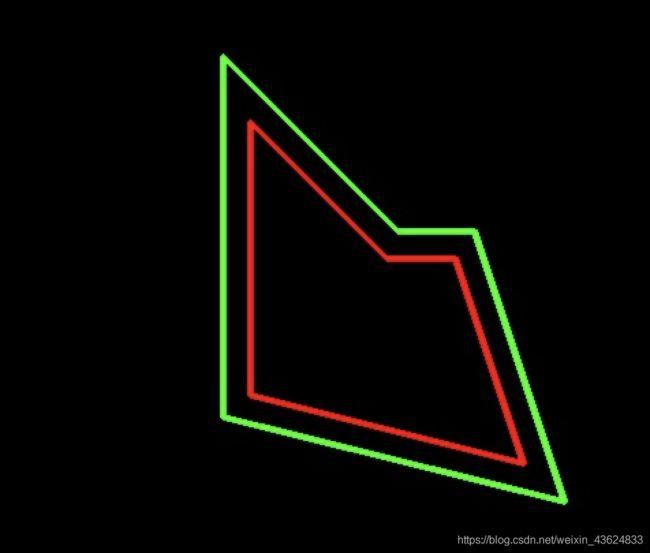
多边形轮廓 等距离外扩
多边形(轮廓点)等距离外扩
1.需要安装一个python包
安装 pyclipper python 的话,直接pip install pyclipper
地址:https://pypi.org/project/pyclipper/
中文文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhigu/p/11943118.html
2.轮廓点等距离外扩
def equidistant_zoom_contour(contour, margin):
"""
等距离缩放多边形轮廓点
:param contour: 一个图形的轮廓格式[[[x1, x2]],...],shape是(-1, 1, 2)
:param margin: 轮廓外扩的像素距离,margin正数是外扩,负数是缩小
:return: 外扩后的轮廓点
"""
pco = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
##### 参数限制,默认成2这里设置大一些,主要是用于多边形的尖角是否用圆角代替
pco.MiterLimit = 10
contour = contour[:, 0, :]
pco.AddPath(contour, pyclipper.JT_MITER, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
solution = pco.Execute(margin)
solution = np.array(solution).reshape(-1, 1, 2).astype(int)
return solution
调用示例子:
import pyclipper
import math
from shapely.geometry import LineString, Polygon, MultiLineString, Point, MultiPoint
poly = np.array([[[200, 200]], [[200, 300]], [[400, 350]], [[350, 200]], [[300, 200]], [[200, 100]]])
contour1 = equidistant_zoom_contour(poly, 20)
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3))
cv2.polylines(img, [poly], True, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.polylines(img, [contour1], True, (0, 255, 0), 3)
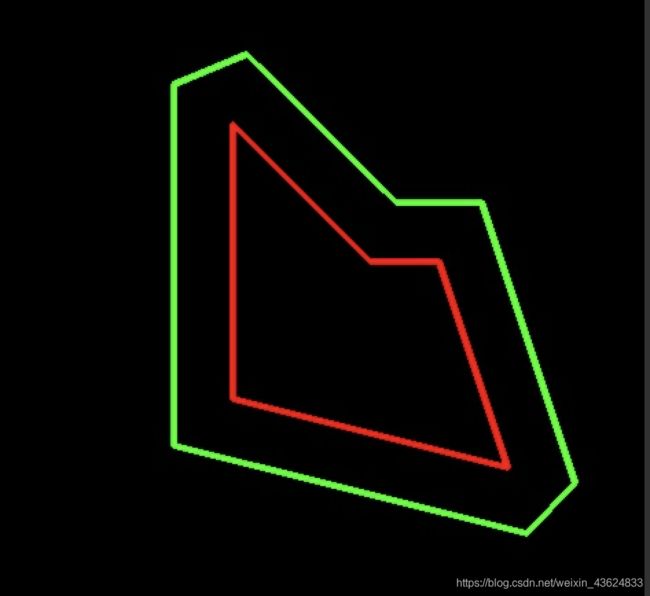
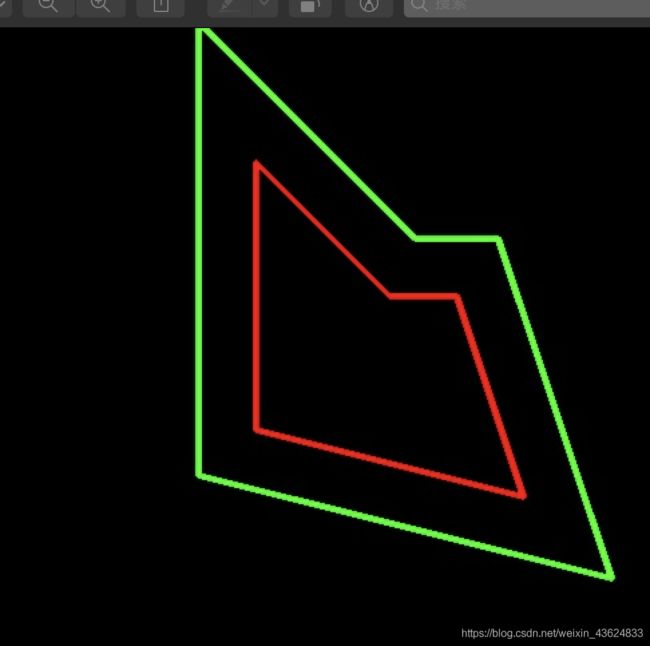
3.轮廓点等比例缩放
def perimeter(poly):
p = 0
nums = poly.shape[0]
for i in range(nums):
p += abs(np.linalg.norm(poly[i % nums] - poly[(i + 1) % nums]))
return p
def proportional_zoom_contour(contour, ratio):
"""
多边形轮廓点按照比例进行缩放
:param contour: 一个图形的轮廓格式[[[x1, x2]],...],shape是(-1, 1, 2)
:param ratio: 缩放的比例,如果大于1是放大小于1是缩小
:return:
"""
poly = contour[:, 0, :]
area_poly = abs(pyclipper.Area(poly))
perimeter_poly = perimeter(poly)
poly_s = []
pco = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
pco.MiterLimit = 10
if perimeter_poly:
d = area_poly * (1 - ratio * ratio) / perimeter_poly
pco.AddPath(poly, pyclipper.JT_MITER, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
poly_s = pco.Execute(-d)
poly_s = np.array(poly_s).reshape(-1, 1, 2).astype(int)
return poly_s
调用示范:
import pyclipper
import math
from shapely.geometry import LineString, Polygon, MultiLineString, Point, MultiPoint
poly = np.array([[[200, 200]], [[200, 300]], [[400, 350]], [[350, 200]], [[300, 200]], [[200, 100]]])
contour1 = proportional_zoom_contour(poly, 1.5)
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3))
cv2.polylines(img, [contour1], True, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.polylines(img, [poly], True, (0, 0, 255), 3)
其中 pco.MiterLimit = 10这个参数默认是2,如果是默认的值结果图第一个,改成10的话,结果图就是第二个,是一个尖角的区别
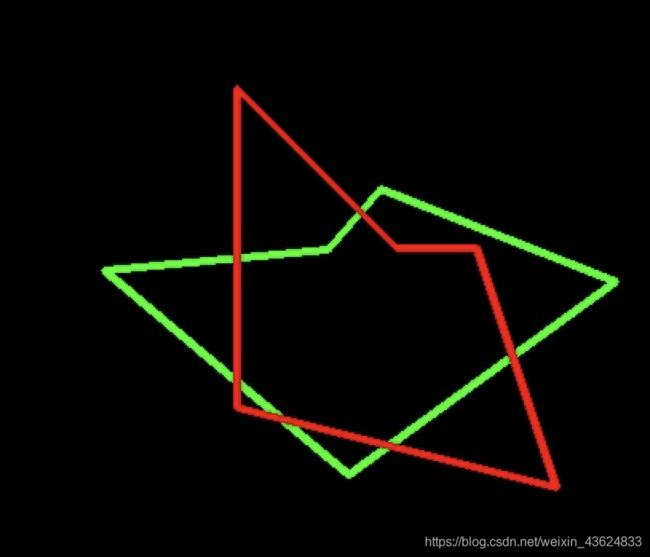
4.图形轮廓点的旋转
# 获取一个形状的质心
def get_centroid(coord):
coord = np.array(coord)
shape = coord.shape
if len(shape) == 1 and len(coord) == 2: # point
return coord
if len(shape) == 1 and len(coord) == 4: # bounding box
return tuple([(coord[0] + coord[2]) // 2, (coord[1] + coord[3]) // 2])
elif len(shape) == 2 and shape[-1] == 2:
if shape[0] == 2: # 如果是直线
cen = LineString(coord).centroid
else:
cen = Polygon(coord).centroid
return tuple(map(int, [cen.x, cen.y]))
elif len(shape) == 3 and shape[1:] == (1, 2): # contour
cen = Polygon(coord.squeeze()).centroid
return tuple(map(int, [cen.x, cen.y]))
else:
raise Exception('coordinate error, must be bbox or contour shape:{}'.format(coord))
def point_Srotate(im_w, im_h, angle, spin_point, origin_point):
"""
:param im_w: 原始点所在的图片的宽度
:param im_h: 原始点所在的图片的高度
:param angle: 旋转的角度
:param spin_point: 旋转的点
:param origin_point: 参考点
:return: 旋转过后的点
"""
row, col = im_h, im_w
# P(x1, y1),绕某个像素点Q(x2, y2)
x1, y1 = spin_point
x2, y2 = origin_point
y1 = row - y1
y2 = row - y2
x = (x1 - x2) * math.cos(math.pi / 180.0 * angle) - (y1 - y2) * math.sin(math.pi / 180.0 * angle) + x2
y = (x1 - x2) * math.sin(math.pi / 180.0 * angle) + (y1 - y2) * math.cos(math.pi / 180.0 * angle) + y2
x = x
y = row - y
return [x, y]
调用示范
import pyclipper
import math
from shapely.geometry import LineString, Polygon, MultiLineString, Point, MultiPoint
# 以多边形轮廓的质心为参照点进行旋转
poly = np.array([[[200, 200]], [[200, 300]], [[400, 350]], [[350, 200]], [[300, 200]], [[200, 100]]])
origin_point = get_centroid(poly)
spin_list = []
for con in poly:
print('con', con)
new = point_Srotate(500, 500, 50, con[0], origin_point)
spin_list.append(new)
spin_con = np.array(spin_list).reshape(-1, 1, 2).astype(int)
img = np.zeros((500, 500, 3))
cv2.polylines(img, [spin_con], True, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.polylines(img, [poly], True, (0, 0, 255), 3)
5.其他外扩的函数
def extend_contour2(contour, margin):
# 每个点相对于质心进行外扩一定的距离
"""
:param contour: 轮廓点集合
:param margin: 外扩的距离
:return: 外扩后的轮廓点集
"""
#### 求该轮廓的质心 ####
gravity_point = get_centroid(contour)
#### 获取最左下的点 ####
# min_x = np.minimum(contour)
#### 计算所有的轮廓点与质心所组成的向量,计算向量的模
vector_arr = contour - np.array(gravity_point)
vector_length = np.linalg.norm(vector_arr, axis=2)
#### 计算所有的点针对对外扩的像素需要放大多少倍
ratio = 1 + margin / vector_length
ratio = np.concatenate([ratio, ratio], axis=1)
#### 进行坐标的缩放
contour_ext = (vector_arr[:, 0, :] * ratio + np.array(gravity_point)).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
contour_ext = contour_ext.astype(int)
return contour_ext
def coordinate_conversion(reference_point, contour, ratio):
# 对凸多边形有用,对凹多边形容易变形,成比例缩放轮廓
"""
:param reference_point: 参照点的坐标
:param contour: 图像的轮廓点
:param ratio: 缩放的比例
:return: 以参照点不变将轮廓点获取缩放后的轮廓点坐标
"""
contour_trans_array = (contour - np.array(reference_point)) * ratio + np.array(reference_point)
contour_trans_array = contour_trans_array.astype(int)
return contour_trans_array