornerL);
isFindR = findChessboardCorners(rgbImageR, boardSize, cornerR);
if (isFindL == true && isFindR == true)
{
cornerSubPix(grayImageL, cornerL, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, 1), TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImageL, boardSize, cornerL, isFindL);
imshow("chessboardL", rgbImageL);
imagePointL.push_back(cornerL);
cornerSubPix(grayImageR, cornerR, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 20, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImageR, boardSize, cornerR, isFindR);
imshow("chessboardR", rgbImageR);
imagePointR.push_back(cornerR);
goodFrameCount++;
cout << "the image" << goodFrameCount << " is good" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "the image is bad please try again" << endl;
}
if (waitKey(10) == 'q')
{
break;
}
}
//计算实际的校正点的三维坐标,根据实际标定格子的大小来设置
calRealPoint(objRealPoint, boardWidth, boardHeight, frameNumber, squareSize);
cout << "cal real successful" << endl;
//标定摄像头
double rms = stereoCalibrate(objRealPoint, imagePointL, imagePointR,
cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL,
cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR,
Size(imageWidth, imageHeight), R, T, E, F, CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS,
TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS, 100, 1e-5));
cout << "Stereo Calibration done with RMS error = " << rms << endl;
stereoRectify(cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL, cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR, imageSize, R, T, Rl,
Rr, Pl, Pr, Q, CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY, -1, imageSize, &validROIL, &validROIR);
//摄像机校正映射
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrixL, distCoeffL, Rl, Pl, imageSize, CV_32FC1, mapLx, mapLy);
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrixR, distCoeffR, Rr, Pr, imageSize, CV_32FC1, mapRx, mapRy);
Mat rectifyImageL, rectifyImageR;
cvtColor(grayImageL, rectifyImageL, CV_GRAY2BGR);
cvtColor(grayImageR, rectifyImageR, CV_GRAY2BGR);
imshow("RecitifyL Before", rectifyImageL);
imshow("RecitifyR Before", rectifyImageR);
cout << "按Q1退出..." << endl;
//经过remap之后,左右相机的图像已经共面并且行对准了
Mat rectifyImageL2, rectifyImageR2;
remap(rectifyImageL, rectifyImageL2, mapLx, mapLy, INTER_LINEAR);
remap(rectifyImageR, rectifyImageR2, mapRx, mapRy, INTER_LINEAR);
cout << "按Q2退出..." << endl;
imshow("rectifyImageL", rectifyImageL2);
imshow("rectifyImageR", rectifyImageR2);
outputCameraParam();
//显示校正结果
Mat canvas;
double sf;
int w, h;
sf = 600. / MAX(imageSize.width, imageSize.height);
w = cvRound(imageSize.width * sf);
h = cvRound(imageSize.height * sf);
canvas.create(h, w * 2, CV_8UC3);
//左图像画到画布上
Mat canvasPart = canvas(Rect(0, 0, w, h));
resize(rectifyImageL2, canvasPart, canvasPart.size(), 0, 0, INTER_AREA);
Rect vroiL(cvRound(validROIL.x*sf), cvRound(validROIL.y*sf),
cvRound(validROIL.width*sf), cvRound(validROIL.height*sf));
rectangle(canvasPart, vroiL, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8);
cout << "Painted ImageL" << endl;
//右图像画到画布上
canvasPart = canvas(Rect(w, 0, w, h));
resize(rectifyImageR2, canvasPart, canvasPart.size(), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
Rect vroiR(cvRound(validROIR.x*sf), cvRound(validROIR.y*sf),
cvRound(validROIR.width*sf), cvRound(validROIR.height*sf));
rectangle(canvasPart, vroiR, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 8);
cout << "Painted ImageR" << endl;
//画上对应的线条
for (int i = 0; i < canvas.rows; i += 16)
line(canvas, Point(0, i), Point(canvas.cols, i), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, 8);
imshow("rectified", canvas);
cout << "wait key" << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
其效果见下图:
10.其中一些函数的说明:
1.findChessboardCorners:寻找棋盘图中棋盘角点
2.find4QuadCornerSubpix:对粗提取的角点进行精确化
3.cornerSubPix:在角点检测中精确化角点位置
4.drawChessboardCorners:将发现到的所有角点绘制到所提供的图像上
5.calibrateCamera:利用定标来计算摄像机的内参数和外参数
6.projectPoints:通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到新的投影点
7.利用标定结果对棋盘图进行矫正
1)initUndistortRectifyMap用来计算畸变映射,remap把求得的映射应用到图像上
2)undistort一个函数搞定
8.stereoCalibrate:双目摄像机标定,计算了两个摄像头进行立体像对之间的转换关系,根据左右相机的参数矩阵,生成两个相机之间的关系矩阵,以及基本和本质矩阵
9.stereoRectify:作用是为每个摄像头计算立体校正的映射矩阵。所以其运行结果并不是直接将图片进行立体矫正,而是得出进行立体矫正所需要的映射矩阵